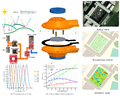
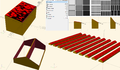
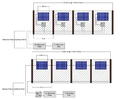
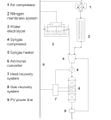
The measurement of outdoor environmental and climatic variables is needed for many applications such as precision agriculture, environmental pollution monitoring, and the study of ecosystems. Some sensors deployed for these purposes such as temperature, relative humidity, atmospheric pressure, and carbon dioxide sensors require protection from climate factors to avoid bias. Radiation shields hold and protect sensors to avoid this bias, but commercial systems are limited, often expensive, and difficult to implement in low-cost contexts or large deployments for collaborative sensing. To overcome these challenges, this work presents an open source, easily adapted and customized design of a radiation shield. The device can be fabricated with inexpensive off-the-shelf parts and 3-D printed components and can be adapted to protect and isolate different types of sensors. Two material approaches are tested here: polylactic acid (PLA), the most common 3-D printing filament, and acrylonitrile styrene acrylate (ASA), which is known to offer better resistance against UV radiation, greater hardness, and generally higher resistance to degradation. To validate the designs, the two prototypes were installed on a custom outdoor meteorological system and temperature and humidity measurements were made in several locations for one month and compared against a proprietary system and a system with no shield. The 3-D printed materials were also both tested multiple times for one month for UV stability of their mechanical properties, their optical transmission and deformation under outdoor high-heat conditions. The results showed that ASA is the preferred material for this design and that the open source radiation shield could match the performance of proprietary systems. The open source system can be constructed for about nine US dollars, which enables mass development of flexible weather stations for monitoring needed in smart agriculture.
- Full source Available online: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/XE49Y
- Subject areas: Engineering, Instrumentation, Internet of things
- Hardware type: Measuring physical properties and in-lab sensors,Field measurements and sensors, Electrical engineering and computer science
- Open source license: GNU GPL v3 for documents and CERN OHL v2 for hardware
- Cost of hardware: 5.70 - 9.00 USD
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Climatic variables; environmental variables; Internet of Things (IoT); low cost; radiation shield; 3-D printing; open hardware; environmental monitoring; sensing; environmental sensing; additive manufacturing; smart agriculture
See also[edit | edit source]
- Applications of Open Source 3-D Printing on Small Farms
- Open-Source Script for Design and 3D Printing of Porous Structures for Soil Science
- Low-cost air, noise, and light pollution measuring station with wireless communication and tinyML

- Coal with Carbon Capture and Sequestration is not as Land Use Efficient as Solar Photovoltaic Technology for Climate Neutral Electricity Production
- Dual use of land for PV farms and agriculture literature review
- sheep
- Israeli white plastic reflectors
- A Farmer's Guide to Going Solar (NREL)
- German guidelines: https://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/ise/en/documents/publications/studies/APV-Guideline.pdf
- 2021 review
- Miskin, C.K., Li, Y., Perna, A., Ellis, R.G., Grubbs, E.K., Bermel, P. and Agrawal, R., 2019. Sustainable co-production of food and solar power to relax land-use constraints. Nature Sustainability, 2(10), pp.972-980.
- Retrofitting solar parks for agrivoltaics
- Shading PV
- Alexis' talk at American Solar Grazing Association2021
In the News[edit source]
- Agrivoltaics: solar energy + better crops Climate and Nature
- Why solar power and farmers’ fields could be the perfect combination TVO
- Solar farms and sheep show the makings of a clean energy classic duo Business Renewables
- Agrivoltaics charge up St. Albert-area farms St Albert Gazette
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms are creating ideal growing conditions Western Wheel
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms create ideal growing conditions Voxpopuli
- 3D printed clamps for front-surface PV mounting on wood racking PV Magazine
- Harvesting the Sun to Grow in the Shade Garden Culture Magazine
- What crops fit with vertical agrivoltaics? PV Magazine
- Agrivoltaics – Keeping the farm in the solar farm Green Energy Futures
- Solar
- Papers
- London
- Ontario
- Canada
- Projects
- Agrivoltaics
- Solar power
- Solar energy
- Photovoltaics
- Sustainable development
- Agriculture
- SDG02 Zero hunger
- SDG07 Affordable and clean energy
- SDG09 Industry innovation and infrastructure
- Distributed manufacturing
- Farming
- Gardening
- Open hardware
- Recycling
- 3D printing
- Polymers
- Plastic
- Materials
- Environmental monitoring