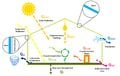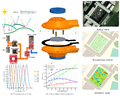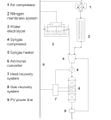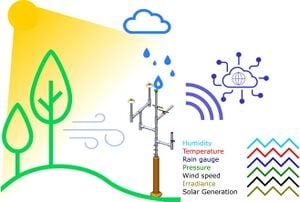
Measuring climatic conditions is a fundamental task for a wide array of scientific and practical fields. Weather variables change depending on position and time, especially in tropical zones without seasons. Additionally, the increasing development of precision or smart agriculture makes it necessary to improve the measurement systems while widely distributing them at the location of crops. For these reasons, in this work, the design, construction and fabrication of an adaptable autonomous solar-powered climatic station with wireless 3G or WiFi communication is presented. The station measures relative humidity, temperature, atmospheric pressure, precipitation, wind speed, and light radiation. In addition, the system monitors the charge state of the main battery and the energy generated by the photovoltaic module to act as a reference cell for solar energy generation capability and agrivoltaic potential in the installation area. The station can be remotely controlled and reconfigured. The collected data from all sensors can be uploaded to the cloud in real-time. This initiative aims at enhancing the development of free and open source hardware that can be used by the agricultural sector and that allows professionals in the area to improve harvest yield and production conditions.
- Full source Available online: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/NTVXG
- Subject areas: Engineering, Instrumentation, Internet of things
- Hardware type: Measuring physical properties and in-lab sensors, Field measurements and sensors, Electrical engineering and computer science
- Open source license: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike license
- Cost of hardware: USD 512 (WiFi communication) - USD 565 (3G communication)
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Climate; Internet of Things (IoT); Photovoltaic energy; Wireless communication; Meteorology; Climatic variables; environmental variables; Internet of Things (IoT); low cost; radiation shield; 3-D printing; open hardware; environmental monitoring; sensing; environmental sensing; additive manufacturing; smart agriculture
See also[edit | edit source]
- Applications of Open Source 3-D Printing on Small Farms
- Open-Source Script for Design and 3D Printing of Porous Structures for Soil Science
- Low-cost air, noise, and light pollution measuring station with wireless communication and tinyML

- Coal with Carbon Capture and Sequestration is not as Land Use Efficient as Solar Photovoltaic Technology for Climate Neutral Electricity Production
- Dual use of land for PV farms and agriculture literature review
- sheep
- Israeli white plastic reflectors
- A Farmer's Guide to Going Solar (NREL)
- German guidelines: https://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/ise/en/documents/publications/studies/APV-Guideline.pdf
- 2021 review
- Miskin, C.K., Li, Y., Perna, A., Ellis, R.G., Grubbs, E.K., Bermel, P. and Agrawal, R., 2019. Sustainable co-production of food and solar power to relax land-use constraints. Nature Sustainability, 2(10), pp.972-980.
- Retrofitting solar parks for agrivoltaics
- Shading PV
- Alexis' talk at American Solar Grazing Association2021
In the News[edit source]
- Agrivoltaics: solar energy + better crops Climate and Nature
- Why solar power and farmers’ fields could be the perfect combination TVO
- Solar farms and sheep show the makings of a clean energy classic duo Business Renewables
- Agrivoltaics charge up St. Albert-area farms St Albert Gazette
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms are creating ideal growing conditions Western Wheel
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms create ideal growing conditions Voxpopuli
- 3D printed clamps for front-surface PV mounting on wood racking PV Magazine
- Harvesting the Sun to Grow in the Shade Garden Culture Magazine
- What crops fit with vertical agrivoltaics? PV Magazine
- Agrivoltaics – Keeping the farm in the solar farm Green Energy Futures
- Solar
- Papers
- London
- Ontario
- Canada
- Projects
- Agrivoltaics
- Solar power
- Solar energy
- Photovoltaics
- Sustainable development
- Agriculture
- SDG02 Zero hunger
- SDG07 Affordable and clean energy
- SDG09 Industry innovation and infrastructure
- Distributed manufacturing
- Farming
- Gardening
- Open hardware
- Recycling
- 3D printing
- Environmental monitoring