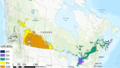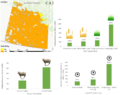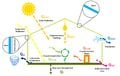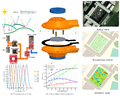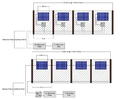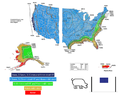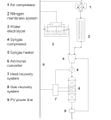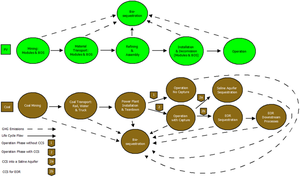
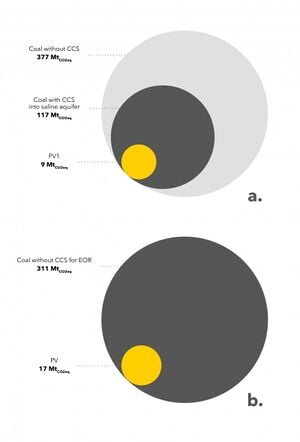
Avoiding climate destabilization caused by greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, requires climate-neutral electricity sources. It has been proposed that the GHG emissions from coal-fired power plants can be offset by carbon capture and sequestration or bio-sequestration. However, solar photovoltaic (PV) technology has recently declined so far in costs it now offers both technical and economic potential to offset all of coal-fired electricity use. PV only emits GHGs during fabrication and not during use. To determine which technical solution to climate-neutral electricity generation should be preferred, this study aggregates and synthesizes life cycle analysis studies for exergy, GHG emissions and land transformation for climate-neutral electricity. The results show that because of lower exergy efficiencies coal plants emit 13–18 times more GHG and transform 5–13 times more land than PV. Optimal bio-sequestration of coal-fired GHG requires 62% of U.S. arable land or 89% of all U.S land with average forest cover. Carbon capture and storage and enhanced oil recovery can improve coal performance, but for all cases the results clearly show that PV is a far more effective use of land. Overall, for the first time this study found climate-neutral photovoltaic farms are a preferred solution to climate-neutral coal fired electricity generation.
Results[edit | edit source]
See also Papers about coal[edit | edit source]
- Potential lives saved by replacing coal with solar photovoltaic electricity production in the U.S.
- Decarbonizing the boardroom? Aligning electric utility executive compensation with climate change incentives
See also other papers looking for land area for PV[edit | edit source]
- Aquavoltaics: Synergies for dual use of water area for solar photovoltaic electricity generation and aquaculture
- General Design Procedures for Airport-Based Solar Photovoltaic Systems
- Economic impact of substituting solar photovoltaic electric production for tobacco farming

- Coal with Carbon Capture and Sequestration is not as Land Use Efficient as Solar Photovoltaic Technology for Climate Neutral Electricity Production
- Dual use of land for PV farms and agriculture literature review
- sheep
- Israeli white plastic reflectors
- A Farmer's Guide to Going Solar (NREL)
- German guidelines: https://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/ise/en/documents/publications/studies/APV-Guideline.pdf
- 2021 review
- Miskin, C.K., Li, Y., Perna, A., Ellis, R.G., Grubbs, E.K., Bermel, P. and Agrawal, R., 2019. Sustainable co-production of food and solar power to relax land-use constraints. Nature Sustainability, 2(10), pp.972-980.
- Retrofitting solar parks for agrivoltaics
- Shading PV
- Alexis' talk at American Solar Grazing Association2021
In the News[edit source]
- Agrivoltaics: solar energy + better crops Climate and Nature
- Why solar power and farmers’ fields could be the perfect combination TVO
- Solar farms and sheep show the makings of a clean energy classic duo Business Renewables
- Agrivoltaics charge up St. Albert-area farms St Albert Gazette
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms are creating ideal growing conditions Western Wheel
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms create ideal growing conditions Voxpopuli
- 3D printed clamps for front-surface PV mounting on wood racking PV Magazine
- Harvesting the Sun to Grow in the Shade Garden Culture Magazine
- What crops fit with vertical agrivoltaics? PV Magazine
- Agrivoltaics – Keeping the farm in the solar farm Green Energy Futures
In the News[edit | edit source]
- Cover the U.S. in 89 Percent Trees—Or Go Solar Michigan Tech News 20.9k,
Science Daily 5.2k Environmental News Network 596k Udaipurkiran
- Coal plant offsets with carbon capture means covering 89 percent of the US in forests Phys.org 6.9k, Manufacturing.net 175k
- Coal-fired Power Plants Require 13 Times More Bio-Sequestration to be Carbon Neutral than Solar IEEE Global Spec 22.5k
- Coal plant offsets with carbon capture means covering 89 percent of the US in forests Eureka Alert 27.6k,
- Offsetting Coal Plants With Carbon Capture Would Mean Covering 89% of the U.S. in Forests R&D magazine 161k
- Coal Plant Offsets with Carbon Capture Means Covering 89 Percent of the U.S. In Forests Newswise 185k
- Offsetting coal plant emissions is unrealistic, study finds Earth.com 331k
- Coal plant offsets with carbon seize means overlaying 89 % of the US in forests (News) Press Cute
- Coal plant offsets with carbon seize means protecting 89 p.c of the US in forests Today Chan
- Want to Offset US Coal Emissions? Better Start Planting Courthouse News
- Research: Cover the U.S. In 89 percent trees, or go solar Tunisiesoir
- Coal plant offsets with carbon capture means covering 89 percent of the US in forests Science Blog 196k
- It Would Take A Forest The Size of the US To Offset Its Coal Emissions Newsy 171k\, Channel 5 Nashville 52.9k, T&D 341k, Yahoo 7, Toshiba 11.8k, Start Lenvovo 730, ABC Channel 7 Denver 27.9k, Fox47
- New production technique to cuts cost of solar cells by more than 10pct EQ International
- Coal-fired power plants require 13 times more land to be carbon neutral than the manufacturing of solar panels PV Buzz
- https://www.hulu.com/watch/1334926
- Compensar emissões de usinas de carvão com captura de carbono exigiria uma cobertura de 89% dos EUA com florestas EcoDebate (Spanish)
- Science: Coal plant offsets with carbon capture means covering 89 percent of the US in forests [Report] Infosurhoy
- Carbon-neutral coal 'doesn't make sense,' scientists say EE News 112k, Governors Wind and Energy Coalition
- 需要多少田地的柳枝稷和樹林才能抵消燃煤產生的能量? Ifunn 40.1k
- Biosekwestracja emisji z elektrowni węglowych to mrzonka Kopalniawidzy(Polish) 173k
- Offsetting Just One Coal Plant's Emissions Requires a Maryland-Sized Forest Iverse 6.8k
- Best Way To Capture Carbon Emissions? Don't Create Them In The First Place Clean Technica 25k
- Cover the U.S. in 89 Percent Trees—Or Go Solar Science and Technology Research News
- To make coal as carbon neutral as solar requires vast swaths of land Anthropocene Magazine
- Study: Forest prkotection also needed to combat climate change Press of Atlantic City 69k* Cubrir los EE.UU. en un 89% de árboles o usar energía solar EcoInventos 58.8k
- Estados Unidos plantea compensar gases de efecto invernadero La Verdad 29.2k Venezuelan regional newspaper.
- Study: Forest protection also needed to combat climate change NJ Environmental News
- Can Bio-Sequestration Offset Coal Plant Emissions The Virginia Engineer
- Study: Vast forests needed to offset effects of burning coal for electricity Missoula Current