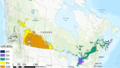
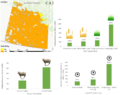
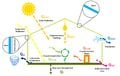
Large-scale development of solar-generated electricity is hindered in some regions of the U.S. by land use competition and localized social resistance. One approach to alleviate these coupled challenges is agrivoltaics: the strategic co-location of solar photovoltaics and agriculture. To explore the opportunities and barriers for agrivoltaics, in-depth interviews with solar industry professionals were conducted and findings suggest that the potential for an agrivoltaic project to retain agricultural interests and consequently increase local support for development is the most significant opportunity of dual use solar. Capable of increasing community acceptance, participants expect agrivoltaics to play an important role in future solar endeavors, especially in places where development may be perceived as a threat to agricultural interests. The results further reveal the interconnections among the various dimensions of social acceptance and suggest that the growth of agrivoltaics is contingent on market adoption of the technology through community acceptance and supportive local regulatory environments. As solar photovoltaic systems transcend niche applications to become larger and more prevalent, the dimensions of social acceptance, including the opportunities and barriers associated with each dimension, can help inform decision making to enhance the growth of agrivoltaics and thus photovoltaic development. The findings can help land use planners, solar developers, and municipal governments make informed decisions that strategically and meaningfully integrate agriculture and solar, and in turn provide multiple benefits including the retention of agricultural land, local economic development, and broad adoption of solar energy technologies.
External resources for agrivoltaics[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]

- Coal with Carbon Capture and Sequestration is not as Land Use Efficient as Solar Photovoltaic Technology for Climate Neutral Electricity Production
- Dual use of land for PV farms and agriculture literature review
- sheep
- Israeli white plastic reflectors
- A Farmer's Guide to Going Solar (NREL)
- German guidelines: https://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/ise/en/documents/publications/studies/APV-Guideline.pdf
- 2021 review
- Miskin, C.K., Li, Y., Perna, A., Ellis, R.G., Grubbs, E.K., Bermel, P. and Agrawal, R., 2019. Sustainable co-production of food and solar power to relax land-use constraints. Nature Sustainability, 2(10), pp.972-980.
- Retrofitting solar parks for agrivoltaics
- Shading PV
- Alexis' talk at American Solar Grazing Association2021
In the News[edit source]
- Agrivoltaics: solar energy + better crops Climate and Nature
- Why solar power and farmers’ fields could be the perfect combination TVO
- Solar farms and sheep show the makings of a clean energy classic duo Business Renewables
- Agrivoltaics charge up St. Albert-area farms St Albert Gazette
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms are creating ideal growing conditions Western Wheel
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms create ideal growing conditions Voxpopuli
- 3D printed clamps for front-surface PV mounting on wood racking PV Magazine
- Harvesting the Sun to Grow in the Shade Garden Culture Magazine
- What crops fit with vertical agrivoltaics? PV Magazine
- Agrivoltaics – Keeping the farm in the solar farm Green Energy Futures