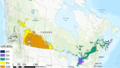
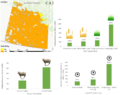
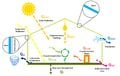
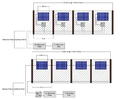
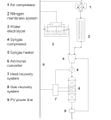
To support the broader realization of agrivoltaics in the U.S., this research provides a multidimensional assessment of the socio-political barriers and opportunities for development. A synthesis of five empirical studies is presented: 1) an investigation of the impediments to farmer adoption; 2) an exploration of development challenges from the perspective of solar industry professionals; 3) a survey gauging public support and siting preferences for agrivoltaics; 4) a life cycle assessment of a pasture-based agrivoltaic system; and 5) the development of a comprehensive legal framework for agrivoltaics in the U.S. The assessment reveals the intersectionality among key stakeholders, communities, the environment, and legal frameworks, which can inform agrivoltaic decision making, stakeholder relations, and policy design globally. The primary socio-political barriers identified include: techno-economic challenges, community resistance, lack of financial incentive for both sectors, and restrictive local land use policy. The central socio-political opportunities include: income diversification, enhanced community relations and acceptance, energy demand and emissions reduction, and policy integration between key sectors. These findings demonstrate the need for multidimensional and interdisciplinary approaches to agrivoltaic development and an increased research focus on socio-political considerations.
From AgriVoltaics 2021.
See also[edit | edit source]

- Coal with Carbon Capture and Sequestration is not as Land Use Efficient as Solar Photovoltaic Technology for Climate Neutral Electricity Production
- Dual use of land for PV farms and agriculture literature review
- sheep
- Israeli white plastic reflectors
- A Farmer's Guide to Going Solar (NREL)
- German guidelines: https://www.ise.fraunhofer.de/content/dam/ise/en/documents/publications/studies/APV-Guideline.pdf
- 2021 review
- Miskin, C.K., Li, Y., Perna, A., Ellis, R.G., Grubbs, E.K., Bermel, P. and Agrawal, R., 2019. Sustainable co-production of food and solar power to relax land-use constraints. Nature Sustainability, 2(10), pp.972-980.
- Retrofitting solar parks for agrivoltaics
- Shading PV
- Alexis' talk at American Solar Grazing Association2021
In the News[edit source]
- Agrivoltaics: solar energy + better crops Climate and Nature
- Why solar power and farmers’ fields could be the perfect combination TVO
- Solar farms and sheep show the makings of a clean energy classic duo Business Renewables
- Agrivoltaics charge up St. Albert-area farms St Albert Gazette
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms are creating ideal growing conditions Western Wheel
- Sheep, solar and crops. How some Alberta farms create ideal growing conditions Voxpopuli
- 3D printed clamps for front-surface PV mounting on wood racking PV Magazine
- Harvesting the Sun to Grow in the Shade Garden Culture Magazine
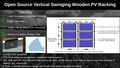
- What crops fit with vertical agrivoltaics? PV Magazine
- Agrivoltaics – Keeping the farm in the solar farm Green Energy Futures
- Solar
- Papers
- Agrivoltaics
- Solar power
- Solar energy
- Photovoltaics
- Sustainable development
- Agriculture
- SDG02 Zero hunger
- SDG07 Affordable and clean energy
- SDG08 Decent work and economic growth
- SDG09 Industry innovation and infrastructure
- SDG12 Responsible consumption and production
- Energy
- Land use
- Energy policy
- Farming
- FAST Completed
- Sheep