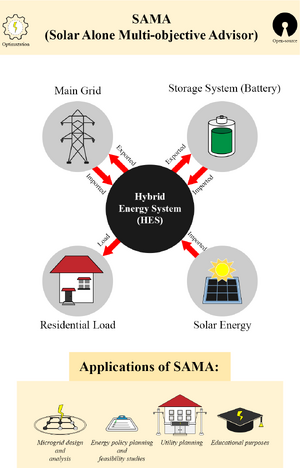

Although there are many software tools for simulations of hybrid energy systems, Homer Pro and Homer Grid are the only tools offering optimal sizing of hybrid energy systems. Originally developed as open-source software, they have been closed, which limits user-developers abilities to adapt and improve the software. In addition, all current proprietary offering suffer from the following limitations: i) high costs that limit accessibility to low-resource labs and individuals, ii) incapable of conducting multi-objective optimization, iii) constrained on any new innovations in hybrid energy system design and operation, iv) difficulties for users to specifically define prices and costs in inputs, v) inability to model different electric utility billing structures, vi) complex pricing methodology, and vii) the absence of machine learning-based predictive modeling. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces and validates SAMA (Solar Alone Multi-objective Advisor), an open-source microgrid optimization software program designed to optimize hybrid energy system sizes economically using metaheuristic algorithms based on specific load profiles and meteorological data. Through rigorous validation exercises, SAMA's outcomes are compared against those generated by the Homer Pro software across distinct climatic conditions and geographical locations (i.e., Sacramento, California in the marine west coast and New Bern in humid continental climate zones of U.S., respectively). The results demonstrate congruence between SAMA and Homer Pro. SAMA can be used for a diverse array of applications from renewable energy systems to off-grid and grid-tied configurations, and from policy formulation to feasibility assessment. Unique features of SAMA include multi-objective optimizer, levelized emission optimization, different pre-defined utility billing structures, and a top-down pricing methodology. These features further enhance SAMA’s adaptability, allowing users to tailor the software to their specific needs and system configurations. Finally, the paper anticipates future advancements that could refine component modeling, accelerate optimization processes, and incorporate advanced data analysis techniques such as machine learning to predict energy demand and production patterns.
Free source code = https://osf.io/geqwf/ Methods: Solar Alone Multi-objective Advisor (SAMA) User Manual: https://osf.io/7ztae
Highlights[edit | edit source]
- SAMA, a new open-source microgrid optimization software, was introduced an validated.
- Validation compared SAMA's results with industry-standard, Homer Pro proved accuracy.
- Results for different locations and climates, confirming SAMA's reliability and accuracy.
- SAMA introduces unique emission optimization and top-down pricing methodology for first time.
- SAMA is open-source and free, which ensures accessibility and fosters innovation.
- SAMA is broadly applicable for renewable, off-grid, grid-tied, and backup power systems.
How to Use SAMA[edit | edit source]
Media[edit | edit source]
See Also[edit | edit source]
Read More[edit | edit source]
- Achieving 100% Renewable and Self-Sufficient Electricity in Impoverished, Rural, Northern Climates: Case Studies from Upper Michigan, USA
- Low emissions analysis platform model for renewable energy: Community-scale case studies in Nigeria
- Demonstration of the integrated rural energy planning framework for sustainable energy development in low-income countries: Case studies of rural communities in Nigeria
- Decentralized Renewable Hybrid Mini-Grids for Rural Communities: Culmination of the IREP Framework and Scale up to Urban Communities
- Economic viability of captive off-grid solar photovoltaic and diesel hybrid energy systems for the Nigerian private sector
- Simulations of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions from Low-Cost Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic and Cogeneration Systems for New Communities
- Economics of Grid-Tied Solar Photovoltaic Systems Coupled to Heat Pumps: The Case of Northern Climates of the U.S. and Canada
- Decarbonizing rural residential buildings in cold climates: A techno-economic analysis of heating electrification
- Policies to Overcome Barriers for Renewable Energy Distributed Generation: A Case Study of Utility Structure and Regulatory Regimes in Michigan
- Emerging economic viability of grid defection in a northern climate using solar hybrid systems
- The Potential for Grid Defection of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises Using Solar Photovoltaic, Battery and Generator Hybrid Systems
- Can grid-tied solar photovoltaics lead to residential heating electrification? A techno-economic case study in the midwestern U.S.
- Adapting the European typology approach for building stock energy assessment (TABULA) concept for the developing world: The Nigerian case study