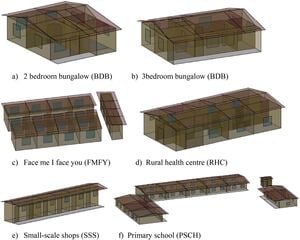
Although developing countries are rapidly urbanizing, many of their citizens still live in rural environments and the majority of the energy use is dominated by the built environment. This study aims to demonstrate the adaptation of the European typology approach for building stock energy Assessment (TABULA) project to the developing world to enable leapfrogging rural regions to sustainable energy-based societies. A case study is performed that considers ten locations across different geopolitical zones and the different climatic zones of the most populous country in sub-Saharan Africa: Nigeria. The objective is to analyse the energy performance of the low-cost building stock and assess the potential for energy and economic savings. Applying the reference building approach, building typologies were identified consisting residential and non-residential function buildings. Building simulation and composite scenario analyses were carried out and considered indoor environmental quality for adaptive comfort strategies, building retrofits by improving the building envelope and energy efficiency measures for equipment and building operation. The results for Nigeria are provided as examples of disaggregated energy characteristics of the built environment and low-cost building stock, and then a wider application to other developing countries is discussed with inherent policy implications for an effective policy mix such that takes cognisance of the tenets of Energy Modelling for Policy Support (EMoPS) and inform the design of de-factor green energy polices geared towards rehabilitating the local built environment.
Highlights[edit | edit source]
- The European Typology Approach for BUiLding stock energy Assessment (TABULA) project is adapted to the developing world.
- Identification of reference building and development of energy performance typologies for low-cost building stock.
- Dynamic building simulation and composite scenario analyses carried out.
- Detailed benchmark energy models to inform design and implementation of energy policies.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Low emissions analysis platform model for renewable energy: Community-scale case studies in Nigeria
- Demonstration of the integrated rural energy planning framework for sustainable energy development in low-income countries: Case studies of rural communities in Nigeria
- Decentralized Renewable Hybrid Mini-Grids for Rural Communities: Culmination of the IREP Framework and Scale up to Urban Communities
- Economic viability of captive off-grid solar photovoltaic and diesel hybrid energy systems for the Nigerian private sector
- Simulations of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions from Low-Cost Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic and Cogeneration Systems for New Communities
- A Free and open-source microgrid optimization tool: SAMA the Solar Alone Multi-Objective Advisor




