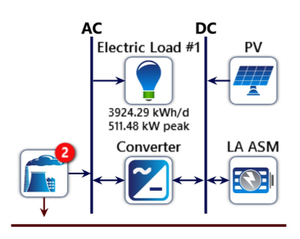
The Integrated Rural Energy Planning (IREP) framework offers a unified road map for locating, planning and operating decentralized renewable hybrid off-grid energy systems for localized (rural) applications in low-income countries. This paper presents the culmination of the IREP framework and aims to illustrate the final step of the IREP framework for two communities in Nigeria. It is focused on two aspects. Firstly, the techno-economic modeling (investment and operation optimization) of a hybrid mini-grid system using HOMER Pro, a techno-economic evaluation tool; and evaluating the benefits of demand side management (DSM) based on energy efficiency on the overall system economics using a scenario-based approach. Secondly, the conceptualization of a sustainable business model using the business model canvas scheme to deliver measurable socio-economic impacts in these communities. The results provide valuable insights into rural electrification via renewable hybrid mini-grids powered primarily with solar photovoltaic technology. Transcending mere electricity access, electricity is provided for productive uses (considering disaggregated end-uses) by harnessing other dispatchable renewable energy resources such as waste biomass. Given high share of rural population in developing countries, these insights are applicable in these regions and further the realization of the United Nations' goal of sustainable energy (SDG7) and sustainable cities and communities (SDG11).
See also[edit | edit source]
- A Free and open-source microgrid optimization tool: SAMA the Solar Alone Multi-Objective Advisor
- Demonstration of the integrated rural energy planning framework for sustainable energy development in low-income countries: Case studies of rural communities in Nigeria
- Low emissions analysis platform model for renewable energy: Community-scale case studies in Nigeria
- Economic viability of captive off-grid solar photovoltaic and diesel hybrid energy systems for the Nigerian private sector
- Adapting the European typology approach for building stock energy assessment (TABULA) concept for the developing world: The Nigerian case study
- Levelized cost of electricity for solar photovoltaic, battery and cogen hybrid systems
- Performance of U.S. hybrid distributed energy systems: Solar photovoltaic, battery and combined heat and power
- Emerging economic viability of grid defection in a northern climate using solar hybrid systems
- The Potential for Grid Defection of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises Using Solar Photovoltaic, Battery and Generator Hybrid Systems
- Review of solar levelized cost
- PV and CHP Hybrid System
- Hybrid photovoltaic-trigeneration systems
- Simulations of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions from Low-Cost Hybrid Solar Photovoltaic and Cogeneration Systems for New Communities
- Photovoltaic plus combined heat and power
- Achieving 100% Renewable and Self-Sufficient Electricity in Impoverished, Rural, Northern Climates: Case Studies from Upper Michigan, USA





