
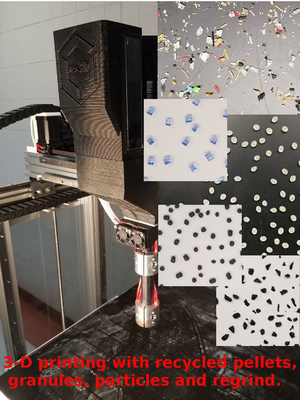
Although distributed additive manufacturing can provide high returns on investment, the current markup on commercial filament over base polymers limits deployment. These cost barriers can be surmounted by eliminating the entire process of fusing filament by three-dimensional (3-D) printing products directly from polymer granules. Fused granular fabrication (FGF) (or fused particle fabrication (FPF)) is being held back in part by the accessibility of low-cost pelletizers and choppers. An open-source 3-D printable invention disclosed here allows for precisely controlled pelletizing of both single thermopolymers as well as composites for 3-D printing. The system is designed, built, and tested for its ability to provide high-tolerance thermopolymer pellets with a number of sizes capable of being used in an FGF printer. In addition, the chopping pelletizer is tested for its ability to chop multi-materials simultaneously for color mixing and composite fabrication as well as precise fractional measuring back to filament. The US$185 open-source 3-D printable pelletizer chopper system was successfully fabricated and has a 0.5 kg/h throughput with one motor, and 1.0 kg/h throughput with two motors using only 0.24 kWh/kg during the chopping process. Pellets were successfully printed directly via FGF as well as indirectly after being converted into high-tolerance filament in a recyclebot.
Trouble Shooting[edit | edit source]

No current to motor[edit | edit source]
- If power supply is plugged in and hooked up to motor and motor does not run, check to make sure voltage output wires are properly connected to terminals
- the voltage terminals are shown properly connected to the red and blue wires
- Red wire connects to the (-V) terminal in the middle, blue wire connects to (+V) terminal (second from right)
- there should be one unconnected terminal between these two, otherwise the current will be zero
Filament gets stuck in rotating blade[edit | edit source]
- This usually occurs when the filament is significantly smaller than the feed hole diameter and deflects away from the blade. The result is the filament getting caught and sheared in the blade rather than being evenly cut.
Inspired Designs[edit | edit source]
See also[edit source]
RepRapable Recyclebot and the Wild West of Recycling[edit source]
Recycling Technology[edit source]
- Recyclebot
- RepRapable Recyclebot: Open source 3-D printable extruder for converting plastic to 3-D printing filament
- Open Source 3-D Filament Diameter Sensor for Recycling, Winding and Additive Manufacturing Machines
- Improving recyclebot concepts
- 3-D Printable Polymer Pelletizer Chopper for Fused Granular Fabrication-Based Additive Manufacturing
- Mechanical Properties of Direct Waste Printing of Polylactic Acid with Universal Pellets Extruder: Comparison to Fused Filament Fabrication on Open-Source Desktop Three-Dimensional Printers
- Fused Particle Fabrication 3-D Printing: Recycled Materials' Optimization and Mechanical Properties
- Multi-material distributed recycling via material extrusion: recycled high density polyethylene and poly (ethylene terephthalate) mixture
- Mechanical Properties and Applications of Recycled Polycarbonate Particle Material Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing
- Wood Furniture Waste-Based Recycled 3-D Printing Filament
- Solar powered distributed customized manufacturing
- Mechanical Properties of Ultraviolet-Assisted Paste Extrusion and Postextrusion Ultraviolet-Curing of Three-Dimensional Printed Biocomposites
- Open Source Waste Plastic Granulator
- Open-Source Grinding Machine for Compression Screw Manufacturing
- Sustainability and Feasibility Assessment of Distributed E-Waste Recycling using Additive Manufacturing in a Bi-Continental Context
- Finding Ideal Parameters for Recycled Material Fused Particle Fabrication-Based 3D Printing Using an Open Source Software Implementation of Particle Swarm Optimization
- Waste Plastic Direct Extrusion Hangprinter
- Hangprinter for Large Scale Additive Manufacturing using Fused Particle Fabrication with Recycled Plastic and Continuous Feeding
Distributed Recycling LCA[edit source]
- Tightening the loop on the circular economy: Coupled distributed recycling and manufacturing with recyclebot and RepRap 3-D printing
- Technical pathways for distributed recycling of polymer composites for distributed manufacturing: Windshield wiper blades
- Plastic recycling in additive manufacturing: A systematic literature review and opportunities for the circular economy
- Energy Payback Time of a Solar Photovoltaic Powered Waste Plastic Recyclebot System
- Life cycle analysis of distributed recycling of post-consumer high density polyethylene for 3-D printing filament
- Evaluation of Potential Fair Trade Standards for an Ethical 3-D Printing Filament
- Life cycle analysis of distributed polymer recycling
- Distributed recycling of post-consumer plastic waste in rural areas
- Ethical Filament Foundation
- Green Fab Lab Applications of Large-Area Waste Polymer-based Additive Manufacturing
- Systems Analysis for PET and Olefin Polymers in a Circular Economy
- Potential of distributed recycling from hybrid manufacturing of 3-D printing and injection molding of stamp sand and acrylonitrile styrene acrylate waste composite
- Towards Distributed Recycling with Additive Manufacturing of PET Flake Feedstocks
Literature Reviews[edit source]
- Waste plastic extruder: literature review
- Life cycle analysis of polymer recycling literature review
- Solar powered recyclebot literature review
- Waste plastic extruder: literature review
- Life cycle analysis of polymer recycling literature review
Externals[edit source]
- Economist article on U. of Washington's HDPE boat, Oprn3dp.me
- https://ultimaker.com/en/resources/52444-ocean-plastic-community-project
- Another possible solution - reusable containers [1]
- Commercial https://dyzedesign.com/pulsar-pellet-extruder/
- ---
- Cruz, F., Lanza, S., Boudaoud, H., Hoppe, S., & Camargo, M. Polymer Recycling and Additive Manufacturing in an Open Source context: Optimization of processes and methods. [2]
- Investigating Material Degradation through the Recycling of PLA in Additively Manufactured Parts
- Mohammed, M.I., Das, A., Gomez-Kervin, E., Wilson, D. and Gibson, I., EcoPrinting: Investigating the use of 100% recycled Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) for Additive Manufacturing.
- Kariz, M., Sernek, M., Obućina, M. and Kuzman, M.K., 2017. Effect of wood content in FDM filament on properties of 3D printed parts. Materials Today Communications. [3]
- Kaynak, B., Spoerk, M., Shirole, A., Ziegler, W. and Sapkota, J., 2018. Polypropylene/Cellulose Composites for Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, p.1800037. [4]
- O. Martikka et al., "Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed Wood-Plastic Composites", Key Engineering Materials, Vol. 777, pp. 499-507, 2018 [5]
- Yang, T.C., 2018. Effect of Extrusion Temperature on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Wood Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composite (WFRPC) Components Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers, 10(9), p.976. [6]
- Romani, A., Rognoli, V., & Levi, M. (2021). Design, Materials, and Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing in Circular Economy Contexts: From Waste to New Products. Sustainability, 13(13), 7269. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/13/7269/pdf
In the News[edit | edit source]
- Michigan Tech researchers invent 3D Printable Polymer Pelletizer Chopper 3Ders 105k Long Room
- Cutting 3D Printing Costs with an Open Source Material Pelletizer 3D Print 48k, Ichiban Electronic
- Make your own filament with this 3D Printable Pelletizer from MTU 3D Printing Industry 63.5k
- Il chopper per pelletizzatore il polimerico stampabile in 3d dalla Michigan Technological University Stamperein 3D
- Forscher aus Michigan entwickeln einen 3D-gedruckten Polymer-Granulator-Zerhacker - 3DRuck
- The Filament Pelletizer For Fused Granular Fabrication Hackaday 9.2k







