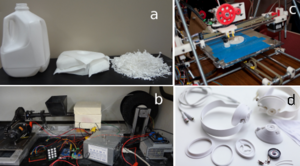
The growth of desktop 3-D printers is driving an interest in recycled 3-D printer filament to reduce costs of distributed production. Life cycle analysis studies were performed on the recycling of high density polyethylene into filament suitable for additive layer manufacturing with 3-D printers. The conventional centralized recycling system for high population density and low population density rural locations was compared to the proposed in home, distributed recycling system. This system would involve shredding and then producing filament with an open-source plastic extruder from post-consumer plastics and then printing the extruded filament into usable, value-added parts and products with 3-D printers such as the open-source self replicating rapid prototyper, or RepRap. The embodied energy and carbon dioxide emissions were calculated for high density polyethylene recycling using SimaPro 7.2 and the database EcoInvent v2.0. The results showed that distributed recycling uses less embodied energy than the best-case scenario used for centralized recycling. For centralized recycling in a low-density population case study involving substantial embodied energy use for transportation and collection these savings for distributed recycling were found to extend to over 80%. If the distributed process is applied to the U.S. high density polyethylene currently recycled, more than 100 million MJ of energy could be conserved per annum along with the concomitant significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. It is concluded that with the open-source 3-D printing network expanding rapidly the potential for widespread adoption of in-home recycling of post-consumer plastic represents a novel path to a future of distributed manufacturing appropriate for both the developed and developing world with lower environmental impacts than the current system.
Highlights[edit | edit source]

- Life cycle analysis performed on recycling of high density polyethylene (HDPE).
- HDPE filament is used additive manufacturing with open-source 3-D printers.
- Compared energy & greenhouse gas emissions for distributed vs centralized recycling.
- Distributed recycling has lower environmental impact than centralized recycling.
Key Findings[edit | edit source]
Energy Demand & Greenhouse Gas Emissions.
| Case | Energy Demand (MJ/kg HDPE) | Percent Reduction (%) for Distributed Recycling | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (kg CO2 eq per kg HDPE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distributed Recycling: Insulated RecycleBot | 8.74 | 0.52 | |
| Virgin Resin | 79.67 | 89 | 1.82 |
| Centralized Recycling – High Density Population: Detroit | 9 | 3 | 0.63 |
| Centralized Recycling – Low Density Population: Copper Harbor (monthly) | 28.4 | 69 | 2.65 |
| Centralized Recycling – Low Density Population: Copper Harbor (bi-weekly) | 48.9 | 82 | 4.04 |
See also[edit source]
RepRapable Recyclebot and the Wild West of Recycling[edit source]
Recycling Technology[edit source]
- Recyclebot
- RepRapable Recyclebot: Open source 3-D printable extruder for converting plastic to 3-D printing filament
- Open Source 3-D Filament Diameter Sensor for Recycling, Winding and Additive Manufacturing Machines
- Improving recyclebot concepts
- 3-D Printable Polymer Pelletizer Chopper for Fused Granular Fabrication-Based Additive Manufacturing
- Mechanical Properties of Direct Waste Printing of Polylactic Acid with Universal Pellets Extruder: Comparison to Fused Filament Fabrication on Open-Source Desktop Three-Dimensional Printers
- Fused Particle Fabrication 3-D Printing: Recycled Materials' Optimization and Mechanical Properties
- Multi-material distributed recycling via material extrusion: recycled high density polyethylene and poly (ethylene terephthalate) mixture
- Mechanical Properties and Applications of Recycled Polycarbonate Particle Material Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing
- Wood Furniture Waste-Based Recycled 3-D Printing Filament
- Solar powered distributed customized manufacturing
- Mechanical Properties of Ultraviolet-Assisted Paste Extrusion and Postextrusion Ultraviolet-Curing of Three-Dimensional Printed Biocomposites
- Open Source Waste Plastic Granulator
- Open-Source Grinding Machine for Compression Screw Manufacturing
- Sustainability and Feasibility Assessment of Distributed E-Waste Recycling using Additive Manufacturing in a Bi-Continental Context
- Finding Ideal Parameters for Recycled Material Fused Particle Fabrication-Based 3D Printing Using an Open Source Software Implementation of Particle Swarm Optimization
- Waste Plastic Direct Extrusion Hangprinter
- Hangprinter for Large Scale Additive Manufacturing using Fused Particle Fabrication with Recycled Plastic and Continuous Feeding
Distributed Recycling LCA[edit source]
- Tightening the loop on the circular economy: Coupled distributed recycling and manufacturing with recyclebot and RepRap 3-D printing
- Technical pathways for distributed recycling of polymer composites for distributed manufacturing: Windshield wiper blades
- Plastic recycling in additive manufacturing: A systematic literature review and opportunities for the circular economy
- Energy Payback Time of a Solar Photovoltaic Powered Waste Plastic Recyclebot System
- Life cycle analysis of distributed recycling of post-consumer high density polyethylene for 3-D printing filament
- Evaluation of Potential Fair Trade Standards for an Ethical 3-D Printing Filament
- Life cycle analysis of distributed polymer recycling
- Distributed recycling of post-consumer plastic waste in rural areas
- Ethical Filament Foundation
- Green Fab Lab Applications of Large-Area Waste Polymer-based Additive Manufacturing
- Systems Analysis for PET and Olefin Polymers in a Circular Economy
- Potential of distributed recycling from hybrid manufacturing of 3-D printing and injection molding of stamp sand and acrylonitrile styrene acrylate waste composite
- Towards Distributed Recycling with Additive Manufacturing of PET Flake Feedstocks
Literature Reviews[edit source]
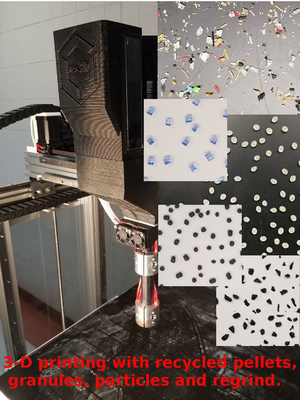
- Waste plastic extruder: literature review
- Life cycle analysis of polymer recycling literature review
- Solar powered recyclebot literature review
- Waste plastic extruder: literature review
- Life cycle analysis of polymer recycling literature review
Externals[edit source]
- Economist article on U. of Washington's HDPE boat, Oprn3dp.me
- https://ultimaker.com/en/resources/52444-ocean-plastic-community-project
- Another possible solution - reusable containers [1]
- Commercial https://dyzedesign.com/pulsar-pellet-extruder/
- ---
- Cruz, F., Lanza, S., Boudaoud, H., Hoppe, S., & Camargo, M. Polymer Recycling and Additive Manufacturing in an Open Source context: Optimization of processes and methods. [2]
- Investigating Material Degradation through the Recycling of PLA in Additively Manufactured Parts
- Mohammed, M.I., Das, A., Gomez-Kervin, E., Wilson, D. and Gibson, I., EcoPrinting: Investigating the use of 100% recycled Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) for Additive Manufacturing.
- Kariz, M., Sernek, M., Obućina, M. and Kuzman, M.K., 2017. Effect of wood content in FDM filament on properties of 3D printed parts. Materials Today Communications. [3]
- Kaynak, B., Spoerk, M., Shirole, A., Ziegler, W. and Sapkota, J., 2018. Polypropylene/Cellulose Composites for Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, p.1800037. [4]
- O. Martikka et al., "Mechanical Properties of 3D-Printed Wood-Plastic Composites", Key Engineering Materials, Vol. 777, pp. 499-507, 2018 [5]
- Yang, T.C., 2018. Effect of Extrusion Temperature on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Wood Fiber-Reinforced Polylactic Acid Composite (WFRPC) Components Using Fused Deposition Modeling. Polymers, 10(9), p.976. [6]
- Romani, A., Rognoli, V., & Levi, M. (2021). Design, Materials, and Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing in Circular Economy Contexts: From Waste to New Products. Sustainability, 13(13), 7269. https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/13/7269/pdf
Media[edit | edit source]
- Study: Recycling plastic at home saves energy and dramatically cuts 3D printing costs - CNN/Money, Gigaom
- Save Money and the Planet: Turn Your Old Milk Jugs into 3D Printer Filament- MTU News,Science Codex, Science Daily, Humanitarian News, ECN, Science Blog, EIA (India)
- Turning old plastic into 3D printer filament is greener than conventional recycling - 3Ders
- 3D printing with old milk jugs saves both money and energy Geek.com
- MTU professor turns waste plastic into 3D printer filament - Modern Plastics & Polymers
- Turning old milk jugs into 3D printer filament - Phys.org, Product Design and Development
- Michigan Tech Prof Says You Can Save Big With Milk Jug Recycling For 3D Printing - CBS Detroit
- How 3D printer can help you protect environment - Yahoo News,Business Standard, Daijiworld, IANS Live, Daily India Mail, Vancouver Desi, Malaysian Sun
- New Process Recycles Milk Jugs Into 3D Printer Filament - Red Orbit
- 3D Printer Filament Recycling is Super Green - Engineering.com
- Need 3D printer filament? Got milk? - Ars Technica
- Zelf je verpakkingen omsmelten nog milieuvriendelijker dan officieel recyclen - C2W (Dutch Chemistry magazine)
- 3D Printing: A Better Way To Recycle - Earthtechling
- DIY recycling the most energy efficient - Recycling International
- laverdad.es
- How can 3D printers help in energy conservation? - The Hindu
- 3D Printing Offers New Way to Recycle and Save Money- Franchise Herald
- Make Your Own 3-D Printer Filament From Old Milk Jugs — Exponentially Cheaper Than Buying Filament, Research Shows - Cleantechnica
- 3D Printing Plastic — Distributed Recyling and Distributing the Benefits - 3D Printing Industry
- Save the planet: Turn old milk jugs into 3D printer filament - CrowdfundingPR
- Recycling Milk Jugs into 3D Printer Filament Saves Money and the Environment - 3D Printer World
- Research: LCA of distributed recycling of post-consumer high density polyethylene for 3D printing filament - NVC Netherlands
- Can We 3D Print our Way to Sustainability? - Earth Island Journal
- Plastic: New Technology Promises Greener 3-D Printing NBC News New York, Miami Sun Times, NBC Bay Area
- Una revisión al impacto ambiental de la impresión 3D Impresiontresde




