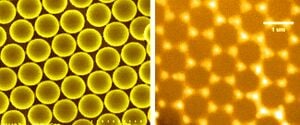
This paper presents a novel design for the top contact of thin film photovoltaic (PV) solar cells. The new top contact is formed by fabricating a 20nm thin honeycomb shaped silver mesh on top of an ultra-thin 13nm of indium tin oxide. The new top contact offers the potential to reduce the series resistance of the cell while increasing the light current via plasmonic resonance. Using the nano-bead lithography technique the honeycomb top contact was fabricated and electrically characterized. The experimental results verified the new contact reduces the sheet resistance by about 40%. Numerical simulations were then used to analyze the potential performance enhancement in the cell. The results suggest the proposed top contact integrated with a typical thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon PV device would lead to more than an 8% improvement in the overall efficiency of the cell.
Method[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
- Plasmonic enhancement of amorphous silicon solar photovoltaic cells with hexagonal silver arrays made with nanosphere lithography
- Fabricating Ordered 2-D Nano-Structured Arrays Using Nanosphere Lithography
- A new method of preparing highly conductive ultra-thin indium tin oxide for plasmonic-enhanced thin film solar photovoltaic devices
- Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Influence of Oxygen Concentration on the Performance of Ultra-Thin RF Magnetron Sputter Deposited Indium Tin Oxide Films as a Top Electrode for Photovoltaic Devices
- Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Controlling optical absorption in metamaterial absorbers for plasmonic solar cells
- Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices
- Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review
- Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation
- Effect of ambient combinations of argon, oxygen, and hydrogen on the properties of DC magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide films
- A novel synthesis of tin oxide thin films by the sol-gel process for optoelectronic applications
- Enhancement of hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells with front-surface hexagonal plasmonic arrays from nanoscale lithography
- Ambiance-dependent Agglomeration and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Response of Self-assembled Silver Nano-particles for Plasmonic Photovoltaic Devices
- Optimal Design of Thin-film Plasmonic Solar Cells using Differential Evolution Optimization Algorithms
- Optoelectronic Properties: Carrier Transport, Recombination, and Stability





