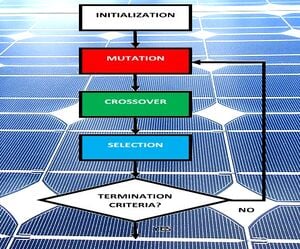
An approach using a differential evolution (DE)optimization algorithm is proposed to optimize design parameters for improving the optical absorption efficiency of plasmonic solar cells (PSC). This approach is based on formulating the parameters extraction as a search and optimization process in order to maximize the optical absorption in the PSC. Determining the physical parameters of three-dimensional (3-D) PSC is critical for designing and estimating their performance, however, due to the complex design of the PSC, parameters extraction is time and calculation intensive. In this paper, this technique is demonstrated for the case of commercial thin-film hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) solar photovoltaic cells enhanced through patterned silver nano-disk plasmonic structures. The DE optimization of PSC structures was performed to execute a real-time parameter search and optimization. The predicted optical enhancement (OE) in optical absorption in the active layer of the PSC for AM-1.5 solar spectrum was found to be over 19.45% higher compared to the reference cells. The proposed technique offers higher accuracy and automates the tuning of control parameters of PSC in a time-efficient manner.
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Differential Evolution; Optimization Algorithm; Plasmonic Solar Cells; Solar Photovoltaic; Amorphous Silicon ; Metamaterials ; Solar cells ; Semiconductors
See also[edit | edit source]
- Enhancement of hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells with front-surface hexagonal plasmonic arrays from nanoscale lithography
- Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices
- Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review
- Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation
- Influence of Oxygen Concentration on the Performance of Ultra-Thin RF Magnetron Sputter Deposited Indium Tin Oxide Films as a Top Electrode for Photovoltaic Devices
- A new method of preparing highly conductive ultra-thin indium tin oxide for plasmonic-enhanced thin film solar photovoltaic devices
- Plasmonic enhancement of amorphous silicon solar photovoltaic cells with hexagonal silver arrays made with nanosphere lithography
- Fabricating Ordered 2-D Nano-Structured Arrays Using Nanosphere Lithography
- Ambiance-dependent Agglomeration and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Response of Self-assembled Silver Nano-particles for Plasmonic Photovoltaic Devices
- Scalable honeycomb top contact to increase the light absorption and reduce the series resistance of thin film solar cells
- Optoelectronic Properties: Carrier Transport, Recombination, and Stability





