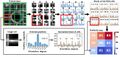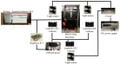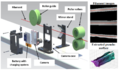
This study analyzes a low-cost reliable real-time optical monitoring platform for fused filament fabrication-based open source 3D printing. An algorithm for reconstructing 3D images from overlapping 2D intensity measurements with relaxed camera positioning requirements is compared with a single-camera solution for single-side 3D printing monitoring. The algorithms are tested for different 3D object geometries and filament colors. The results showed that both of the algorithms with a single- and double-camera system were effective at detecting a clogged nozzle, incomplete project, or loss of filament for a wide range of 3D object geometries and filament colors. The combined approach was the most effective and achieves 100% detection rate for failures. The combined method analyzed here has a better detection rate and a lower cost compared to previous methods. In addition, this method is generalizable to a wide range of 3D printer geometries, which enables further deployment of desktop 3D printing as wasted print time and filament are reduced, thereby improving the economic advantages of distributed manufacturing.
- Open source code for Matlab https://osf.io/hwdzm/
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Real-time monitoring, 3D printing, Optical monitoring, RepRap, Open hardware, Quality assurance
See also[edit | edit source]
- ---
- OS Computer Vision for Distributed Recycling and Additive Manufacturing
- Additional OS Computer Vision Applications
- ---
- Mechanical Properties of Components Fabricated with Open-Source 3-D Printers Under Realistic Environmental Conditions
- The Effects of PLA Color on Material Properties of 3-D Printed Components
- Viability of Distributed Manufacturing of Bicycle Components with 3-D Printing: CEN Standardized Polylactic Acid Pedal Testing
- Improved model and experimental validation of deformation in fused filament fabrication of polylactic acid