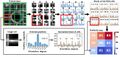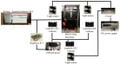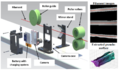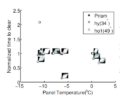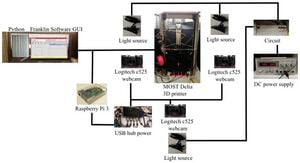
Prosumer (producing consumer)-based desktop additive manufacturing has been enabled by the recent radical reduction in 3-D printer capital costs created by the open-source release of the self-replicating rapid prototype (RepRap). To continue this success, there have been some efforts to improve reliability, which are either too expensive or lacked automation. A promising method to improve reliability is to use computer vision, although the success rates are still too low for widespread use. To overcome these challenges an open source low-cost reliable real-time optimal monitoring platform for 3-D printing from double cameras is presented here. This error detection system is implemented with low-cost web cameras and covers 360 degrees around the printed object from three different perspectives. The algorithm is developed in Python and run on a Raspberry Pi3 mini-computer to reduce costs. For 3-D printing monitoring in three different perspectives, the systems are tested with four different 3-D object geometries for normal operation and failure modes. This system is tested with two different techniques in the image pre-processing step: SIFT and RANSAC rescale and rectification, and non-rescale and rectification. The error calculations were determined from the horizontal and vertical magnitude methods of 3-D reconstruction images. The non-rescale and rectification technique successfully detects the normal printing and failure state for all models with 100% accuracy, which is better than the single camera set up only. The computation time of the non-rescale and rectification technique is two times faster than the SIFT and RANSAC rescale and rectification technique.
- Open source code : https://osf.io/b9h7y/
- Models : https://osf.io/utp6g/
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Real-time monitoring, 3D printing, Optical monitoring, RepRap, Open hardware, Quality assurance, 2-D reconstruction; error detection; reliability; computer analysis
See also[edit | edit source]
- OS Computer Vision for Distributed Recycling and Additive Manufacturing
- Other OS Computer Vision Applications
- Mechanical Properties of Components Fabricated with Open-Source 3-D Printers Under Realistic Environmental Conditions
- The Effects of PLA Color on Material Properties of 3-D Printed Components
- Viability of Distributed Manufacturing of Bicycle Components with 3-D Printing: CEN Standardized Polylactic Acid Pedal Testing