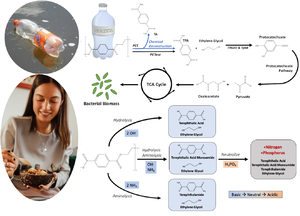
Most polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic waste is landfilled or pollutes the environment. Additionally, global food production must increase to support the growing population. This article explores the feasibility of using microorganisms in an industrial system that upcycles PET into edible microbial protein powder to solve both problems simultaneously. Many microorganisms can utilize plastics as feedstock, and the resultant microbial biomass contains fats, nutrients, and proteins similar to those found in human diets. While microbial degradation of PET is promising, biological PET depolymerization is too slow to resolve the global plastic crisis and projected food shortages. Evidence reviewed here suggests that by coupling chemical depolymerization and biological degradation of PET, and using cooperative microbial communities, microbes can efficiently convert PET waste into food.
Highlights[edit | edit source]
- Innovative solutions are needed to resolve the ongoing global issues of excess plastic waste and food insecurity.
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymers can be depolymerized and biodegraded by naturally occurring microorganisms, although rates of degradation are too slow to independently form the foundation of a biotechnological process and help to resolve the global plastic crisis.
- Chemical depolymerization of PET can deconstruct plastics into aromatic building blocks.
- Microorganisms can more rapidly break down the aromatic building blocks of PET after chemical depolymerization, greatly improving rates of biodegradation.
- Single-cell protein (SCP) is a food source that is derived from microbial cells. Microbial cells grown on waste products offer a promising source of alternative protein and other nutrients.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Feeding Everyone No Matter What - The full book main page
- David Denkenberger and Joshua Pearce, Feeding Everyone No Matter What: Managing Food Security After Global Catastrophe , 1st Edition, Academic Press, 2015
- Free Preview: Google books
- Cover on Academia
- Facebook page
- Alternative Foods as a Solution to Global Food Supply Catastrophes
- Resilience to global food supply catastrophes
- Feeding Everyone if the Sun is Obscured and Industry is Disabled
- Cost-Effectiveness of Interventions for Alternate Food to Address Agricultural Catastrophes Globally
- Feeding Everyone: Solving the Food Crisis in Event of Global Catastrophes that Kill Crops or Obscure the Sun
- Food without sun: Price and life-saving potential
- Cost-effectiveness of interventions for alternate food in the United States to address agricultural catastrophes
- Micronutrient Availability in Alternative Foods During Agricultural Catastrophes
- Preliminary Automated Determination of Edibility of Alternative Foods: Non-Targeted Screening for Toxins in Red Maple Leaf Concentrate
- Open Source Software Toolchain for Automated Non-Targeted Screening for Toxins in Alternative Foods
- Scaling of greenhouse crop production in low sunlight scenarios
- Potential of microbial protein from hydrogen for preventing mass starvation in catastrophic scenarios
- U.S. Potential of Sustainable Backyard Distributed Animal and Plant Protein Production During & After Pandemics
- Global distribution of forest classes and leaf biomass for use as alternative foods to minimize malnutrition
- Long-term cost-effectiveness of interventions for loss of electricity/industry compared to artificial general intelligence safety
- Long term cost-effectiveness of resilient foods for global catastrophes compared to artificial general intelligence safety
- Rapid repurposing of pulp and paper mills, biorefineries, and breweries for lignocellulosic sugar production in global food catastrophes
- Nutrition in Abrupt Sunlight Reduction Scenarios: Envisioning Feasible Balanced Diets on Resilient Foods
- Methane Single Cell Protein: securing protein supply during global food catastrophes
- Killing two birds with one stone: chemical and biological upcycling of polyethylene terephthalate plastics into food
- How Easy is it to Feed Everyone? Economic Alternatives to Eliminate Human Nutrition Deficits
- Quantifying Alternative Food Potential of Agricultural Residue in Rural Communities of Sub-Saharan Africa
- Yield and Toxin Analysis of Leaf Protein Concentrate from Common North American Coniferous Trees
- Toxic Analysis of Leaf Protein Concentrate Regarding Common Agricultural Residues
- Towards Sustainable Protein Sources: The Thermal and Rheological Properties of Alternative Proteins
Additional Information[edit source]
- ALLFED
- Dave Denkenberger Publications
- OSE Wiki "Synfood" (i.e. protein and other dietary components from microbial organisms fed on gas or other hydrocarbons)





