Human civilization's food production system is currently unprepared for catastrophes that would reduce global food production by 10% or more, such as nuclear winter, supervolcanic eruptions or asteroid impacts. Alternative foods that do not require much or any sunlight have been proposed as a more cost-effective solution than increasing food stockpiles, given the long duration of many global catastrophic risks (GCRs) that could hamper conventional agriculture for 5 to 10 years.
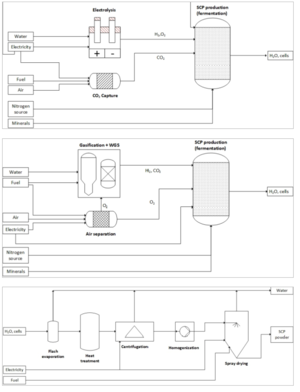
Microbial food from single cell protein (SCP) produced via hydrogen from both gasification and electrolysis is analyzed in this study as alternative food for the most severe food shock scenario: a sun-blocking catastrophe. Capital costs, resource requirements and ramp up rates are quantified to determine its viability. Potential bottlenecks to fast deployment of the technology are reviewed.
The ramp up speed of food production for 24/7 construction of the facilities over 6 years is estimated to be lower than other alternatives (3-10% of the global protein requirements could be fulfilled at end of first year), but the nutritional quality of the microbial protein is higher than for most other alternative foods for catastrophes. Results suggest that investment in SCP ramp up should be limited to the production capacity that is needed to fulfill only the minimum recommended protein requirements of humanity during the catastrophe. Further research is needed into more uncertain concerns such as transferability of labor and equipment production. This could help reduce the negative impact of potential food-related GCRs.
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Low sunlight; Nuclear winter; Existential risk; alternative food; existential risk; global catastrophic risk; public health; sustainable food systems; Single Cell Protein; Hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria; Food Security; Nuclear Winter
See also[edit | edit source]
- Feeding Everyone No Matter What - The full book main page
- David Denkenberger and Joshua Pearce, Feeding Everyone No Matter What: Managing Food Security After Global Catastrophe , 1st Edition, Academic Press, 2015
- Free Preview: Google books
- Cover on Academia
- Facebook page
- Alternative Foods as a Solution to Global Food Supply Catastrophes
- Resilience to global food supply catastrophes
- Feeding Everyone if the Sun is Obscured and Industry is Disabled
- Cost-Effectiveness of Interventions for Alternate Food to Address Agricultural Catastrophes Globally
- Feeding Everyone: Solving the Food Crisis in Event of Global Catastrophes that Kill Crops or Obscure the Sun
- Food without sun: Price and life-saving potential
- Cost-effectiveness of interventions for alternate food in the United States to address agricultural catastrophes
- Micronutrient Availability in Alternative Foods During Agricultural Catastrophes
- Preliminary Automated Determination of Edibility of Alternative Foods: Non-Targeted Screening for Toxins in Red Maple Leaf Concentrate
- Open Source Software Toolchain for Automated Non-Targeted Screening for Toxins in Alternative Foods
- Scaling of greenhouse crop production in low sunlight scenarios
- Potential of microbial protein from hydrogen for preventing mass starvation in catastrophic scenarios
- U.S. Potential of Sustainable Backyard Distributed Animal and Plant Protein Production During & After Pandemics
- Global distribution of forest classes and leaf biomass for use as alternative foods to minimize malnutrition
- Long-term cost-effectiveness of interventions for loss of electricity/industry compared to artificial general intelligence safety
- Long term cost-effectiveness of resilient foods for global catastrophes compared to artificial general intelligence safety
- Rapid repurposing of pulp and paper mills, biorefineries, and breweries for lignocellulosic sugar production in global food catastrophes
- Nutrition in Abrupt Sunlight Reduction Scenarios: Envisioning Feasible Balanced Diets on Resilient Foods
- Methane Single Cell Protein: securing protein supply during global food catastrophes
- Killing two birds with one stone: chemical and biological upcycling of polyethylene terephthalate plastics into food
- How Easy is it to Feed Everyone? Economic Alternatives to Eliminate Human Nutrition Deficits
- Quantifying Alternative Food Potential of Agricultural Residue in Rural Communities of Sub-Saharan Africa
- Yield and Toxin Analysis of Leaf Protein Concentrate from Common North American Coniferous Trees
- Toxic Analysis of Leaf Protein Concentrate Regarding Common Agricultural Residues
- Towards Sustainable Protein Sources: The Thermal and Rheological Properties of Alternative Proteins
Additional Information[edit source]
- ALLFED
- Dave Denkenberger Publications
- OSE Wiki "Synfood" (i.e. protein and other dietary components from microbial organisms fed on gas or other hydrocarbons)






