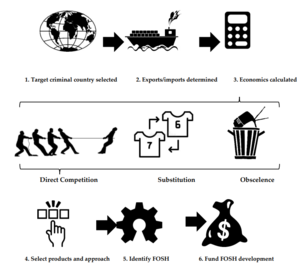
Free and open-source hardware (FOSH) development has been shown to increase innovation and reduce economic costs. This article reviews the opportunity to use FOSH as a sanction to undercut imports and exports from a target criminal country. A formal methodology is presented for selecting strategic national investments in FOSH development to improve both national security and global safety. In this methodology, first the target country that is threatening national security or safety is identified. Next, the top imports from the target country as well as potentially other importing countries (allies) are quantified. Hardware is identified that could undercut imports/exports from the target country. Finally, methods to support the FOSH development are enumerated to support production in a commons-based peer production strategy. To demonstrate how this theoretical method works in practice, it is applied as a case study to a current criminal military aggressor nation, who is also a fossil-fuel exporter. The results show that there are numerous existing FOSH and opportunities to develop new FOSH for energy conservation and renewable energy to reduce fossil-fuel-energy demand. Widespread deployment would reduce the concomitant pollution, human health impacts, and environmental desecration as well as cut financing of military operations.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Towards national policy for open source hardware research: The case of Finland
- Open source decarbonization for a sustainable world
- Economic Savings for Scientific Free and Open Source Technology: A Review
- Sponsored Libre Research Agreements to Create Free and Open Source Software and Hardware
- Quantifying the Value of Open Source Hardware Development
- Open-source, self-replicating 3-D printer factory for small-business manufacturing
- Global value chains from a 3D printing perspective
- Emerging Business Models for Open Source Hardware
- Making the Tools to Do-It-Together: Open-source Compression Screw Manufacturing Case Study
- Emerging economic viability of grid defection in a northern climate using solar hybrid systems
- The Potential for Grid Defection of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises Using Solar Photovoltaic, Battery and Generator Hybrid Systems
- Levelized cost of electricity for solar photovoltaic, battery and cogen hybrid systems
- Performance of U.S. hybrid distributed energy systems: Solar photovoltaic, battery and combined heat and power
- Policies to Overcome Barriers for Renewable Energy Distributed Generation: A Case Study of Utility Structure and Regulatory Regimes in Michigan
- Examining interconnection and net metering policy for distributed generation in the United States
- A review of the value of solar methodology with a case study of the U.S. VOS
- Economics of Grid-Tied Solar Photovoltaic Systems Coupled to Heat Pumps: The Case of Northern Climates of the U.S. and Canada
- Economic Impact of DIY Home Manufacturing of Consumer Products with Low-cost 3D Printing from Free and Open Source Designs
- Professors Want to Share: Preliminary Survey Results on Establishing Open Source Endowed Professorships
- Canadian professors’ views on establishing open source endowed professorships
- Equitable Research Capacity Towards the Sustainable Development Goals: The Case for Open Science Hardware
- Can grid-tied solar photovoltaics lead to residential heating electrification? A techno-economic case study in the midwestern U.S.
- Business Models for Open Source Hardware Repositories
- Leveraging Open Source Development Value to Increase Freedom of Movement of Highly Qualified Personnel




