Distributed generation with solar photovoltaic (PV) technology is economically competitive if net metered in the U.S. Yet there is evidence that net metering is misrepresenting the true value of distributed solar generation so that the value of solar (VOS) is becoming the preferred method for evaluating economics of grid-tied PV. VOS calculations are challenging and there is widespread disagreement in the literature on the methods and data needed. To overcome these limitations, this study reviews past VOS studies to develop a generalized model that considers realistic future avoided costs and liabilities. The approach used here is bottom-up modeling where the final VOS for a utility system is calculated. The avoided costs considered are: plant O&M fixed and variable; fuel; generation capacity, reserve capacity, transmission capacity, distribution capacity, and environmental and health liability. The VOS represents the sum of these avoided costs. Each sub-component of the VOS has a sensitivity analysis run on the core variables and these sensitivities are applied for the total VOS. The results show that grid-tied utility customers are being grossly under-compensated in most of the U.S. as the value of solar eclipses the net metering rate as well as two-tiered rates. It can be concluded that substantial future work is needed for regulatory reform to ensure that grid-tied solar PV owners are not unjustly subsidizing U.S. electric utilities.
Highlights[edit | edit source]
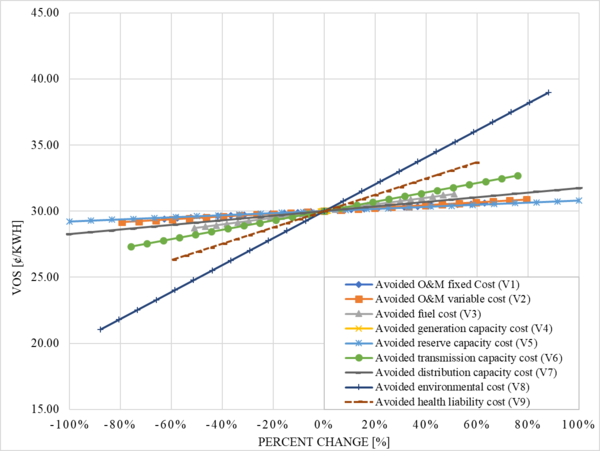
- Distributed generation solar photovoltaic (PV) economically competitive if net metered in U.S.
- Value of solar (VOS) is becoming preferred method for evaluating economics of grid-tied PV.
- Here review VOS calculations, inputs and sensitivity analysis on all core variables.
- Results: VOS eclipses the net metering rate as well as two-tiered rates in US.
- Regulatory reform needed: solar PV owners are unjustly subsidizing electric utilities.
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Photovoltaic; Utility policy; Distributed generation;Value of solar;Net metering; Economics; Levelized cost of electricity
See also[edit | edit source]
- Review of solar levelized cost
- Levelized cost of electricity for solar photovoltaic, battery and cogen hybrid systems
- Emerging economic viability of grid defection in a northern climate using solar hybrid systems
- The Potential for Grid Defection of Small and Medium Sized Enterprises Using Solar Photovoltaic, Battery and Generator Hybrid Systems
- Policies to Overcome Barriers for Renewable Energy Distributed Generation: A Case Study of Utility Structure and Regulatory Regimes in Michigan
- Examining interconnection and net metering policy for distributed generation in the United States
- Energy Policy for Energy Sovereignty: Can policy tools enhance energy sovereignty?
- The energy crises revealed by COVID: Intersections of Indigeneity, inequity, and health
- Applying a Relationally and Socially Embedded Decision Framework to Solar Photovoltaic Adoption: A Conceptual Exploration
- Economics of Grid-Tied Solar Photovoltaic Systems Coupled to Heat Pumps: The Case of Northern Climates of the U.S. and Canada
- Decarbonizing rural residential buildings in cold climates: A techno-economic analysis of heating electrification
- Strategic Investment in Open Hardware for National Security
- Open source decarbonization for a sustainable world
- Can grid-tied solar photovoltaics lead to residential heating electrification? A techno-economic case study in the midwestern U.S.
- Economics of Open-Source Solar Photovoltaic Powered Cryptocurrency Mining





