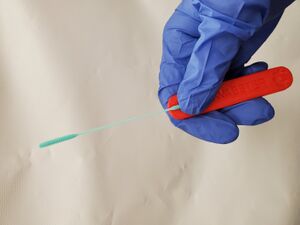
Access to nasopharyngeal swabs for sampling remain a bottleneck in some regions for COVID-19 testing. This study develops a distributed manufacturing solution using only an open source manufacturing tool chain consisting of two types of open source 3-D printing and batch UV curing, and provides a parametric fully free design of a nasopharyngeal swab. The swab was designed using parametric OpenSCAD in two components (a head with engineered break point and various handles), which has several advantages: i) minimizing print time on relatively slow SLA printers, ii) enabling the use of smaller print volume open source SLA printers, iii) reducing the amount of relatively expensive UV resin, and iv) enabling production of handle on more accessible material extrusion 3-D printers. A modular open source UV LED box was designed, fabricated for $45 and tested for batch curing. Swabs can be fabricated for $0.06-$0.12/swab. The results of the mechanical validation tests showed that the swabs could withstand greater forces than would be expected in normal clinical use. The swabs were also able to absorb a significant amounts of synthetic mucus materials and passed abrasion and handling tests. The results show the open source swab are promising candidates for clinical trials.
- All source code on OSF https://osf.io/z5jgu/
- Swab design NIH:
- UV curing box design on OCI:
- Github repo:[1]
Keywords[edit | edit source]
open hardware, COVID-19, medical hardware, nasopharyngeal swab, nasal swab, UV curing, SLA, RepRap, 3-D printing, additive manufacturing
See also[edit | edit source]
- Open-Source Medical Hardware for Pandemics
- A review of open source ventilators for COVID-19 and future pandemics
- Maximizing Returns for Public Funding of Medical Research with Open-source Hardware
- Economic Potential for Distributed Manufacturing of Adaptive Aids for Arthritis Patients in the U.S.
- 3-D printing open-source click-MUAC bands for identification of malnutrition
- Emergence of Home Manufacturing in the Developed World: Return on Investment for Open-Source 3-D Printers
- Quantifying the Value of Open Source Hardware Development
- Additively Manufactured Parametric Universal Clip-System: An Open Source Approach for Aiding Personal Exposure Measurement in the Breathing Zone
- Economic Impact of DIY Home Manufacturing of Consumer Products with Low-cost 3D Printing from Free and Open Source Designs
See also COVID-19 resources from MOST[edit | edit source]
- 2020 Michigan Tech Open Sustainability Technology Group COVID19 Projects & Publications