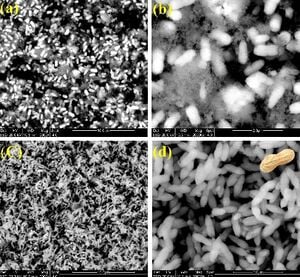
This paper describes a simple, low-temperature and cost effective chemical precipitation method in aqueous media to synthesis uniformly distributed zinc oxide (ZnO) microstructures for the fabrication of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). The size and morphology of the ZnO microstructures are systematically controlled by adjusting the concentration of the precursors, zinc acetate dihydrate and ammonium hydroxide. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are used for the structural characterizations and photoluminescence and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy are used to characterize the optical properties of the ZnO, respectively. The results reveal that ZnO crystallites exhibit hexagonal wurtzite structure with preferential orientation along c-axis. The effect of ammonia concentration on the crystallinity, morphology and optical properties of ZnO microstructures and the concomitant effect on the efficiency of dye-sensitized solar cells is also quantified. The peanut-shaped ZnO microstructure, which was found to increase DSSCs performance over other microstructure, is studied in detail in order to develop a formation mechanism. A sandwich type eosin yellow sensitized solar cell is prepared using peanut-shaped ZnO microstructures, which showed an efficiency of 0.37%. Ammonia was found to play a crucial role in the evolution of ZnO morphologies. These results are promising and provide a path towards low-cost high-performance DSSCs based on peanut-shaped ZnO microstructures and produced with only relatively simple wet chemistry synthesis.
See also[edit | edit source]
- Effect of ambient combinations of argon, oxygen, and hydrogen on the properties of DC magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide films
- Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- A novel synthesis of tin oxide thin films by the sol-gel process for optoelectronic applications
- Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices
- Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review
- Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation
- Effect of microwave power irradiation on TiO2 nano-structures and binder free paste screen printed dye sensitized solar cells
- Dual morphology titanium dioxide for dye sensitized solar cells
- Reaction Induced Multifunctional TiO2 Rod/Spherical Nanostructured Materials for Screen Printed Dye Sensitized Solar Cells
- Enhanced Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Performance using Strontium Titanate Perovskite Integrated Photoanodes Modified with Plasmonic Silver Nanoparticles
- Microwave-Assisted Synthesized Gadolinium Doped Barium Strontium Titanate Nanostructures: Structural and Optical Properties for DSSC Applications
- Impact of Coupled Plasmonic Effect with Multishaped Silver Nanoparticles on Efficiency of Dye Sensitized Solar Cells
- The use of urea as an N-doping 3D hierarchical preserving agent for titanium dioxide nanostructures tailored for dye-sensitized solar cells
- Visible light driven photocatalytic performance of 3D TiO2/g-C3N5 nanocomposites via Z-scheme charge transfer promotion for water purification
- Fabrication of Bimetallic Inlaid Working Electrode for Highly Efficient Dye Sensitized Solar Cells





