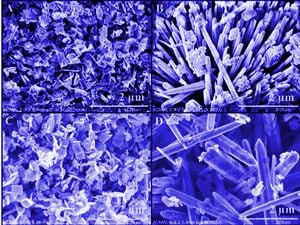
Nickel doped zinc oxide (Ni/ZnO) nanostructures have the potential to improve the performance of electrochemical capacitors. This study investigates the preparation of Ni/ZnO nanomaterials by facile co-precipitation (CPM) and hydrothermal (HTM) methods. The effect of the synthesis methods on the optical, structural, chemical and morphological properties of ZnO products is investigated using ultra violet (UV)-visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX), room temperature photoluminescence (PL), fourier transform infrared (FTIR) and Raman spectroscopy. Finally, the electrochemical performance of the synthesized nanorods was examined by the fabrication of a supercapacitor using standard three electrode cell configurations and tested with a cyclic voltammogram (CV) and galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) measurements. The results showed that the samples synthesized by HTM exhibited improved electrochemical capacitance performance with higher current density. The discharge curves are linear in the total range of potential with constant slopes, showing perfect capacitance. In conclusion, Ni/ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by this method with further optimization have the potential to lead to high-efficiency supercapacitors.
Keywords[edit | edit source]
zinc oxide, Ni doped ZnO, co precipitation method, hydrothermal synthesis, electro-chemical performance





