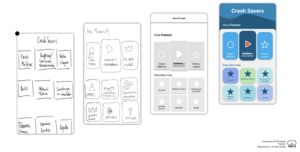
The physical simulator is the core of the psychomotor component of the training, but successful application of an appropriate hemorrhage control technique requires a more complete understanding of the demands of specific clinical scenarios. As such, we have designed a web and phone-based application that includes a gamified environment for learning and user engagement that complements the physical model. The CrashSavers Virtual Application serves as a home base for the user and includes (1) step-by-step instructions on how to construct our low-cost simulator, (2) didactic material on anatomical knowledge and clinical decision making for appropriate hemorrhage control techniques, (3) a virtual simulator to master the steps of these individual techniques, and (4) a self-assessment component.
The game-style application includes didactic material on anatomical knowledge and decision making. Additionally, there is a video instruction on how to appropriately perform the hemorrhage control techniques of interest (pressure, packing, tourniquet use, and foley catheter deployment) based on the simulator and real-life scenarios.
Finally, the educational component of the application will include a virtual simulator to master the steps of these individual techniques. There will also be after completion of all educational modules, users will graduate to perform the skills on the physical simulator model.
Users
The country of Guatemala, like many LMIC countries, lacks an organized EMS system and there is very little established infrastructure for prehospital care. All prehospital care is provided by three independent firefighting companies, largely utilizing volunteer services. Transport vehicles and other medical equipment are rarely available, and often firefighters buy the necessary equipment at their own expense. Given the lack of formalized prehospital infrastructure, there is also a gap in medical training and education of these prehospital staff. Anyone with a 6th-grade education is eligible to become a firefighter in Guatemala, and must subsequently complete a 2 week, 160-hour course endorsed by USAID. One of the firefighter training programs offers an optional 2.5 year EMT course, but very few actually complete this. Due to the lack of training and volunteer status of most of the firefighters who provide pre-hospital care, the majority of prehospital care consists of a "scoop and run" approach rather than taking vital signs, doing ultrasounds, or providing significant stabilization prior to transport to definitive care. Ultimately, 8,500 firefighters with basic first aid training and little to no equipment attend to the emergency needs of 18 million Guatemalans. These volunteers would greatly benefit from formalized training in hemorrhage control techniques.
Skills Acquisition
Effective hemorrhage control requires prompt, decisive action and forceful application of pressure or a tourniquet. Using our program, the user will learn how to externally compress a wound, apply a tourniquet, and deploy foley catheters to arrest hemorrhage to a physical model of a lower extremity. The model has been constructed of low-cost materials available at a hardware store (PVC pipe, wire mesh, metal racking, springs, tubing, plumber's tape) integrated with an electrical and fluid pumping system.
Full details on the simulator construction and manual can be viewed here
In brief, the user will apply direct compression, packing, a tourniquet, and/or a foley catheter to our physical simulator model to arrest 'hemorrhage' (simulated by red fluid).
The user will have two means of feedback
(1) direct visualization of the arrest of hemorrhage
(2) a readout of the pressure applied by the user, measured by sensors in the model and shown in the accompanying smartphone application.
Effective application of pressure, packing, tourniquet, and/or foley catheter tamponade in our system will directly translate into clinical effectiveness of these skills as we will measure the pressure exerted in order to arrest hemorrhage.
Example of skill Acquisition - Foley Catheters
Foley catheter hemorrhage control will be used in two different scenarios. In the first, the patient has a deep, narrow wound in an extremity, likely due to a penetrating injury. Foley catheters provide a low-cost method of performing direct compression to the deep wound without additional ischemia of the extremity distal to the injury as is the case when a tourniquet is used. This is particularly useful given the extended transfer times from rural areas, as well as the long wait times for definitive surgery once the patient has arrived at a trauma center. In the second scenario, foley catheters can be used to control hemorrhage at anatomical junctions, such as the axilla or groin, in which tourniquets cannot be applied.