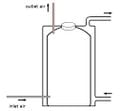
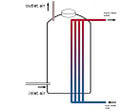
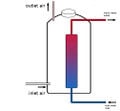
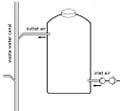
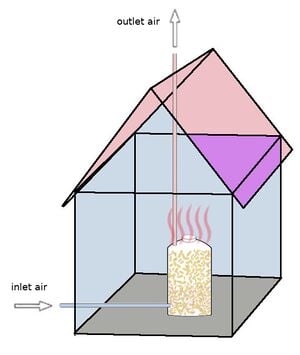
 Silo à compost à l'intérieur d'une maison d'habitation.
Silo à compost à l'intérieur d'une maison d'habitation.Le silo de chauffage à compost est la partie centrale d'un chauffage à compost interne . Le processus de compostage se déroule dans un silo hermétique, placé dans une partie appropriée du bâtiment. La chaleur produite peut être distribuée par un circuit de chauffage, alors qu'un modèle simple d'un tel silo chauffant à compost ne nécessite pas de circulation d'eau, rayonnant la chaleur directement vers l'intérieur de la maison. En automne, le silo est rempli de biomasse fraîche , après quoi le silo fournit une chaleur confortable tout au long de l'hiver.
Contenu
Construction
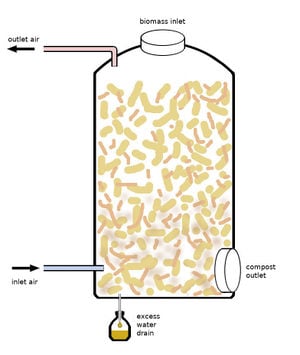 Construction du silo
Construction du siloL’air d’entrée et l’air de sortie fournissent l’ apport d’oxygène nécessaire aux microbes et aux invertébrés présents dans le silo. Pour éviter les mauvaises odeurs, l'air évacué doit sortir à l'air libre et doit être protégé contre l'arrivée d'animaux (souris).
L'humidité dans le silo doit être suffisamment élevée pour soutenir le processus de compostage, offrant ainsi des conditions optimales pour les microbes et les champignons. Après un démarrage réussi, le processus de décomposition produit de l'eau supplémentaire, qui est évacuée au fond du silo. Cette eau peut être versée en haut du silo pour une meilleure répartition des microbes dans tout le volume de traitement. S'il est pompé périodiquement ou continuellement vers le haut et laissé rincer à travers le silo, l'ensemble du système devient similaire au compostage humide (Projet CROP du DLR [1] [2] ).
En option, le processus de compostage dans le silo peut être utilisé pour chauffer l'eau, ce qui nécessite l'installation supplémentaire d'une conduite d'eau verticale dans le silo, éventuellement en combinaison avec un ballon de stockage d'eau chaude.
Préchauffage de l'air d'admission
 Prototype
Prototype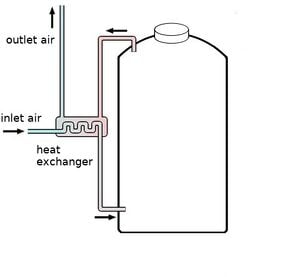 Utilisation d'un échangeur de chaleur pour l'air d'entrée
Utilisation d'un échangeur de chaleur pour l'air d'entrée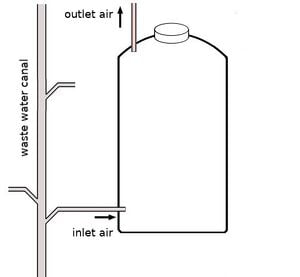 Utilisation d'un canal d'eaux usées existant pour l'air d'entrée
Utilisation d'un canal d'eaux usées existant pour l'air d'entréeL'air de sortie laisse échapper une partie de la chaleur. Il existe quelques solutions pour réduire cela :
- Un échangeur de chaleur en option peut être intégré, qui extrait la chaleur de l'air de sortie et augmente la température de l'air entrant.
- Raccordement de l'arrivée d'air à un canal d'eaux usées. La construction utilise la ventilation du canal tout en empêchant de manière adéquate l'afflux d'eaux usées dans le silo. Habituellement, de l’air chaud s’élève d’un canal d’eaux usées. Bien que nauséabond, l’air contient suffisamment d’oxygène pour le bien-être des microbes et des invertébrés.
Conditions d'utilisation
La quantité de chaleur produite est limitée. La taille du silo de chauffage du compost doit être adaptée aux besoins réels en énergie thermique du bâtiment. Par exemple, le concept House-in-a-House lui convient en raison de ses très faibles besoins en chauffage. Pour les calculs, se référer au paragraphe correspondant dans le chauffe-composteur .
Systèmes existants
Prototype de taille 300 litres pour une étude de faisabilité. Il sert à la recherche sur les fonctionnalités et à leur optimisation. Le système fonctionne depuis septembre 2017 et se porte très bien.
Extensions prévues
Paroi double couche pour évacuer l'air chaud vers d'autres pièces. L'excès de chaleur peut être évacué du bâtiment.
Distribution de la chaleur à l'aide de circuits de chauffage réguliers
Avec stockage d'eau chaude à l'intérieur du silo
Version avec un seul tuyau d'air
Béton et Tuiles
L'installation finale pour chauffer une maison d'habitation sera réalisée à partir de fines couches de béton recouvertes de tuiles. Cela ressemblera à un poêle en faïence.
Double paroi
Le silo sera à double paroi, ce qui permettra une meilleure canalisation de l'air chaud. Si l’on souhaite réduire la chaleur, par exemple lors d’une chaude journée de printemps, l’excès de chaleur peut être évacué à l’air libre.
Chauffage à l'eau
Un réservoir de stockage de chaleur pour l’eau chaude sera placé au centre du silo. Le réservoir absorbe l'énergie thermique du processus de décomposition environnant. L'eau chaude peut être utilisée pour un usage domestique. Les meilleures performances sont obtenues s’il est construit sous forme de stockage de charges en couches ou stratifié.
Combinaison avec une fonction WC
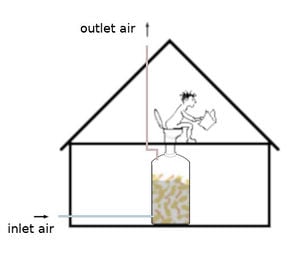 Silo chauffant à compost avec fonction de toilettes supplémentaire à l'intérieur d'une maison d'habitation
Silo chauffant à compost avec fonction de toilettes supplémentaire à l'intérieur d'une maison d'habitationLe silo à chauffage à compost peut être étendu à un système de toilettes à chauffage à compost intégré . Le système sert à la fois de chauffage et de toilettes. Le silo est rempli de déchets de biomasse (bois déchiqueté, etc.), qui constituent la base du processus de décomposition humide. De la biomasse supplémentaire (fèces et urine) peut être ajoutée. Le processus de décomposition décompose les excréments avant qu’ils n’atteignent le fond du silo, ce qui en fait une petite usine de clarification biologique.
La combinaison d'un silo chauffant à compost avec une fonction toilettes offre de nombreux avantages :
- Aucun système de rinçage à l’eau n’est requis. Cela permet d'économiser beaucoup d'eau fraîche.
- Aucun raccordement à un canal d'égout public n'est requis, car il s'agit d'un système autonome.
- Les matières inorganiques qui en résultent (eau, CO2) ne polluent pas l'environnement. L'eau de sortie contient des minéraux précieux et peut être directement utilisée comme engrais liquide pour le jardin.
- La biomasse supplémentaire s'ajoute à l'énergie thermique nécessaire au chauffage de la maison.
- S'il est construit correctement, le léger vide des tuyaux de ventilation empêche toute odeur dans la maison, ce qui est mieux que tout autre système de toilettes.
Pour plus de commodité, l'entrée des toilettes est située à l'étage, où l'entrée régulière de biomasse est combinée avec un siège de toilette. Contrairement aux toilettes sèches, les excréments sont traités dans un environnement humide et sont donc décomposés beaucoup plus rapidement.
Version avec un seul tube
Dans les appartements en location, vous ne pouvez généralement pas simplement faire un grand trou dans le toit ou dans le mur extérieur. Par conséquent, il sera décrit ici comment un silo de chauffage de compost peut être réalisé sans conduite d'air d'entrée. Il suffit de raccorder le système au réseau d'égouts. L'air soufflé est directement extrait de l'air ambiant via une soufflante, c'est-à-dire que la soufflante pousse l'air ambiant dans le silo. L'air évacué s'échappe par le tuyau d'égout. Un clapet anti-retour empêche le flux d'air dans la mauvaise direction lorsque le ventilateur ne fonctionne pas.
Grâce à cette disposition, il est possible de réaliser de petits systèmes pour la cuisine, dans lesquels pourrissent principalement les déchets de cuisine organiques. Avec un dimensionnement adapté, la structure s'insère sous le plan de travail.
Considérations de sécurité
Protection contre le feu
La chaleur dégagée peut provoquer une combustion spontanée indésirable. La décomposition biologique peut augmenter la température au-delà de 60 degrés Celsius, lorsque des processus chimiques purs se déclenchent et poussent la température jusqu'à un niveau dangereux. Cela peut se produire surtout si de l'herbe mouillée est remplie. La condition dépend de l'humidité et de la concentration en oxygène.
La chaleur extrême est un effet indésirable pouvant entraîner la destruction du silo. De plus, le bâtiment autour du silo peut être en danger. Des précautions doivent donc être prises pour réduire les conséquences d'un incendie.
- Sélection de matériaux de construction ignifuges pour silos et tuyaux (par exemple béton , acier )
- Installation d'un système d'extinction d'incendie automatisé. Il peut s'agir d'un simple récipient d'eau placé au-dessus du silo, qui verse son contenu dans le silo lorsqu'une soupape de sécurité déclenchée par la chaleur s'ouvre.
Ouverture d'urgence
Si un nourrisson ou un animal vivant tombe accidentellement par l'entrée du silo, il existe un risque d'étouffement. La construction doit permettre dans ce cas une ouverture de secours. Un secouriste doit pouvoir pénétrer immédiatement dans le silo. Ceci peut être réalisé par un couvercle amovible et une échelle disponible en permanence, par exemple.