This data-driven, gender-specific, easy to print, environmentally friendly, hygienic, and cruelty-free simulator can be locally made to provide the highest fidelity orthopedic surgical simulation training at the lowest cost in resource-constrained settings.
Materials and Equipment[edit | edit source]
3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3 with Bicortical Anatomy and Cancellous Bone Microstructure[edit | edit source]
- Fused Deposition Modelling 3D Printer (on-site access to a 3D printer and materials is not required)
- White Polylactic Acid (PLA) Filament
- STL Files for 3D Printed Adult Male or Female Tibial Bone Models #3
Soft Tissue Layer for Plunge Depth Measurement[edit | edit source]
- Modelling Clay
- Cellophane
- Depth Gauge
- Airtight Storage Container or Resealable Bag (to prevent clay from drying out to permit reuse)
Powered Orthopedic Surgical Drill and 4.0 mm Drill Bit[edit | edit source]
Any powered orthopedic surgical drill that is compatible with 4.0 mm drill bits can be used.
The Arbutus Medical HEX Drill Kit uses autoclavable drill covers to permit faster turnaround on reprocessing orthopedic surgical drills in resource-constrained settings.[1]
Each Arbutus Medical HEX Drill Kit contains aː
- 3-Jaw Chuck Adapter
- Modified DeWalt Drill
- DrillCover Hex Linen
- Chuck Key
- Battery Charger
- Rechargeable Lithium-Ion Battery
- Storage Bag (not shown)
The Arbutus Medical HEX Drill Kit does not include drill bits so the learner must obtain 4.0 mm drill bits separately.
Miscellaneous Supplies[edit | edit source]
- Vise Clamp
- Eye Protection
- Gloves
- 4.5 mm Combination Drill Sleeve
- Syringe
- Water (to simulate sterile normal saline)
- Shallow Container (to collect irrigation solution)
- Training Logbook
Assembly Instructions[edit | edit source]
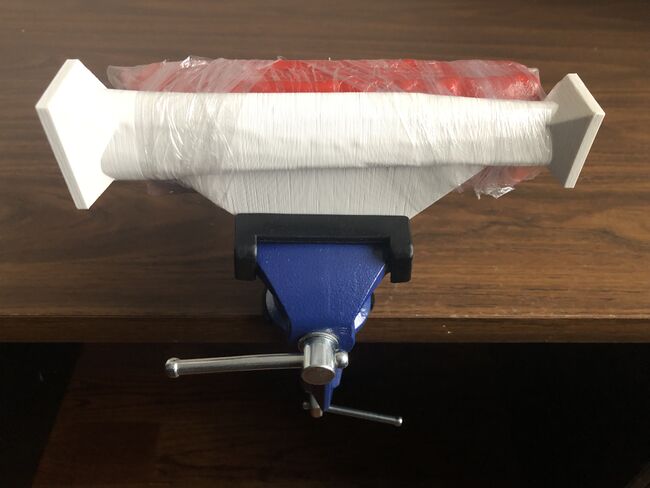
Set Up Tibial Shaft Simulator[edit | edit source]
- Secure one Vise Clamp to a flat, stable surface.
- Open the jaws of the Vise Clamp to permit insertion of 3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3.
- Identify the threaded screw that connects the jaws of the Vise Clamp.

- Identify the semi-engraved drilling direction arrow on the base of 3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3.
- Orient 3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3 in the Vise Clamp so the drilling direction arrow is pointing in a right-to-left direction.

- Place Model #3 inside the Vise Clamp.
- To maximize stability, (i) the model vise attachment should be centered and rest on the threaded screw that connects the jaws of the vise clamp, and (ii) the model vise attachment should be well secured between the tightly closed jaws of the vise clamp.
- Place the shallow container on the floor to collect the irrigation solution during bicortical drilling skills training.

- Check the stability of the model by pushing down on the top of the left and right ends of the model.
- If the model drops down, check and reposition the vise attachment over the threaded screw inside the body of the vise clamp (if needed) and be sure to clamp the jaws together more tightly.

- Check the orientation of the 3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3 by identifying the semi-engraved drilling direction arrow on the base of Model #3.
- If the arrow is not pointing in a right-to-left direction, remove and re-orient the 3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3 so the drilling direction arrow is pointing in a right-to-left direction.
Add the Clay Backstop for Recording Plunge Depth[edit | edit source]
Wrap one layer of a 6.0 cm wide long cellophane strip tightly around the clay backstop and 3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3 to secure the clay backstop up against the lateral side of the 3D Printed Tibial Bone Model #3 so the clay is well molded against the far cortex.[2]
Assemble the Powered Surgical Drill[edit | edit source]
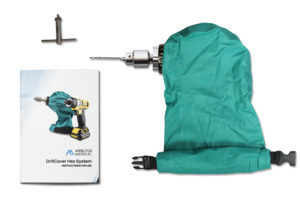
- Follow the drill manufacturer's instructions to assemble the orthopedic surgical drill and insert a 4.0 mm drill bit.
Final Preparations for Skills Training[edit | edit source]
- Download and print the Training Logbook.
Acknowledgements[edit | edit source]
This work is funded by a grant from the Intuitive Foundation. Any research, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this work are those of the author(s), and not of the Intuitive Foundation.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Arbutus Medical. Hex Drill Kit - Orthopedic Surgical Drill [Internet]. Arbutus Medical. Arbutus Medical; 2021 [cited 2021 Nov 28]. Available from: https://arbutusmedical.com/drillcover-hex/.
- ↑ John A. Ruder, Blake Turvey, Joseph R. Hsu, Brian P. Scannell, Effectiveness of a Low-Cost Drilling Module in Orthopaedic Surgical Simulation, Journal of Surgical Education, Volume 74, Issue 3, 2017, Pages 471-476, ISSN 1931-7204, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsurg.2016.10.010.






