History[edit | edit source]
- 1968: The Sword of Damocles
- First Head-Mounted-Display
- 1980s : The term "virtual reality" was popularized by Jaron Lanier
- Founder of the VPL Research
- 1991: Sega announces the Sega VR headset for arcade games
- 1992: Computer Gaming World predicts "Affordable VR by 1994".
- 2007: Google introduces Street View
- 2012: Kickstart campaign for Oculus Rift
- 2014: Facebook purchases Oculus VR for 2$ billion
Applications of Virtual Reality[edit | edit source]
Education[edit | edit source]
- Explore the solar system
- Surgery simulations
- Children could follow lessons from home
Military[edit | edit source]
- Flight simulator
- Simulation of a battlefield
- Control of a drone
Engineering[edit | edit source]
- Better view of 3D-models
- Architects could use virtual reality to enter a house before it is build
Entertainment[edit | edit source]
- Explore a city
- Games
- Movies
Outlook[edit | edit source]
Full Immersion[edit | edit source]
Technology in the future[edit | edit source]
Technology's influence in our life will rise, as it always did. This is both economical and social caused. New and improved technologies is one of the main subjects of the free market system, as well as every new generation grows up with new technologies and uses it in a 'higher level' every time. In cases like energy systems, changes in the used technology are neccessary to hold the standard after fossil fuels are used up.
Microchip Materials[edit | edit source]
Since computers have become an ever-growing part of our lives there has always been the need to get its components smaller in size. Smaller components do not occupy space that might be used otherwise and allow other features to be implemented, allow for more computing power on the same space or reduce the problem of overheating due to a lesser amount of heat emitting material.
Ever since the time when computers went into mass production chips have mostly been build on the basis of silicon crystals grown to fit the specific needs of the computer and then cut in very thin layers called "dies". For the last years alternatives for silicon as a material and even for electrical circuits as a whole are being developed.
Alternative Microchips Materials[edit | edit source]
Next-generation computer chips can not get much faster without overheating. One possible solution for this problem is the usage of carbon nanotubes that carry the excess heat away from the microchips so processing speeds could rise even more. These nanotubes may be imagined as chimneys sitting on the microchip. After these nanotubes were able to be produced effectively in bigger amounts a major problem was to get a good foundation for the chimneys to stand on if we stay in this picture, or to be more scientific – a bridge that transports the heat from the metal of the microchip to the organic material of the nanotube was needed. It turned out that organic molecules including aminopropyl-trialkoxy-silane (APS) and cysteamine created strong bonds between the nanotubes and the metal of the microchip. Also the distance between each side of the nanotube layer was reduced by this method. The scientific basis has been achieved by this research, yet it is still a long way to go until we will have carbon nanotubes in our hands inside our smart phones.
Another postsiliconic idea is to use graphene (single layers of graphite/a crystalline allotrope of carbon) to build transistors. These are already working at very high frequencies but are lacking in intrinsic voltage gain thus far. The approach of using bilayer graphene transistors has taken the technology a large step forward but it will still take time until we see this technology on a daily basis. Molybdenum disulfide is also in the running to be an alternative to either graphene or present silicon models.
On the search for better and alternative capacitor solutions Korean researchers found out that chemically treated used cigarette filters outperform carbon, graphene and carbon nanotubes in energy storage. So yet another approach was found to possibly fulfill our upcoming technological needs.
Communication and Lifestyle[edit | edit source]
The way humans communicate has changed every age and this modification won't stop. Recognition of speech technologies was improved to a standard that is usable in the daily routine. In non-official matters written letters got replaced with e-mails and short messages affected a drop in verbal communication. The next steps will follow the same rules: Less time and efforts for communication to cause more efficiency. Efficiency in communication leads to efficiency in using and planing our time. Strictly individual appointment calendars are outdated, inefficient for team-working and socialization. Firms like Facebook already led ways for a new standard of communication and socialization and the trend is not about to fall. That means technology will follow it steps for an automatisation of communication, sharing of information, setting plans for our time and most left matters of our daily life.
Energy systems[edit | edit source]
'Worn off' technologies[edit | edit source]
How toys will shape future robots[edit | edit source]
Toys in future will shape future robots. What was it about this robot that had appealed so much to its owner? It's a question that Tilden and other roboticists think is important – not just for toy design, but the future of robotics. For too long, robots have suffered from an image problem.
They are often perceived as mechanical, cold and threatening in our culture and it's difficult to reverse that impression. This view of robots could be changed if they were designed to appeal to us with the same familiarity and, indeed, personality that our childhood toys once possessed.
More and more children want a toy which can speak or do something. The best example for this is Furby. Evrybody like this toy and in the past it was the most famous toy in the world. an other example was the Robosapien. He was developed to give children the feeling that robots aren't something threatening. The Robosapiens can dances, raps and a lot of more funny things. Seeing the Robosapien as a pal was far more important than seeing it as a hyperintelligent, futuristic machine.
Could other successful toys provide similar cues for robot designers? Perhaps – and it needn't even be toy robots. The most important thing for a child is to be proud about the toy and that it surprise them. So the question for the future have to be how the devoleper of robots create it to surprise the humanity to be surprise about robots and learn to like them. Benefits from the toy development could be a good first step to reach their targets.
Long-distance virtual telepathy[edit | edit source]
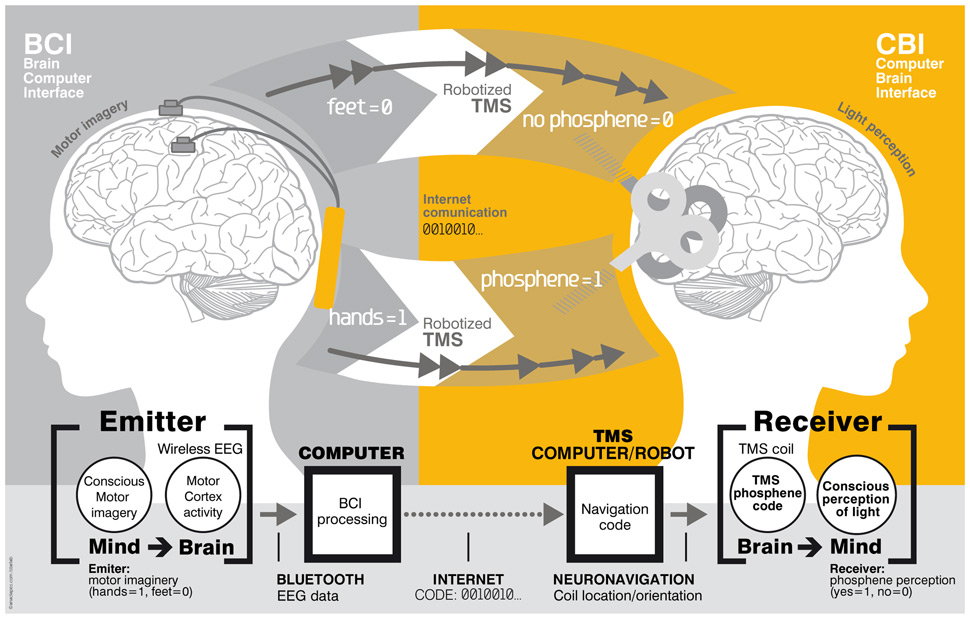
Telepathy is an very interesting thema. Not for nothing this it is used in so many films which surprise their tans. An international team of neuroscientists and robotics engineers study how the viability of direct brain-to-brain communication in humans could work. The highly novel findings describe the successful transmission of information via the Internet between the intact scalps of two human subjects – located 5,000 miles apart.
One of this professors says: "We wanted to find out if one could communicate directly between two people by reading out the brain activity from one person and injecting brain activity into the second person, and do so across great physical distances by leveraging existing communication pathways," explains co-author Alvaro Pascual-Leone, PhD, Director of the Berenson-Allen Center for Noninvasive Brain Stimulation at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Professor of Neurology at Harvard Medical School. "One such pathway is, of course, the Internet, so our question became, 'Could we develop an experiment that would bypass the talking or typing part of Internet and establish direct brain-to-brain communication between subjects located far away from each other in India and France?'" It turned out the answer was "=yes.="
To get an better overview about this complex thema I will give you two experiments to this study which I found on an internet page with whom I hope you could better follow what happened here:
In the neuroscientific equivalent of instant messaging, Pascual-Leone and his colleagues successfully transmitted the words "hola" and "ciao" in a computer-mediated brain-to-brain transmission, from a location in India to a location in France, using internet-linked electroencephalogram (EEG) and robot-assisted and image-guided transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) technologies.Previous studies on EEG-based brain-computer interaction (BCI) have typically made use of communication between a human brain and computer. In these studies, electrodes attached to a person's scalp record electrical currents in the brain as a person realises an action-thought, such as consciously thinking about moving the arm or leg. The computer then interprets that signal and translates it to a control output, such as a robot or wheelchair.
But, in this new study, the research team added a second human brain on the other end of the system. Four healthy participants, aged 28 to 50, participated in the study. One of the four subjects was assigned to the brain-computer interface (BCI) branch and was the sender of the words; the other three were assigned to the computer-brain interface (CBI) branch of the experiments and received the messages and had to understand them.
Using EEG, the research team first translated the greetings "hola" and "ciao" into binary code, then emailed the results from India to France. There a computer-brain interface transmitted the message to the receiver's brain through non-invasive brain stimulation. The subjects experienced this as phosphenes, flashes of light in their peripheral vision. The light appeared in numerical sequences that enabled the receiver to decode the information in the message, and while the subjects did not report feeling anything, they did correctly receive the greetings.
A second similar experiment was conducted between people in Spain and France, the end result being a total error rate of just 15 percent, 11 percent on the decoding end and five percent on the initial coding side.
"By using advanced precision neurotechnologies including wireless EEG and robotised TMS, we were able to directly and noninvasively transmit a thought from one person to another, without them having to speak or write," says Pascual-Leone. "This in itself is a remarkable step in human communication, but being able to do so across a distance of thousands of miles is a critically important proof-of-principle for the development of brain-to-brain communications. We believe these experiments represent an important first step in exploring the feasibility of complementing or bypassing traditional language-based or motor-based communication."
At the end it is to say that it needs a long time to become a good study about this thema and that it need much time to envolve a proper technology to telepathy informations. But in future it will be possible if they work in same speed like they do at this moment.
- ---
More to expand on :
1 Hardware
2 Software
3 Usage
4 Implementation
5 Concerns and challenges
Communication[edit | edit source]
- (mobile) phone
- world wide web
- networking
○ intranet ○ globalization
- knowledge
○ e-learning ○ social aspects (facebook etc.)
Digital infrastructure[edit | edit source]
Smart Grids
A smart grid is the plan of a new electrical grid which uses communications technology to improve the efficiency of the production and distribution of electricity. The behaviour of the suppliers and the consumers are gathered in an automated way and then used for dynamic adjustments of the grid.
intelligence city
military
○ IT warfare
○ inventions
Disadvantages of technology[edit | edit source]
Technology also has some negative aspects. It is very hard to protect privacy on the Internet and it's impossible to control who receives the data you entered. Big companies can draw up detailed profiles of users based on their searches of web pages. It is also possible that our ability to communicate with real persons diminishes, and there is an increasing dependence on mobile devices and social networks. Some people feel unwell if they do not have the possibility to check the latest news on facebook etc.
Increasing stress related to being available all the time: [ http://www.theguardian.com/science/2015/jan/18/modern-world-bad-for-brain-daniel-j-levitin-organized-mind-information-overload]
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ^ Rheingold, H. Virtual Reality. Summit, New York, 1991.
External links[edit | edit source]
- Wikipedia:Technology
- Wikipedia:History of technology
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Iron_Bridge
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moon_landing
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manhattan_Project
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Large_Hadron_Collider
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Project_Orion_(nuclear_propulsion)
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wearable_technology (Wearable Technology)
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Holography
- http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20141009-how-toys-will-shape-future-robots (toys for future)
- http://www.hongkiat.com/blog/tablet-computing-fad-or-future/ (Tablets)
- http://www.perrypedia.proc.org/wiki/Hologramm
- http://www.golem.de/0908/68901.html
- http://www.futuretimeline.net/blog/computers-internet-blog.htm#.VEeRYU1d7cs
- http://www.golem.de/news/anode-aus-titandioxid-neuer-akku-laedt-in-wenigen-minuten-1410-109829.html
- http://spectrum.ieee.org/semiconductors/nanotechnology/gain-from-graphene
- http://spectrum.ieee.org/semiconductors/nanotechnology/graphenes-new-rival
- http://spectrum.ieee.org/nanoclast/semiconductors/nanotechnology/used-cigarette-filters-could-enable-next-generation-of-supercapacitors
- http://web.archive.org/web/20151127155630/http://www.technologyreview.com:80/news/519421/the-first-carbon-nanotube-computer/
- http://sites.ieee.org/uss-enterprise/carbon-nanotubes-could-solve-overheating-problem-for-next-generation-computer-chips/