Even though there is a vast advancement in the generation of electricity, some of the rural areas of Bangladesh still do not have access to it. Again, electricity is generated by using conventional fossil fuel technologies. So to generate bulk amount of power without using conventional techniques leads us to an innovative solution-solar power. An approach towards achieving rural electrification in Bangladesh is the use of a solar DC Nano grid system- an isolated grid which can generate and distribute power to a cluster of households at close proximity reliably. My research work proposes a model of DC Nano grid integrated with solar PV module which can supply electricity up to 20 households at a distance of about 1 km. This work provides simulation results of boost converter, bidirectional converter and MPPT algorithm (P&O) which are used for obtaining 48V DC output voltage at DC bus. It also provides the simulation results of converters dedicated at each voltage levels at the load side to meet the peak maximum demand of the households. Along with this, availability of dc loads and cost estimation of the proposed Nano grid are presented which encourages the implementation of this Nano grid system.
Introduction[edit | edit source]
Power is one of the key requirements for the development of economies and upgrading of standards of living of developing countries. The need for the continuous availability of an energy source led to the usage of fossil fuels. But today, the harmful effects of fossil fuels on the environment has created an interest towards finding an alternative source for electric power generation. A solution to this is the use of renewable sources. There are many renewable sources available across the world such as wind energy, solar energy, hydro energy, geothermal energy, biomass, biogas etc. Among all the renewable sources, solar energy is reliable, cost effective on a long run, noise free, pollution free and also a free natural source. In Bangladesh, approximately 38% of its total population does not have any access to the grid electricity. In addition, there are more than 20% areas of total area of Bangladesh where providing grid electricity is costly. Solar power can be an alternative energy source for the electrification of these off-grid areas. Bangladesh is very much favorable for solar energy harnessing and most of the flat land of the country is open to bright sunshine most of the time of the year as summer time is dominant here. So in my research work, I have proposed a stand-alone system for the traditional consumption of domestic electric use at residential units in Bangladesh. The standalone system using solar power as the energy source is termed as Nano grid. Although there is no universal definition of Nano grid, this term is most often used to refer isolated very small grids, power output typically ranging in from few hundred watts to few kilo watts. Nano grids are small micro grids, typically serving a single building or a single load. Normally a basic installation of 1.5 to 3 kWp PV system is made to distribute the power to the households from this system. Nano grids are scalable at different DC voltage levels. Unlike AC grid, scaling up the generation is simple here. However, the energy conversion efficiency is quite low in this case. The efficiency of solar cells depends on many factors such as temperature, insolation, spectral characteristics of sunlight, dirt, shadow, and so on. In addressing the poor efficiency of PV system some methods are proposed for improving the efficiency of solar PV system by implementing a new concept called maximum power point tracking (MPPT). A MPPT is used for extracting the maximum power from the solar PV module and transferring that power to the load. Again the output of the solar panel is continuously varying which leads to an instability in the bus voltage level. To overcome this stability problem, a closed loop system is incorporated to the converters which can detect the variations in the input and maintains the constant bus voltage. One major thing is also observed that most of the household loads in rural areas can operate on DC voltage. The majority of these rural households' electricity demands are basic lighting load, fan load, charging mobile phones, watching TV which can operate at different DC voltage level. So DC-DC converters are used to step up or step down the voltage levels as per the ratings of the appliances to which they deliver power.
Modelling of Nano Grid[edit | edit source]
Nano grid refers to a small scale of the power network, with low voltage levels used on the distribution network and power ratings are also very small. Schematic layout of DC Nano grid integrated with solar PV generation is shows in fig. 1.1. This DC Nano grid integrated with solar PV generation is making a combination of different type of solar PV modules, MPPT algorithm, DC/DC converter, connected DC loads and battery energy storage system.

Solar PV panels are used to generate electricity from the solar energy. However the efficiency of the solar power system is very low. For improving the efficiency of solar PV system a concept called maximum power point tracking (MPPT) is implemented. The DC-DC converter is responsible for transferring maximum power from the solar PV module. MPPT is used for extracting the maximum power from the solar PV module and transferring that power to the load. After the PV panels working on maximum power point, the different units of the Nano grid such as solar panels, energy storage units are interfaced to a common DC bus using different power electronic converters. These converters help to match the dynamic behavior of various units in the Nano grid while regulating the voltages at DC bus to a fixed value of 48 V. The converters used in this purpose are boost converters and bidirectional DC-DC converter. Again after stabilizing the bus voltage to a constant 48 V, three different buck converters are needed to supply loads at voltage levels: 6 V, 12 V & 24V.
Load Definition of An Ideal Household[edit | edit source]
The ratings of DC loads of an ideal house of a DC Nano grid and their operating voltage, power rating, No. of pieces & operating hours are shown in the table below:
Average load consumption[edit | edit source]
| Loads | Operating Voltage [V] | Power Ratings [W] | Number of pieces | Operating time [Hr/day] |
| Lights | 12 | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| Fans | 12 | 24 | 2 | 12 |
| DC Motor | 24 | 240 | 1 | 2 |
| Televisions | 12 | 50 | 1 | 3 |
| Phone | 6 | 5 | 4 | 1 |
| Refrigerators | 24 | 45 | 1 | 24 |
Here,
So the total power consumption per day by a household: 𝐸𝑑(𝑠𝑖𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒) = 2.426 𝑘𝑊ℎ𝑟
Daily Load of DC Nano Grid System[edit | edit source]
We considered total N=20 households in the cluster, and the energy consumption of each of the households is almost same. So the Total daily load DC Nano grid system,
ED = 48.52 kWHr
Calculating the Maximum Demand of the system[edit | edit source]
Max. Demand on the system = Max. Demand of 24V appliances + Max. Demand of 12V appliances + Max. Demand of 6V appliances
2415W
Total Cost[edit | edit source]
The total cost of the solar system without taking into account any subsidy, CDCgrid can be evaluated using equation:
CDCgrid = CPVpanel + CBattery + COther + CMaintenance
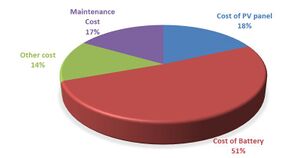
Important Parameters of DC Nano Grid System[edit | edit source]
Cost of Per Unit Energy in DC Grid System = 3.58Tk./Unit
Payback Period = 9 years
Environmental Impacts: In the proposed DC Nano Grid PV system, it can reduce 296 tons CO2 emissions during the 25 years of project life.
Conclusion[edit | edit source]
The scarcity of energy in Bangladesh is mainly due to the dependency of its power generation on imported fossil fuel and natural gas. DC solar Nano grid may be the efficient solution to our power generation shortage problem. The modeling of the DC Nano grid is done by using MATLAB Simulink. Again the DC bus voltage is maintained constant using closed-loop PI controllers and loads are supplied at 3 different voltage levels at the consumer premises. Also, an analytical study is done on the per unit cost of energy of the DC Nano grid. The study demonstrated that by using the DC Nano grid, the cost of electricity will be reduced significantly which motivates the implementation of this Nano grid system.
References[edit | edit source]
- Taif Hossain Rocky, Rafiul Islam, Uttam Kumar Saha, Nano solar grid (NSG): A solution for rural market power crisis, in 2nd International Conference on Green Energy and Technology, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5-6 September 2014, pp. 14-17.
- M. Rezwan Khan, Edward D. Brown, "DC nanogrids: A low cost PV based solution for livelihood enhancement for rural Bangladesh," in 3rd International Conference on the Developments in Renewable Energy Technology (ICDRET), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 29-31 May 2014, pp. 1 – 5.
- M. Mahmudul Hasan Sajeeb, Aminur Rahman, Feasibility analysis of solar DC Nano grid for off grid rural Bangladesh, in 2015 3rd International Conference on Green Energy and Technology (ICGET), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 11-12 September,2015, pp. 3 – 7.
- Trishan Esram, Patrick L. Chapman, "Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques," IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 439-449, June. 2007.
- Rajesh M Pindoriya, N. M. Pindoriya, S. Rajendran, "Simulation of DC/DC converter for DC nano-grid integrated with solar PV generation," in IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies - Asia (ISGT-ASIA), Bangkok, Thailand, 3-6 Nov. 2015, pp. 1–6.