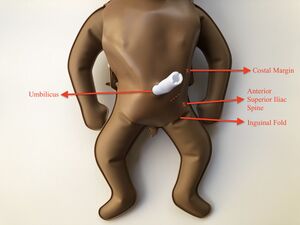
This knowledge module allows medical officers (non-specialist physicians) and general surgeons to become confident and competent in the procedural steps and post-operative care for neonatal colostomy procedures performed in low to middle income countries (LMICs).
Procedure Steps for Descending Colostomy with Separated Stomas[edit | edit source]
The simulator will be integrated into the enterocutaneous anastomosis activities of the stoma creation procedure (see step 15 below).
- Initiate general anesthesia.
- Position patient in supine position.
- Clean and drape to expose only the lower abdomen below the umbilicus.
- Make skin incision in the oblique left lower quadrant.
- Deepen incision to expose muscle.
- Ensure hemostasis.
- Cut muscles and secure hemostasis.
- Open peritoneum between 2 hemostats.
- Identify sigmoid colon (taenia coli, no attached omentum) and trace proximally until the junction with descending colon is reached (fixed end).
- Withdraw a loop of the proximal sigmoid colon out of the abdomen.
- Create a window in the sigmoid colon mesentery, and divide the loop. Ensure hemostasis.
- Place the proximal limb in the upper lateral end of the wound and the distal limb in the lower medial end of the wound.
- Close the fascia between the 2 limbs using Vicryl 3-0 or PDS 3-0 suture. Ensure closure is not too tight around the 2 limbs.
- Close the skin between the 2 bowel limbs using Vicryl 4-0 or PDS 4-0 suture.
- Secure the proximal limb to the fascia using Vicryl or PDS 4-0 seromuscular stitches at the 4 quadrants. Then suture the full thickness of the bowel edge to the skin (leaving a 1-2 cm spout), circumferentially, 5 mm apart. Ensure these stitches are not too tight.
- Repeat the same technique with the distal limb. While doing this, place the stitches in such a way as to narrow the bowel opening to admit just the little finger. Suture flush to skin without creating spout.
- Wash out the lumen of the distal limb using warm normal saline instilled through an appropriate size Foley's catheter or similar soft tube.
- Inspect both stomas to ensure that they remain pink and viable.
- Clean wound and surrounding gently with appropriate antiseptic and dry with sterile gauze.
- Apply dressing to the skin bridge.
- Apply Vaseline gauze (lubricated gauze) over the stoma and place sterile gauze over it.
Ideal Features of a Neonatal Stoma[edit | edit source]
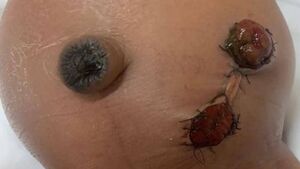
- Proper siting on the abdomen
- No stenosis
- Adequate peristomal skin protection
- No prolapse
- Good spout for functional stoma
- Pink colour
- Everted, protuberant stoma to allow better application of bag and less spillage
- Easy to apply bag or collect stool
Post-Operative Care[edit | edit source]
Fluid Input and Output[edit | edit source]
In the immediate post-operative period, fluid and electrolyte therapy should be continued at maintenance and should contain adequate calories (90 - 120 kcal/kg/day for term neonates and 130 -150 kcal/kg/day for preterm infants). Fluid input and output should be monitored until full oral intake commences.
Nasogastric drainage should be maintained as vomiting may still occur. It also serves as a guide to assess onset of bowel function. Decreasing effluent volume and color indicate progressively improving bowel function. Losses should be frequently replaced with equal and similar volumes.
Warmth and oxygenation should be ensured.
Antibiotics[edit | edit source]
Pre-operative antibiotics should be continued for 72 hours post-operatively. However, if sepsis is established, treatment with antibiotics covering sensitivity profile should be commenced at the dose appropriate for weight.
Laboratory Testing[edit | edit source]
Post-operative review of hematologic and biochemical indices will guide further optimization. As such, a full blood count and serum electrolyte and urea/creatinine should be done 24 hours post-operative and deficiencies corrected.
Pain Control[edit | edit source]
Analgesia using paracetamol injection 10 mg/kg q6-8h will be sufficient. All parenteral medications should preferentially be administered intravenously.
Oral Intake[edit | edit source]
Feeds are commenced after resumption of bowel function which is determined by serial evaluation of the abdomen and nasogastric drainage. Feeds can commence when nasogastric drainage is < 20 ml/kg/day, stoma producing stools and bowel sounds normoactive. Feeds should be started gradually at 0.5 - 1 ml/kg q4h. It is gradually increased until full intake is established. When patient cannot take feeds orally they may be fed via the nasogastric tube or an orogastric tube.
Wound Care[edit | edit source]
Dressing over the stoma should be moist, non-adherent and light to allow easy observation of the stoma. Stoma should be intermittently observed for change in color, bleeding and also for onset of function. When stoma function commences, it is imperative that regular change of stoma dressing should be done. Dressing should be done with soft absorbent napkins in environments where stoma bags cannot be obtained. Zinc oxide paste or other barrier cream such as petroleum jelly should also be applied generously around the wound from the first post-operative day. This reduces the risk of peristomal excoriations.
Early stoma complications should be anticipated so that early management is instituted. Common complications include bleeding, stoma necrosis, wound infection which may progress to dehiscence, skin excoriations, and stoma retraction or prolapse.