This is the literature review for Ghetto2Garden solar power.
Climate[edit | edit source]
Santo Domingo - Latitude: 18°29'N - Longitude: 069°55'W
The average temperature in Santo Domingo is roughly 26oC or approximately 79oF.
There is an average of 8 hours full sun per day January through September and an average of 7 hours full sun per day October through December.[1]
| Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic[2] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily Max Temperature (oF/oC) | 81/27 | 84/29 | 84/29 | 86/30 | 86/30 | 88/31 | 91/33 | 93/34 | 88/31 | 88/31 | 88/31 | 84/29 | 86.8/30.4 |
| Daily Avg Temperature (oF/oC) | 75/24 | 75/24 | 77/25 | 79/26 | 79/26 | 81/27 | 81/27 | 81/27 | 81/27 | 81/27 | 79/26 | 77/25 | 78.7/25.9 |
| Daily Min Temperature (oF/oC) | 61/16 | 66/19 | 68/20 | 70/21 | 72/22 | 73/23 | 75/24 | 72/22 | 72/22 | 72/22 | 70/21 | 66/19 | 69.7/20.9 |
| Monthly Rainfall (in/mm) | 2.52/64 | 2.2/56 | 2.09/53 | 2.8/71 | 7.4/188 | 5.51/140 | 5.71/145 | 7.01/178 | 7.09/180 | 7.4/188 | 3.9/99 | 3.31/84 | 56.93/1,446 |
Biogas[edit | edit source]
Benefits of Biodigestion
This type of system would utilize the available manure as a result of housing the dogs. Fertilizer from the processed organic waste could be sold for profit. Also, biogas is a highly efficient form of energy. Excess natural gas or unprocessed biogas could be sold as well. Some benefits of biogas include: reduction in volume of waste, complete decomposition of waste materials, nutrient capture, recycling, reduction of pathogens, odor reduction, and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.[3]
Using a biodigester may decrease the amount of exposure to pathogens which can be spread to humans by means of premature composting, agricultural run off, and contamination of the water table.

Composition
Biogas, which consists mainly of methane, can be produced when food waste from households, manure, or crops from agriculture are broken down by micro-organisms in digesters and wastewater treatment plants. To upgrade biogas to natural gas or vehicle fuel quality, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulphide, and other contaminants need to be separated out.[5] The composition of a gas issued from a digester depends on the substrate of its organic matter load, and the feeding rate of the digester. Usually the composition includes high amounts of CH4 (methane), CO2 (Carbon Dioxide), and variable amounts of N2, O2, H2O, H2S, NH3, and aromatic compounds.[6]
Typically, biogas is composed of roughly 55 - 65% methane, 35-45% carbon dioxide, a small fraction of Hydrogen Sulfide gas, and other trace gases. This can result in problems because the Hydrogen Sulfide gas, even in small amounts, can be very corrosive and degrade any equipment/parts that are metal. For much more small scale biodigester projects, it may be beneficial to use a packet of non-stainless steel wool in the gas regulator in order to reduce the H2S in the Biogas, as did Practivistas in Chiapas.
Phases of anaerobic digestion
Hydrolysis and acidogenesis:Lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates are hydrolyzed by a series of microorganisms. Hydrolytic enzymes break the polymers into smaller molecules that can be digested by the microorganisms. Lipase converts lipid microorganism waste into fatty acid chains that, when hydrolyzed, form amino acids. Pyruvate and NADH are created by hexoses and pentoses and continue to be broken down into the final endo-products of this phase: lactate, propionate, acetate, and ethanol.
Acetogenesis and dehydrogenation:This phase is primarily responsible for the break down of volatile fatty acids into acetate and H2.
Methanogenesis: Methanogens can only function in anaerobic conditions and are mainly either H2/CO2 and acetate-consumers. These microbes transform the final biochemicals into methane, which is our main source of energy for the system. In some cases,a two step methanogenesis process is necessary to keep the balance of volatile fatty acids and H2 low. This must be tested and maintained to prevent high methane contents in the waste water.[7]
Types of Biodigester Technology
Inoculum/Seed: To begin creating a biodigester, many suggest a preliminary stage to start the growth of the anaerobic bacteria and get an initial pH balance. To begin, fill a large container (suggested 55gal drum) with one part manure and one part water. Test the pH periodically before placing it into the digestor. After placing the first slurry into the digestor, the system should first begin to produce carbon dioxide, and then methane once it reaches stability. Holding a lighter over the system should indicate once the methane is being produced.[8]
Applications of Biogas
One potential application of biogas is its use in fuel cells. Fuel cells transform chemical energy into electrical energy by breaking up the bonds. In biogas, H2 is the biochemical fuel that could be transformed using this method. Due to the high energy capacity of H2, the use of H2 fuel cells in combustion engines can be 2 or 3 times the efficiency of the techniques in use today.[9]
Wind Energy[edit | edit source]
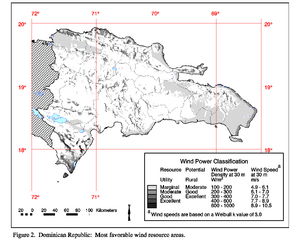
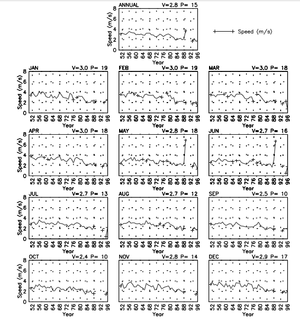
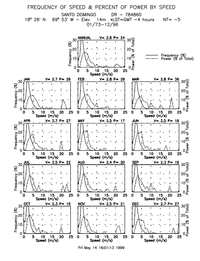
"The wind resource in the Dominican Republic is strongly dependent on elevation and proximity to the coastline. In general, the wind resource is best on hilltops, ridge crests, and coastal locations that have excellent exposure to the prevailing winds from the east. The extreme southwestern and northwestern regions of the country are estimated to have the greatest number of areas with good-to-excellent wind resources for utility-scale applications, because the upper-air winds and ocean winds are greatest in these regions."[10]
"The Dominican Republic has a good wind resource. Many locations boast an average wind speed of over 7 meters per second at 80 meters above sea level, and a number of locations offer average speeds greater than 8 meters per second. One global study found that roughly 13 percent of locations have wind speeds of 7 meters per second or greater, generally considered an indication that low-cost wind energy development is possible. "[11]
"In Santo Domingo, losses due to module temperature would likely be larger than in most locations. The hourly mean ambient temperature in Santo Domingo is always above 20°C, exceeding 28°C in the early afternoon even during the coldest months and staying over 30°C throughout the middle of the day during the summer. This would result in very high module temperatures. However, the average wind speed is also relatively high, with hourly means above 3 meters per second over almost all the daylight hours throughout the year. Winds are also strongest during the early afternoon hours, when temperature is highest. With increased wind speed comes increased heat loss in the module due to convection, and therefore somewhat lower power degradation."[12]
"The best wind resources are found in the southwestern provinces of Pedernales and Barahona and the northwestern provinces of Puerto Plata and Monte Cristi. Significant areas of good-to-excellent wind resource can be found in many other locations, such as well-exposed hilltops and ridge crests of the Samana peninsula and other near-coastal locations throughout the Dominican Republic and the major mountain ranges including Cordillera Septentrional, Cordillera Oriental, Cordillera Central, and Sierra Neiba. The mapping results show many additional areas of moderate wind resource for utility-scale applications or good wind resource for village power applications, including many east-facing coastal locations along the eastern and northern coasts of the Dominican Republic."
"The highest wind resource from June to August and December to February, with a maximum in July and a minimum in October. The diurnal pattern of wind speeds on exposed ridge crests tend to have the highest speeds during the night and early morning hours and lowest during mid-day."[13]
Solar Energy[edit | edit source]
The solar power is a very powerful resource of energy, especially in areas with a vast quantity of sun by year, that's the main reason why the sun is the preferential renewable energy source from the nature; Enclosing tremendous opportunities for almost every country in the world makes it striking in economical and potential energy ways.
"DNI stands for direct Normal Irradiation which is the amount of solar radiation received per unit area by a surface that is always held perpendicular (or normal) to the rays that come in a straight line from the direction of the sun at its current position in the sky. Typically, you can maximize the amount of irradiance annually received by a surface by keeping it normal to incoming radiation. This quantity is of particular interest to concentrating solar thermal installations and installations that track the position of the sun."[14]
GHI stands for Global Horizontal Irradiance. wich it's a geometrical position that claims how the irradiance from the sun affects a certain point on earth.
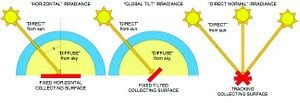
"Judged globally, the solar resource in the Dominican Republic is quite good. Average GHI across the country generally ranges from 210 to 250 watts per square meter (W/m2), making it comparable with that of the U.S. Southwest and generally superior to areas along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea. DNI, on the other hand, although still higher than that of much of the globe, is significantly lower than in the Mediterranean and U.S. Southwest. Average values are mostly between 170 and 250 W/m2. Within the Dominican Republic, irradiance is generally higher in the western half of the country, both for GHI and DNI, with some of the best areas found in the southwest."
"Santo Domingo is the capital and largest city in the Dominican Republic, situated on the Caribbean Sea on the country's southern coast. It is home to roughly one-quarter of the total population, making it the most important potential market for decentralized solar power production."
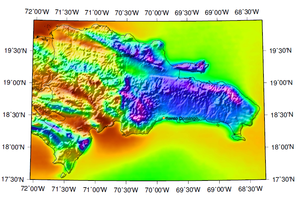
"Santo Domingo's solar resource is very strong by global standards. The average GHI value at the Santo Domingo site is 5.45 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per square meter per day (227.1 W/m2). (See Figure 5.) This compares favorably with most of the rest of the Caribbean region and is significantly higher than the insolation in the areas of Europe and Asia where solar power penetration is currently highest. In Germany, for example, few locations sport a GHI over 3.0 kWh/m2/day, and virtually nowhere is the GHI above 3.5. The DNI average is 4.97 kWh/m2/day (207.1 W/m2) at the Santo Domingo site, again strong when compared globally, although not as much so. (See Figure 6.) The average DIF is 2.04 kWh/m2/day (85.0 W/m2). Compared to the rest of the Dominican Republic, Santo Domingo has a mediocre solar resource, both in terms of GHI and DNI."
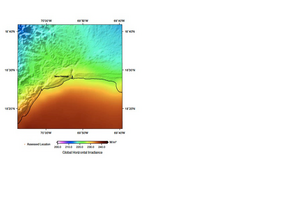
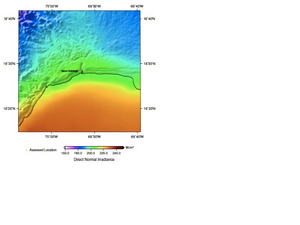
"The monthly mean GHI varies significantly throughout the year. (See Figure 7.) Average GHI is highest in April and May, with the May mean at 6.29 kWh/m2/day (262.1 W/m2). GHI is between 5.82 and 6.08 kWh/m2/day in March, June, July, and August, but it declines sharply throughout the rest of the year, falling below 5.07 kWh/m2/day for each month during October–February."
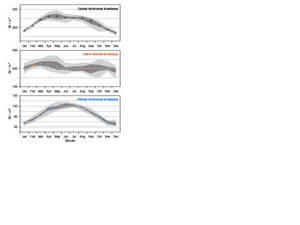
"Monthly mean DNI is much less variable over the course of the year. It peaks in March and April, with a March value of 5.45 kWh/m2/day. DNI is lowest in December, at 4.53kWh/m2/day, but all months during July–January are below4.85. DNI monthly means are more variable year-to-year, however."
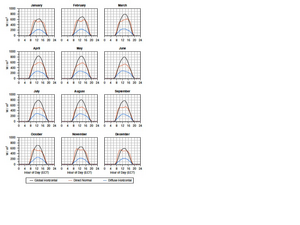
"During the course of the day, GHI peaks in the early afternoon throughout the year, highest between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m. and usually peaking between 1 and 2 p.m. (See Figure 8.) The peak hourly mean is consistently over three times the daily mean. DNI is of course also highest during the middle of the day, but because it involves tracking the sun's movement, the peaks more closely resemble plateaus that last from 10 a.m. to 5 p.m. The largest values for DNI are found in the mid-afternoon during February–May, early afternoon during June–September, and late morning during October–January."
"According to data from the annual reports of the Organismo Coordinator del Sistema Electrico (OC), electricity generation reaches its peak in the late summer months of July and August, with an average of 987,000 megawatt-hours (MWh) generated in July from 2005 to 2009. Monthly generation averages 950,000 MWh or more during May–October but is lower during the other half of the year, particularly in January and February."
"There is consistently a high level of unmet electricity demand in the Dominican Republic as well, often as much as 200,000 MWh per month. There is no clear pattern in the time of the year when unmet demand is highest over the years 2005–2009. Solar irradiance lines up reasonably well with demand, as GHI stays high through all the months of highest electricity use save September and October. DNI matches consumption less well, as it is relatively lower in late summer."
"Daily load curves show that the highest electricity demand occurs in the evening, from 7 p.m. to 11 p.m. This of course means that other solutions will be necessary to meet peak demand. During daylight hours, peak demand varies somewhat depending on the day of the week, falling as early as 12–1 p.m. or as late as 2–3 p.m. This matches up well with the daily variance in irradiance, although more so with GHI than DNI, as DNI dips right in the middle of the day in some months. Concentrated solar thermal power with storage would be an option for using solar energy to serve these evening demands. "[16]
Bicycle Energy[edit | edit source]
The use of bicycles to create electricity is an example of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. In an electrical generator, mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. The electrical generator "uses the mechanical energy supplied to it to force the movement of electric charges present in the wire of its windings through an external electric circuit. This flow of electric charges constitutes the output electric current supplied by the generator. This mechanism can be understood by considering the generator to be analogous to a water pump, which causes the flow of water but does not actually 'create' the water flowing through it."[17]
Power Potential
On average a person generates at least 100 watts per hour. An athlete can generate as much as 500 watts per hour. Unfortunately though, most systems for collecting and generating electrical energy by bicycle are extremely inefficient. Most systems are severely limited by a 12 volt battery's resting potential and its capacity.[18]
Components
Cyclist, Bike, Permanent magnet motor (or stepper motors or car alternators), Bike training stand, Rollers, Attach the motor to the stand (on left hand side of the front wheel), Electricity smoother (capacitor or lead acid battery), Inverter, cables with a 'quick-release.'[19]
Dog Power[edit | edit source]
Because Ghetto2Garden is a shelter for cats and dogs, it is thought that we could potentially "tap" into the kinetic energy of animals playing to create electrical energy. This would be similar to creating electricity using a bicycle. One idea, would be to use a sort of hamster wheel for dogs that diverts a small amount of its electrical energy to power a laser pointer to keep the pups interested in using the fun powered electrical generator. With out an incentive like a laser, it may be hard to keep the animals interested long enough to create much electricity.
Energy Storage[edit | edit source]
When creating electricity using wind, solar or any other kind of renewable energy it may be a good idea to have a way to store it when its not being used. This is especially true if your system is not tied to the grid. Without energy storage it is not possible to use the electrical energy created from solar or wind when it is not sunny or windy. It is obvious that it is not always windy or sunny so this could be a problem. For Ghetto2Garden it may be beneficial to store our kinetic, wind or solar energy by using a battery.
Various types of chargable batteries and their usage-
| Battery Types | Voltage (V) | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Rechargable Alkaline | 1.5 | CD/MP3 players, electronic games, cameras, flash lights... |
| NiMH | 1.2 | Digital cameras, remote controlled cars |
| NiCd | 1.2 | Power Tools |
| Li-ion | 3.6-3.7 | Notebook computers, PDAs, Mobile phones, camcorders, digital cameras |
| Lead Acid | 12V | Car starter battery, lift trucks, golf carts, standby power |
Flooded battery is a type of battery that is usually made by battery companies specifically for solar use. These are usually very long lasting durable batteries with the drawback that they cannot be used inside. The way the battery works includes a release of a flamable gas, and therefore cannot be stored in enclosed spaces without ventilation.[20]
AGM or Absorbed Glass Matt batteries are the high end solution for the Solar Battery problem. They are generally more expensive, but also worth the price that you pay for them because their life span is so much longer and they are able to store energy more efficiently.
Algal Biofuel[edit | edit source]
One potential solution for the cleansing of the waste water that may be formed as a result of processing the fecal matter from the large number of dogs in the Ghetto2Garden program, is the cleansing of the waste water using algae. Recent experiments show that carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus can be effectively removed from waste water to produce large amounts of algal biomass which can then produce a liquid energy that can be used like natural gas or fossil fuels. Algae also have the ability to accumulate toxic heavy metals which are frequently in waste water and allow them to be removed.[21]
Waste water
Waste water is primarily cleansed if it has had the solids removed. Secondarily cleansed if it has undergone some form of biological digestion. Lastly, Tertiary cleansing results in cleansed water that should have only remnants of organic material, no questionable bacteria, and no odor to it, but is otherwise clean water.[22]
Water Diversion hydration station[edit | edit source]
The roof of the shelter will be designed so that rainwater will be captured for the use of the cats and dogs.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ http://www.weather2travel.com/climate-guides/dominican-republic/
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20101108120106/http://smn.cna.gob.mx:80/climatologia/normales/estacion/chis/NORMAL07087.TXT
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20181220152945/http://www.americanbiogascouncil.org:80/biogas_biogasBenefits.asp
- ↑ http://sistemabiobolsa.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/size-chart-biobolsa.pdf
- ↑ http://www.greenlanebiogas.com/about-biogas
- ↑ http://www.biogas-renewable-energy.info/biogas_composition.html
- ↑ http://www.fao.org/docrep/w7241e/w7241e0f.htm
- ↑ https://www.appropedia.org/Biogas_start_up
- ↑ http://www.sciencedirect.com.ezproxy.humboldt.edu/science/article/pii/S0360319913004552
- ↑ http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy99osti/27032.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy99osti/27032.pdf
- ↑ http://blogs.worldwatch.org/revolt/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/WORLDWATCH-DR-ENGLISH.pdf
- ↑ http://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy02osti/27602.pdf
- ↑ http://www.3tier.com/en/support/solar-prospecting-tools/what-direct-normal-irradiance-solar-prospecting/
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20170701204337/http://www.seco.cpa.state.tx.us:80/publications/renewenergy/solarenergy.php
- ↑ http://blogs.worldwatch.org/revolt/wp-content/uploads/2012/07/WORLDWATCH-DR-ENGLISH.pdf
- ↑ http://www.dieselserviceandsupply.com/How_Generators_Work.aspx
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20130922170534/http://www.windstreampower.com/Bike_Power_Generator.php
- ↑ http://www.magnificentrevolution.org/diy/single-bike-generator/
- ↑ http://www.freesunpower.com/batteries.php
- ↑ http://www.oilgae.com:80/algae/cult/sew/sew.html
- ↑ .http://www.oilgae.com:80/algae/cult/sew/tp/tp.html