
This page deals with the theme of the influence of computer development by the military and vice versa.
The development of the first World War - to provide industrial and scientific base of the war - continued in the second world war. In the first world war scientific and industrial innovations were used to defeat the enemy. There were used for the first time combat aircraft, poison gas and flamethrowers. At the time of the second world war benefited in the USA, for example the companies who completed business with the military. They received government subsidies, generous budget and a crisis-proof market.
Modern Infantry[edit | edit source]
This section concentrates on modern weapons and gadgets, either those which are in development or which are used in infantry operations around the world today. In some cases, this includes devices that made it from the military usage into everyday life.
Weapons[edit | edit source]


HK XM25[edit | edit source]
Developed in Germany, this modern grenade launcher is capable of firing programmable grenades which detonate at a customly set range. The grenade does so by "counting" its rotations after it's been fired.
CornerShot[edit | edit source]
A multi-purpose weapon from Israel. It can be mounted with various weapons (e.g. 9mm handgun or 40mm grenade launcher) and allows the wielder to look and fire around corners. Its barrel can be horizontally rotated by 60° in both directions. A camera and display allow to look around corners and fire precisely without exposure to counterattacks.
Armatix iP1[edit | edit source]
This handgun developed in Germany comes with a corresponding wrist watch. If it's more than 25cm away from it, it won't fire. It also allows tracking of statistics (shots per minute) and can be set to only shoot if it's pointed in the direction of a designated target.
MATADOR[edit | edit source]
The MATADOR (Man-portable Anti-Tank, Anti-DOoR), originating from Singapore and Israel, is a rocket launcher which fires rockets with two explosion charges. These charges explode with a slight delay between each other. This makes the weapon capable of blasting a hole into armor, doors or walls and explode a second time behind the obstructions. It's one of the few rocket launchers designed to use in confined spaces.
Gadgets[edit | edit source]

NAVSTAR GPS[edit | edit source]
The Navigational Satellite Timing and Ranging – Global Positioning System is probably one of the most well-known invention by the U.S. Department of Defense, as nowadays it's vastly used as a positioning and navigation system for civilian purposes. Today there are a total of 67 GPS satellites in orbit. By calculating the distance to each of these satellites, GPS can accurately tell the target's location on the earth's surface.
XC6 M2 Military Tablet[edit | edit source]
This is a computer tablet designed for military operations. While it's quite bulky, it offers high sturdiness and readability for in-combat use, a vast amount of storage capacity and various in- and outputs for different devices.
Dragonfly Surveillance Robot[edit | edit source]
This tiny robot can help out the soldiers by scouting ahead into uncertain terrain, being barely noticeable due to its size. This gadget could also be used to look for survivors at accident sides or in collapsed buildings.
Digital weapons systems[edit | edit source]

The research and development conclude that the research of new weapons systems going in the direction of non-lethal weapons. Especially in the microwave and EMP (electromagnetic pulse)-weapons is this observed.
With the explosion of the first atomic bomb tested above ground the researchers noticed that the electromagnetic pulse of the thermonuclear explosion caused such a strong over voltage in electrical devices within range that they were destroyed.
Over time, it has now managed to trigger these electromagnetic pulses without a nuclear explosion. In the near future, airplanes should be equipped with these weapons.
To destroy enemy radar stations a strong signal in the natural frequency of the radar system is triggered from airplanes.
To defend against such attacks, the radars are to be screened and be accessible only with fiber-optic cable from the outside.
UAV (Unmanned aerial vehicle) / drone[edit | edit source]
A UAV is an aircraft without a pilot. There are four kinds of drones:
- Unmanned Air System (UAS)
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)
- Remote Piloted Aircraft Systems (RPAS)
- Model Aircraft
It's flight is either controlled remotely by a pilot on the ground using a computer or autonomously by onboard computers.
UAVs are usually deployed by the military and special forces, but also used in a small but growing number of civil applications, such as policing and firefighting.
Uses in Military[edit | edit source]
Military drones are used for different purposes. Firstly, to education purposes for fighter pilots, therefor warplanes are rebuilt that they can be remotely controlled and used as a target drone. Further they are used for reconnaissance, for example to explore the region and to make enemy camp identify possible before your own troops move. Or foresee a ambush of enemy troops and to take countermeasures. They are also used to clarify IEDs and to gain an overview of the situation from the air to the troops on the ground.
History[edit | edit source]
- The first large-scale production, purpose-built drone was the product of Reginald Denny. He served with the British Royal Flying Corps during World War I, and after the war, in 1919
- 1931 the British Royal Air Force equipped three machines of the type Fairey IIIF under the name Fairey Queen with radio control and uses them as target drones and exercise goals for fighter pilots.
- The US Navy began experimenting with radio-controlled aircraft during the 1930s as well, resulting in the Curtiss "N2C-2" drone in 1937. The N2C-2 was remotely controlled from another aircraft.
DARPA[edit | edit source]
Is an agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of new technologies for use by the military.DARPA was created in 1958 as ARPA. ARPA was renamed in 1972. DARPA study radar, infrared and x-ray/gamma ray. ARPA played an early role in Transit a predecessor to the GPS. DARPA supported the evolution of the ARPANET, Packet Radio Network, Packet Satellite Network , the Internet and research in the A.I. fields of speech recognition and signal processing. many of the successful programs were transitiond to the Services, such as the doundation technoligies in automatic target recognition, space based sensin, propulsion , and materials that were tranferred to the Missle Defense Agency (MDA). In 2011 Darpa hostet the 100-Year-Starship Symposium with the aim of getting the public to start thinking seriously about interstellar travel.
Security[edit | edit source]
Computer Network Defence (CND)[edit | edit source]
Computer Network Defence is a subtopic in Computer Network Operations and comes from the Military. Computer Network Defence include all arrangements which defend the own Computer networks. For a successful Defend of the own Networks they use instruments of Control, Defence and Analysis. The Penetration-test is an attack on a computer system with the intention of finding security holes, in this context security holes in the own networks. The Penetration-test is just one of many Methods of the Computer Network Defence. The Main intention of Computer Network Defence is it to find the security holes in the Computer Network and to fix them fast before anyone can attack the Network. The CNO (Computer Netzwerkoperationen) and the KSA (Kommando Strategische Aufklärung) are responsible for the Network Security in the Military.
Modern vehicles[edit | edit source]
There are different types of modern vehicles like artillery and air defence, engineering and logistic vehicles and also armoured vehicles.
All of these modern vehicles have their own purposes.
Self-propelled artillery vehicle owns a system which is programmed to move toward to its target. They resemble a tank but they are not heavy amoured like them but they are still able to protect their crew against arms. Most of them are equipped with machine guns to shoot on the enemies infantry on the defense. This type of modern vehicle is highly computerized with the ability to self survey firing positions using systems such as GPS and inertial navigation systems.
Engineering vehicles are designed for construction work or for the transportation of combat engineers on the battlefield.
There are also different types of engineering vehicles like the "breaching vehicle" which is equipped with mechanical or other means for the breaching of man made obstacles.
Armoured vehicles are equipped by a an armour and armed with different weapons like tactical offensive, operational mobility and defensive capabillities.
They are used as an example for supporting contingency operations, offensive capabilities and crew protection.
Most of the armoured vehicles are powered by diesel engine.
Cryptography[edit | edit source]
Cryptography (from Greek kryptos "secret" and graphein "writing") is the science of codification. The aim ist to protect communication to all apart from the intendend acceptor. Before electronic processors were used, single letters or grup of letters were simply replaced. This forms of codings are not used anymore, because they are not safe.
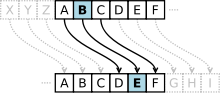

Oldest discoverys of Cryptography are in the third century BC in the old egypt. Unusal hieroglyphs are references for that. Hebrew academics developed 500 - 600 century BC simple sign switch coding. An example for this is the Atbash cipher. 50-60 BC the roman commander Julius Cäsar created the so called Cäsar cipher. In this method every letter is replaced by a in the alphabet three places behind letter (Example: A is replaced by D). Also in the middle age cryptography was used to save diplomatic letters using the Alphabetum Kaldeorum. In the 16. century AC the frenchman Blaise de Vigenère graded the Cäsar cipher up and developed the so called Vigenere cipher. Different to the Cäsar cipher not only one secret alphabet was used, but 26. During the second world war mathematic cryptography made a good progress. The coding machine "ENIGMA", which was used by the german military and thought to be undecipherable, was uncoded by the british project "ULTRA", where the famous british cryptoanalyst Alan Turing was involved.
After the second world war the era of the modern cryptography began. Actuator for this was Claude Shannon, who published 1949 the article "Theory of Secrecy" and who is called the father of the mathematic cryptography. Now the progress in this field was not secret anymore. The privacy was replaced by "security of obscurity". The year 1976 had two good progresses for the cryptography. IBM and NSA developed together DES (Data Encrypted Standard), which set a safe standard of national coding. 2001 it was replaced by the AES. The second big progress 1976 was the public key coding. "New Directions in Cryptography" was the title of the article from Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman. This young new ideas of ciphering put more and more disciplines in to the cryptography, so today mathematics, computer science and electrical engineering are elementary aspects of it.
Ballistic Missile Defense[edit | edit source]
Espionage[edit | edit source]
Espionage is the procure and obtain of unknown information or protected know. Espionage is used by states, political groupings and commercial subjetcs. They used the obtained information in their own bailiwick. States differ in various espionage, which would be military and civilian information extraction, news extraction about human sources, like recruited or infiltrated informants called Human Intelligence, technical espionage, like spy planes, spy satellites, funk enlightenment and tap of telecommunication lines and news gathering, the actual espionage and its defenses against appropriate measures of foreign services, usually with intelligence means.