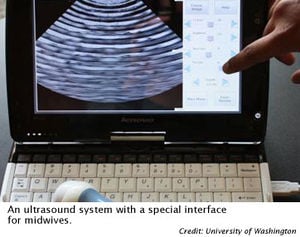
Problem being addressed[edit | edit source]
In the poorest countries, there are 500 million maternal deaths, 3.2 million still births, and 4 million neonatal deaths each year. There are many problems that cause these deaths, but one in particular is the lack of diagnostic capability for birth complications before birth occurs. Ultrasound is often used in developed nations. However, ultrasound machines are quite expensive (around $20,000).
Detailed description of the solution[edit | edit source]
Bringing an ultrasound to resource-poor settings such as Uganda is estimated to cost around $3,500. The ultrasound device is a USB-powered ultrasound probe that functions with a touch screen net-book. The probe uses ultrasound waves and outputs a signal through ultrasound gel in the same way as a more expensive device. The device has been designed using software to teach midwives how to use the device without expensive, extensive, specialized training.
Designed by[edit | edit source]
- Designed by: This device was designed by a Capstone team from the University of Washington. Collaborators include: Waylon Brunette, Wayne Gerard, Matthew Hicks, Alexis Hope, Mitchell Ishimitsu, Pratik Prasad, Ruth Anderson, Gaetano Boriello, Beth Kolko, and Rob Nathan.
- Manufacturer location: The device is made in Washington, USA.
When and where it was tested/implemented[edit | edit source]
This device was tested by midwives in Uganda 2011.
Funding Source[edit | edit source]
Funding was provided by:
- UW Capstone Project Award
- Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation's $100,000 Grand Challenges Exploration Grant
References[edit | edit source]
Peer-reviewed publication[edit | edit source]
Anderson, R., Brunette, W., Gerard, W., Kolko, B., Hope, A., Keh, J., et al. (2012). The Midwife's Assistant: Designing Integrated Learning Tools to Scaffold Ultrasound Practice. ICTD'12, 1, 12-15. Retrieved February 5, 2013. Link available here.
Brunette W, Gerard W, Hicks MA, Hope A, Ishimitsu M, et al. (2010). Portable antenatal ultrasound platform for village midwives. Proceedings of the First ACM Symposium on Computing for Development. Retrieved March 13, 2013. PDF available here.
Kolko, B., Hope, A., Brunette, W., Saville, K., Gerard, W., Kawooya, M., et al. (2012). Adapting Collaborative Radiological Practice to Low-Resource Environments. CSCW'12, 1, 11-15. Retrieved February 5, 2013. Link available here.
Other internally generated reports[edit | edit source]
Mobile Midwives' Ultrasound – Change. (n.d.). Change» ICTD at the University of Washington. Retrieved February 5, 2013. Link available here.
Externally generated reports[edit | edit source]
Baguma R. (2011). U.S. Students design ultrasound for Ugandan midwives. Retrieved March 13, 2013. Link available here.
Round 5. (n.d.). Grand Challenges in Global Health. Retrieved February 5, 2013. Link available here.