Problem being addressed[edit | edit source]
Tuberculosis (TB) is a common and potentially lethal infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. TB kills close to 1.7 million people globally every year and is highly contagious, and is primarily spread through airborne transmission. When infected people cough, sneeze, talk or spit, they propel TB germs, known as bacilli, into the air. A person needs only to inhale a small number of these to be infected. Left untreated, each person with active TB can infect on average between 10 and 15 people every year.
Detailed description of the solution[edit | edit source]
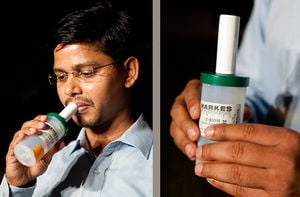
The "E-Nose" is a battery-operated, hand-held unit, similar to a police breathalyzer. A patient blows into the device and sensors pick up TB biomarkers in the breath droplets, resulting in an almost instantaneous and highly accurate diagnosis. Each "E-Nose" costs roughly $20 and its size and battery operation would make it accessible to rural communities in countries such as India with poor or non-existent power supplies.
Designed by[edit | edit source]
- Designed by: The primary research and development has been performed by International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology in New Delhi, India. Lead researchers: Dr. Ranjan Nanda and Dr. Virander Chauhan.
- Manufacturing: The device is not currently at the manufacturing stage. However, manufacturing of the device will be performed by Next Dimension Technologies in California, upon completion of clinical trials.
Testing/Implementation[edit | edit source]
Prototypes were developed in Delhi, India. Five institutes will carry out clinical trials, two in Delhi, and one each in Kolkata, Chennai, and Mumbai.
Funding Source[edit | edit source]
The project received a grant of $950,000 from the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation Grand Challenges Program for a two-year development period.
References[edit | edit source]
Peer-reviewed publication[edit | edit source]
Fend R, Kolk AHJ, Bessant C, et al. (2006.) Prospects for clinical application of Electronic-Nose technology to early detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in culture and sputum. J of Clin Microbiol 44(6):2039-2045. Abstract available here.
Externally generated reports[edit | edit source]
Morrow A. (2011.) Introducing the E-Nose, a sniffer test for tuberculosis. Link available here.
New Medical. (2011.) Electronic Nose can diagnose TB in symptomatic patients. Link available here.
Sinha K. (2011.) Scientists plan to unveil hand-held e-nose to detect TB. Link available here.