Problem being addressed[edit | edit source]
Postpartum hemorrhaging is one of the most severe causes of maternal mortality. PPH (Postpartum hemorrhaging) rates in the developed worlds have severely decreased, but they are still a great threat in developing countries. The World Health Organization suggests that there are over 100,000 deaths due to postpartum hemorrhaging every year.
Detailed description of the solution[edit | edit source]
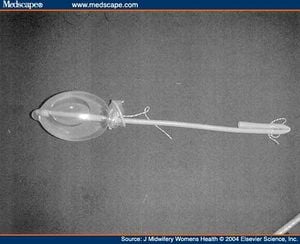
A rubber catheter is used to insert a normal condom into the uterus. It is then inflated with 250-300 ml of isotonic saline solution until the bleeding is controlled. To retain the saline, the proximal end of the catheter is folded and tied with thread. Rolled gauze is packed in the vagina to keep the condom from moving (Akhter).
Designed by[edit | edit source]
- Designed by:
- Manufacturer (if different):
- Manufacturer location:
When and where it was tested/implemented[edit | edit source]
Funding Source[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Peer-reviewed publication[edit | edit source]
Other internally generated reports[edit | edit source]
Externally generated reports[edit | edit source]
Akhter, S., M.R. Begum, and J. Kabir, Condom hydrostatic tamponade for massive postpartum hemorrhage. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics, 2005. 90(2): p. 134-135.