J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Sophivorus (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "[[image:" to "[[Image:") |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Killbio.png|thumb]] | |||
{{MOST}} | {{MOST}} | ||
{{Pearce | {{Source data | ||
| type = Paper | |||
| cite-as = C. Abinaya, M. Marikkannan, M. Manikandan, J. Mayandi, P. Suresh, V. Shanmugaiah, C. Ekstrum, J.M. Pearce, Structural and optical characterization and efficacy of hydrothermal synthesized Cu and Ag doped zinc oxide nanoplate bactericides. ''Materials Chemistry and Physics'' '''184''' (2016), pp. 172–182. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2016.09.039 [https://www.academia.edu/29413026/Structural_and_optical_characterization_and_efficacy_of_hydrothermal_synthesized_Cu_and_Ag_doped_zinc_oxide_nanoplate_bactericides open access] | |||
}} | |||
This study reports on a novel synthesis of pure zinc oxide and both Cu and Ag doped ZnO nanoplates using a simple and low-cost hydrothermal method. The structural and optical properties of the nanoplates were quantified and the materials were tested for antibacterial activity. X-ray diffraction revealed the formation of the wurtzite phase of ZnO and scanning and transmission electron microscopy showed the formation of randomly oriented ZnO nanoplates, having a thickness less than 80 nm and diameter less than 350 nm. The elemental analyses of both the pure and doped samples were evaluated by energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry. The FTIR spectra of ZnO nanomaterials showed the predictable bands at 3385 cm<sup>−1</sup> (O--H stretching), 1637 cm<sup>−1</sup> (stretching vibration of H<sub>2</sub>O), 400 cm<sup>−1</sup>–570 cm<sup>−1</sup> (M--O stretching). The as synthesized samples showed a strong absorption peak in the UV region (∼376 nm) and a near band edge emission at 392 nm with some defect peaks in the visible region. From the XPS spectra the oxidation states of Zn, Cu and Ag were found to be +2, +2 and 0 respectively. ''Escherichia coli'', ''Staphylococcus aureus'' and ''Salmonella typhi'' bacteria were used to evaluate the antibacterial activity of undoped and doped ZnO. Ag doped ZnO exhibited low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values as 40 μg/ml for ''E. coli'' and ''S. aureus'' and 20 μg/ml for ''S. typhi'', which are comparable to commercial antibiotics without optimization. Further, these chemically modified nanoparticles will be applicable in the development of medicine to control the spread and infection of a variety of bacterial strains. | |||
{{Pearce publications notice}} | |||
==Highlights== | == Highlights == | ||
* Distinct ZnO nanoplates were successfully synthesized by facile hydrothermal method. | * Distinct ZnO nanoplates were successfully synthesized by facile hydrothermal method. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
* It projects that, a feasible low cost industrial process can be developed further. | * It projects that, a feasible low cost industrial process can be developed further. | ||
==Keywords== | == Keywords == | ||
Nanostructures; Oxides; Chemical synthesis; Electron microscopy;[[bactericide]]; ZnO; [[zinc oxide]] | Nanostructures; Oxides; Chemical synthesis; Electron microscopy;[[bactericide]]; ZnO; [[zinc oxide]] | ||
==See also== | == See also == | ||
* [[Environmental remediation of real textile dyeing wastewater under visible light and inactivation of pathogenic bacteria using ZnO/CuO nano-needles]] | |||
* [[Inhibition of growth of S. epidermidis by hydrothermally synthesized ZnO nanoplates]] | |||
* [[Antibacterial and anticancer activity of hydrothermally-synthesized zinc oxide nanomaterials using natural extracts of neem, pepper and turmeric as solvent media]] | |||
{{Page data | |||
| title-tag = Synthesized Cu & Ag Doped ZnO Bactericides | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | [[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | ||
[[Category:Materials processing]] | [[Category:Materials processing]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:13, 16 April 2024
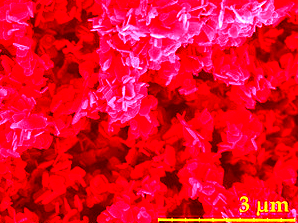
This study reports on a novel synthesis of pure zinc oxide and both Cu and Ag doped ZnO nanoplates using a simple and low-cost hydrothermal method. The structural and optical properties of the nanoplates were quantified and the materials were tested for antibacterial activity. X-ray diffraction revealed the formation of the wurtzite phase of ZnO and scanning and transmission electron microscopy showed the formation of randomly oriented ZnO nanoplates, having a thickness less than 80 nm and diameter less than 350 nm. The elemental analyses of both the pure and doped samples were evaluated by energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry. The FTIR spectra of ZnO nanomaterials showed the predictable bands at 3385 cm−1 (O--H stretching), 1637 cm−1 (stretching vibration of H2O), 400 cm−1–570 cm−1 (M--O stretching). The as synthesized samples showed a strong absorption peak in the UV region (∼376 nm) and a near band edge emission at 392 nm with some defect peaks in the visible region. From the XPS spectra the oxidation states of Zn, Cu and Ag were found to be +2, +2 and 0 respectively. Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhi bacteria were used to evaluate the antibacterial activity of undoped and doped ZnO. Ag doped ZnO exhibited low minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values as 40 μg/ml for E. coli and S. aureus and 20 μg/ml for S. typhi, which are comparable to commercial antibiotics without optimization. Further, these chemically modified nanoparticles will be applicable in the development of medicine to control the spread and infection of a variety of bacterial strains.
Highlights[edit | edit source]
- Distinct ZnO nanoplates were successfully synthesized by facile hydrothermal method.
- Cu and Ag doped ZnO exhibits significant destruction of bacteria with low MIC value.
- Ag:ZnO has a noteworthy bactericidal effect against E. coli, S. aureus & S. typhi.
- It projects that, a feasible low cost industrial process can be developed further.
Keywords[edit | edit source]
Nanostructures; Oxides; Chemical synthesis; Electron microscopy;bactericide; ZnO; zinc oxide
See also[edit | edit source]
- Environmental remediation of real textile dyeing wastewater under visible light and inactivation of pathogenic bacteria using ZnO/CuO nano-needles
- Inhibition of growth of S. epidermidis by hydrothermally synthesized ZnO nanoplates
- Antibacterial and anticancer activity of hydrothermally-synthesized zinc oxide nanomaterials using natural extracts of neem, pepper and turmeric as solvent media





