No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Operation == | == Operation == | ||
The conversion of the energy of the wind into more useful forms can be done using a rotor fitted with blades or sails. Note that a suitable location needs to be chosen for the WECS, preferably an open area<ref>[http://www.greenoptimistic.com/2009/01/18/home-wind-turbine-prove-to-be-less-efficient/ Wind turbines in urbanised areas only 5% efficient]</ref> Also, some general locations lend themselves far better than others for WECS. See [[Wind_power#Determining_the_local_wind_energy_levels|Wind power]] | The conversion of the energy of the wind into more useful forms can be done using a rotor fitted with blades or sails. Note that a suitable location needs to be chosen for the WECS, preferably an open area<ref>[http://www.greenoptimistic.com/2009/01/18/home-wind-turbine-prove-to-be-less-efficient/ Wind turbines in urbanised areas only 5% efficient]</ref> Also, some general locations lend themselves far better than others for WECS. See [[Wind_power#Determining_the_local_wind_energy_levels|Wind power]] | ||
== Windmills == | == Windmills == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 18: | ||
The most modern generations of windmills are more properly called [[wind turbine]]s, or wind generators, and are primarily used to generate [[electricity]]. Modern windmills are designed to convert the energy of the wind into electricity. The largest wind turbines can generate up to 6MW of power (for comparison a modern [[fossil fuel power plant]] generates between 500 and 1,300MW). | The most modern generations of windmills are more properly called [[wind turbine]]s, or wind generators, and are primarily used to generate [[electricity]]. Modern windmills are designed to convert the energy of the wind into electricity. The largest wind turbines can generate up to 6MW of power (for comparison a modern [[fossil fuel power plant]] generates between 500 and 1,300MW). | ||
With increasing environmental concern, and approaching limits to [[fossil fuel]] consumption, [[wind power]] has regained interest as a [[renewable energy]] source. It is increasingly becoming more useful and sufficient in providing energy for many areas of the world. | With increasing environmental concern, and approaching limits to [[fossil fuel]] consumption, [[wind power]] has regained interest as a [[renewable energy]] source. It is increasingly becoming more useful and sufficient in providing energy for many areas of the world, especially in temperate climates. For DIY wind turbines, see [http://peswiki.com/index.php/Directory:Home_Generation:Wind_Turbine here] | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 10 October 2012
A wind energy conversion system (WECS),[1] or wind energy harvester[2] is a machine that, powered by the energy of the wind, generates mechanical energy that can be used to directly power machinery (mill, pump, ...) or to power an electrical generator for making electricity.[3] The term can thus refer to windmills, windpumps as well as wind turbines.
Operation
The conversion of the energy of the wind into more useful forms can be done using a rotor fitted with blades or sails. Note that a suitable location needs to be chosen for the WECS, preferably an open area[4] Also, some general locations lend themselves far better than others for WECS. See Wind power
Windmills
A windmill is a mill powered by the wind. It allows to reduces a solid or coarse substance into pulp or minute grains by crushing, grinding, or pressing.
Windpumps

A windpump is a type of windmill used for pumping water from a well or draining land.
Windturbines
The most modern generations of windmills are more properly called wind turbines, or wind generators, and are primarily used to generate electricity. Modern windmills are designed to convert the energy of the wind into electricity. The largest wind turbines can generate up to 6MW of power (for comparison a modern fossil fuel power plant generates between 500 and 1,300MW).
With increasing environmental concern, and approaching limits to fossil fuel consumption, wind power has regained interest as a renewable energy source. It is increasingly becoming more useful and sufficient in providing energy for many areas of the world, especially in temperate climates. For DIY wind turbines, see here
See also
- energy harvesting
- windmill sail
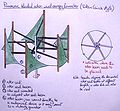
- Comparison of bladed rotors for WECS
- Solar energy conversion system
- High-efficiency HAWT's
Gallery
-
A panemone bladed rotor WECS
-
Another panemone WECS
-
Adding a barrier to a panemone WECS
-
A Lenzv2 savonius bladed rotor WECS
-
A ground sailor bladed rotor WECS
-
A cretan bladed rotor WECS
-
A thai bladed rotor WECS
-
A Darrieus bladed rotor WECS
-
A cambered plate bladed rotor WECS