(Created page with "'''Polyethelene Tube Digesters''' are a type of biodigester quickly gaining popularity in applications throughout the world. Due to their simple construction, easily understandab...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Polyethelene Tube Digesters''' are a type of biodigester quickly gaining popularity in applications throughout the world. Due to their simple construction, easily understandable mechanics, and <ref> | '''Polyethelene Tube Digesters''', also known as '''balloon biogas plants''', are a type of biodigester quickly gaining popularity in applications throughout the world. Due to their simple construction, easily understandable mechanics, widely available inexpensive material, and versatile structure, polyethelene tube digesters are ideal for inital "test" conversions in small-scale applications.<ref> | ||
https://energypedia.info/index.php/Types_of_Biogas_Digesters_and_Plants#cite_note-TBW-0 | |||
</ref>. [[Image: | </ref>. [[Image:TubularPlasticBiodigester.gif|thumb|right|A flexible plastic (polyethelene) type biodigester. [http://www.build-a-biogas-plant.com/images/tubularPlasticBiodigester.gif]]] A polyethelene tube biodigester is typically characterized by a raised inlet trough, a long, flexible fermenting reservoir with a gas vent tube, and a slurry output. | ||
The simple design of a | The exceedingly simple design and low cost of a PET digester and its lack of moving parts means that the system is inherently reliable and cost effective. However, the design may be shortlived in comparison to more traditional digesters ([[Fixed dome digester]],[[Floating Drum Biogas digestor]])due to its construction from polyethelene plastic, which will degrade over time. However, the low cost and easy installation of the digester bag means that the main chamber is simple to replace in the event degredation begins to affect the system's performance. Though the gas inside is being pushed out only by the pressure of the other methane gas inside the digester, the flexible reservoir allows the flow rate to be modified simply by applying additional pressure to the bag- say by placing a rock on it.<ref>http://fastonline.org/CD3WD_40/BIOGSHTM/EN/APPLDEV/DESIGN/DIGESTYPES.HTML</ref>. | ||
== Pros == | == Pros == | ||
*Simple setup | |||
*Low cost | |||
*Shallow installation, ideal for areas with high groundwater table | |||
*Easy to see how much gas is available | |||
*Easily warmed, ideal for warmer climates | |||
== Cons == | == Cons == | ||
*Not as durable as traditional digesters | |||
*Low gas pressure | |||
*Production time highly dependent on ambient temperature | |||
== Comparisons to other digester types == | == Comparisons to other digester types == | ||
'''vs. [[Floating drum biogas digestor|Floating drum digesters]]''' | '''vs. [[Floating drum biogas digestor|Floating drum digesters]]''' | ||
*Lower gas output (depending on size) | |||
*Lower pressure consistency | |||
*Similarly easy to gauge amount of gas available for use | |||
*Less insulated | |||
*Easier to maintain | |||
*Less expensive | |||
'''vs. [[ | '''vs. [[Fixed dome biodigester|Fixed-dome biodigesters]]''' | ||
*Lower gas output (depending on size) | |||
*Similar pressure consistency | |||
*Easier to gauge amount of gas available for use | |||
* | *Less insulated | ||
* | *Easier to maintain | ||
* | *Less expensive | ||
* | |||
== Notes and references == | == Notes and references == | ||
| Line 32: | Line 42: | ||
* [[Biogas]] | * [[Biogas]] | ||
* [[Floating drum biogas digestor]] | * [[Floating drum biogas digestor]] | ||
* [[ | * [[Fixed dome digester]] | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
Revision as of 00:44, 1 December 2012
Polyethelene Tube Digesters, also known as balloon biogas plants, are a type of biodigester quickly gaining popularity in applications throughout the world. Due to their simple construction, easily understandable mechanics, widely available inexpensive material, and versatile structure, polyethelene tube digesters are ideal for inital "test" conversions in small-scale applications.[1].
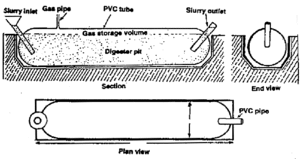
A polyethelene tube biodigester is typically characterized by a raised inlet trough, a long, flexible fermenting reservoir with a gas vent tube, and a slurry output.
The exceedingly simple design and low cost of a PET digester and its lack of moving parts means that the system is inherently reliable and cost effective. However, the design may be shortlived in comparison to more traditional digesters (Fixed dome digester,Floating Drum Biogas digestor)due to its construction from polyethelene plastic, which will degrade over time. However, the low cost and easy installation of the digester bag means that the main chamber is simple to replace in the event degredation begins to affect the system's performance. Though the gas inside is being pushed out only by the pressure of the other methane gas inside the digester, the flexible reservoir allows the flow rate to be modified simply by applying additional pressure to the bag- say by placing a rock on it.[2].
Pros
- Simple setup
- Low cost
- Shallow installation, ideal for areas with high groundwater table
- Easy to see how much gas is available
- Easily warmed, ideal for warmer climates
Cons
- Not as durable as traditional digesters
- Low gas pressure
- Production time highly dependent on ambient temperature
Comparisons to other digester types
- Lower gas output (depending on size)
- Lower pressure consistency
- Similarly easy to gauge amount of gas available for use
- Less insulated
- Easier to maintain
- Less expensive
- Lower gas output (depending on size)
- Similar pressure consistency
- Easier to gauge amount of gas available for use
- Less insulated
- Easier to maintain
- Less expensive