Video summary[edit | edit source]
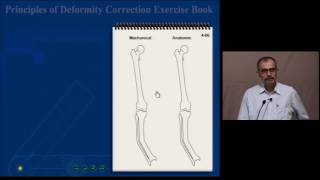
Limb axis planning in the frontal plane
When there is Malalignment or Malorientation in femur or tibia bones, the bone with deformity can be divided into proximal and distal bone segments. The proximal and distal bone segments have their own proximal mechanical axis (PMA) or proximal anatomical axis (PAA) line and distal mechanical axis (DMA) or distal anatomical axis (DAA) line respectively (Fig. 8a)
Bone angulation deformity in the frontal plane
The bone angulation deformity can be seen in either the frontal plane (visible on AP x-rays) or sagittal plane (visible on LAT x-rays) or both.
These angulation deformities can be at one level or location in the bone referred to as 'Uniapical deformity' or it can be at multiple locations also referred to as 'Multiapical deformity' (Fig. 8j)