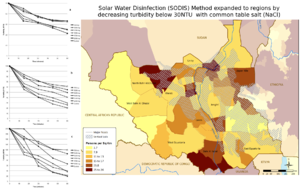
While the solar water disinfection (SODIS) method of treating microbiologically contaminated water at the household level has proven to be effective at reducing incidence of diarrhea, its effectiveness is limited to waters of low turbidity. This study investigates the use of table salt (NaCl) to reduce turbidity in water containing dispersed colloidal clay particles as a means of expanding the user base of SODIS. Jar tests were performed on solutions of a low-activity clay, simulating the general composition of soils of the Vertisol type, which are found in key developing regions. Results show that dispersions exhibited as high as 92% particle removal efficiency. The results of this study suggest that NaCl in combination with as little as 30% bentonite by mass may be used to produce a small-scale jumpstart effect by reducing turbidity to a level suitable for SODIS treatment. Soil type was mapped and overlaid with population estimates in a GIS environment to highlight geographic areas where salt + SODIS may be most viable in the case study of South Sudan. Findings suggest that the NaCl method could expand access to SODIS technology by about 1.56 million people who currently lack access to an improved water source in the case study.
Highlights[edit | edit source]
- Solar water disinfection (SODIS) method needs low turbidity.
- Investigated table salt (NaCl) to reduce the turbidity of suspended colloidal clay
- Vertisol soil dispersions had up to 92% particle removal efficiency.
- NaCl in combination with as little as 30% bentonite jumpstarts turbidity reduction.
- GIS study of South Sudan showed the expansion of SODIS by 1.56 million people.


