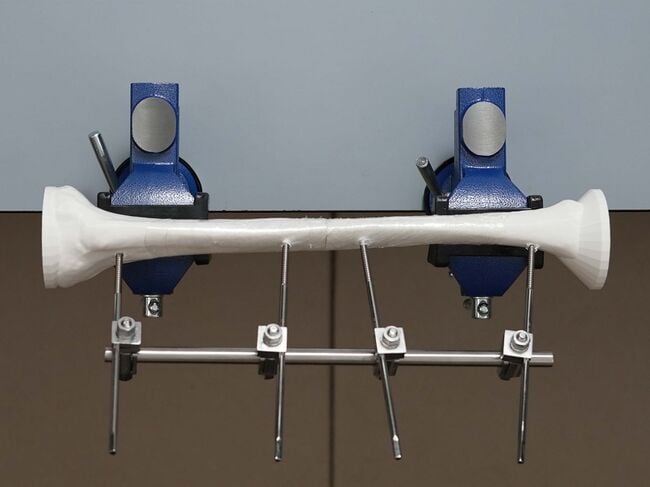
This module allows medical officers and surgeons who are not orthopedic specialists to become confident and competent in irrigation and debridement, powered and manual drilling, positioning and correctly inserting Schanz screws, and constructing the uniplanar external fixator frame as part of external fixation procedures for open tibial shaft fractures performed in regions without specialist coverage. To maximize patient safety, this module teaches learners to use a powered drill to insert self-drilling Schanz screws through the near cortex and then manually advance Schanz screws into the far cortex to avoid plunging.
Any locally available 4.5 or 5.0 mm diameter self-drilling Schanz Screws and compatible uniplanar external fixator hardware, instruments, and powered surgical drill can be used for this skills training module.
| # | Item | Quantity | Reference Image | Function | Reusable for Simulation Training |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Syringe, 50 mL | 1 |  |
Used for irrigation of open wounds | Yes |
| 2 | Bone Reduction Forceps | 1 | 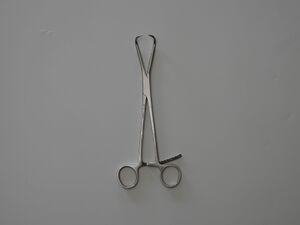 |
Used to manually reduce the fracture, compress the fragments together, and restore alignment | Yes |
| 3 | Bone Holding Forceps, Medium Size | 1 | 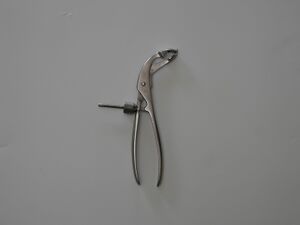 |
Used to maintain reduction | Yes |
| 4 | Scalpel Blade and Handle | 1 |  |
Used to make a stab incision in the soft tissue at the insertion site for each Schanz Screw; and to extend the wound to adequately expose the open fracture for direct visualization of the fracture (if required) | Yes |
| 5 | Dissecting Scissors | 1 | 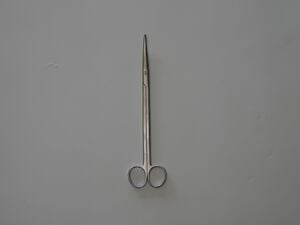 |
Used to dissect through the soft tissue to expose the bone at the insertion site for each Schanz Screw | Yes |
| 6 | Any powered surgical drill that is compatible with 4.5 or 5.0 mm diameter self-drilling Schanz screws can be used for this simulation-based training | 1 |  |
Drives Schanz Screw into fracture fragment, also referred to as "power drive" | Yes |
| 7 | Chuck Key for Surgical Drill | 1 |  |
Used to tighten or loosen the drill over the Schanz screw | Yes |
| 8 | Self-Drilling Schanz Screws, 5.0 mm x 200 mm x 30 mm | 4 |  |
Inserted into fracture fragments, also referred to as "pins" or "half-pins" |
|
| 9 | Drill Sleeve for 4.5 mm or 5.0 mm Schanz Screws | 1 |  |
Used to protect the soft tissue when drilling the far pins | Yes |
| 10 | Universal Chuck with T-Handle | 1 |  |
Allows for manual advancement of the Schanz Screw to the desired depth | Yes |
| 11 | Chuck Key for Universal Chuck with T-Handle | 1 |  |
Used to tighten or loosen the Universal Chuck with T-Handle over the Schanz screw | Yes |
| 12 | Universal Clamp (Single Pin) | 4 |  |
Combines pin-to-rod | Yes |
| 13 | Rod, 11 mm diameter x 300 mm length | 1 |  |
Links pins with clamps, metal rod is cheaper but a carbon fiber rod is radiolucent which permits better visualization of the fracture on X-ray | Yes |
| 14 | 11 mm Spanner with T-Handle | 1 |  |
Assists in final tightening of clamps | Yes |
In real clinical scenarios, 6.0 mm self-drilling Schanz Screws may be used for open tibial shaft fractures that require a more rigid construct.[1]
For the purpose of surgical simulation skills training, 5.0 mm or 4.5 mm diameter self-drilling Schanz Screws should be used because the 3D Printed Tibial Bone Models cannot mechanically tolerate a 6.0 mm diameter self-drilling Schanz Screw.
Hardware Suppliers[edit | edit source]
We recommend obtaining hardware from your local orthopedic surgical hardware supplier. We have included a list of potential surgical hardware suppliers who may ship to your location below:
- Emmanuel Madhu, Managing Director, Ortho Support Limited, University of Abuja Teaching Hospital, Abuja Office, PMB 228, Abuja Gwagwalada, 902101, Nigeria, +234 809 369 4250, ololonwabig2@gmail.com
- Apothecaries Sundries Mfg. Pvt. Ltd. (ASCO), email: info@ascomedical.com, phone: +91 935 099 2022
- Uma Surgicals, email: info@umasurgicals.com, phone: +91-22-23877076 / +91-022-23856015 / +91-022-23855627
- Surgivalley, email: info@surgivalley.com, phone: +923222800090
- Orthopedics International
- Stryker
Acknowledgements[edit | edit source]
This work is funded by a grant from the Intuitive Foundation. Any research, findings, conclusions, or recommendations expressed in this work are those of the author(s), and not of the Intuitive Foundation.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Encinas-Ullán CA, Martínez-Diez JM, Rodríguez-Merchán EC. The use of external fixation in the emergency department: applications, common errors, complications and their treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2020 Apr 2;5(4):204-214. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190029. PMID: 32377388; PMCID: PMC7202044.
