This article describes how liquids and gases move in pumps and motors. The exact movement is a very important element when picking the most efficient pump or engine in a given situation.
Rotary movement[edit | edit source]
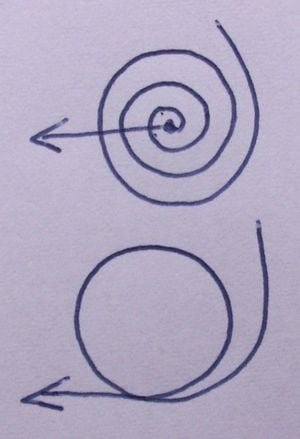
There are 2 types of rotary movement that can be applied. With the first type, the fluid or gas is either brought to a complete stop or accellerated from complete rest. With the second type, the fluid or gas is either accellerated or decreased in speed
The first type occurs in pumps, motors as Tesla turbines, Spiral pumps, screw propellers, ... The second type occurs in pumps, motors as Francis turbines, impellers, rotary vane pumps, quasiturbines, coil pumps, cross-flow fans, ...
The first type of pump is thus primarily useful for pumping fluids or gases that are in complete rest. It is also useful for motors that need to extract every bit of energy from a gas or fluid.
The second type of pump is thus primarily useful for pumping fluids or gases that are already in motion. It is also useful for motors that only need to extract a portion of the energy in a gas or fluid, yet still keep the flow in place.
Practical applications[edit | edit source]
In practice, the first type of pump are ie pumps that need to pump standing water up (although other type of pumps as piston pumps are even better in this); motors of the first type are compressed air motors, and water turbines placed on a flow of water that can be totally halted (ie some freshwater flows).
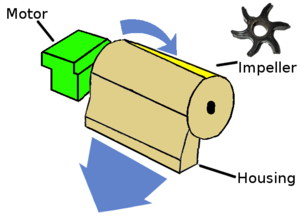
The second type of pump are ie pumps that need to propell a boat or pumps in the middle of a water distribution system, to add speed to the flow. Motors of the second type are water turbines placed on a flow of water that can only be slowed but not halted (ie sea or saltwater rivers, some freshwater flows), ...