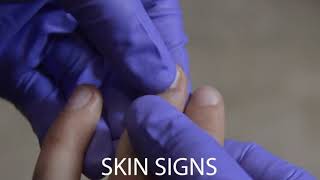
Capillary refill time (CRT) is a measure of the time it takes for a distal capillary bed, such as those found in the fingers or toes, to regain color after pressure has been applied to cause blanching. A prolonged CRT may indicate the presence of circulatory shock.
Procedure for measuring CRT
- Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain informed consent.
- Wear appropriate PPE.
- Position the patient with their hand at the level of their heart (or slightly higher) This will ensure that perfusion of the arteriolar capillaries carrying oxygenated blood, rather than venous stasis, is being assessed.
- Apply cutaneous pressure to the fingertip for five seconds. The pressure applied should be enough to cause blanching as the blood is squeezed out of the tissue.
- Release the pressure.
- Time how long it takes for the skin to return to the same color as the surrounding tissues.
- Document the CRT measurement in seconds, the site where it was undertaken and any factors that may have influenced the reading.
The normal CRT is <2 seconds. A CRT of >2 seconds suggests poor peripheral perfusion and may be an early sign of shock. However, several other factors can cause a prolonged CRT, including:
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Hypothermia
- Cold ambient temperature
- Old age
An alternative site for measuring the CRT is the sternum. This site is frequently used in winter when patients may come from a cold environment, which affects the accuracy of CRT. Be aware, capillary refill is generally considered clinically significant for patients under the age of 6 ONLY due to the multitude of factors that can affect capillary refill times. Despite this, capillary refill is a helpful diagnostic tool that can aid in differential diagnoses in the field.