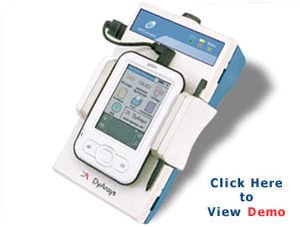
Problem being addressed
Diabetic autonomic neuropathy (DNS) is a common complication of diabetes that affects between 40 and 60 percent of patients (DyAnsys, n.d.). It is a silent killer, which if left untreated can kill within 5 years. There is very little diagnosis of this disease in the developing world.
Detailed description of the solution[edit | edit source]
This device is safe, noninvasive, and uses a portable electrocardiogram (ECG) to measure the activity of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) hence the name ANSiscope. It detects the percentage of autonomic dysfunction. The initial reading takes approximately one minute to show on the device and each reading is updated after each subsequent heartbeat. Different stages of diabetic autonomic neuropathy are indicated on the device: healthy, early, late, advanced and most advanced. The device comes with a battery and a charger, allows for data storage on a USB and can be linked to a printer.
Designed by[edit | edit source]
- Designed by: Dyansys, Inc.
- Manufacturer location: San Mateo, California, United States
When and where it was tested/implemented[edit | edit source]
This device is sold in South Africa and clinical trials were conducted in India.
Funding Source[edit | edit source]
This device receives private and commercial funds.
References[edit | edit source]
Peer-reviewed publication[edit | edit source]
Jawa, Ali, Javed Akram, Ali Jawad, and Rizwan Bokhari. "Diabetic cardiac autonomic neuropathy in well-controlled diabetics within 1 year of diagnosis." Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 15(Suppl1) (2011): S67–S68. Print.
Internally generated reports[edit | edit source]
"Portable Ansiscope." DyAnsys. N.p., n.d. Web. 7 Apr. 2012. Link available here.
Externally generated reports[edit | edit source]
Bateman, Chris. (2007, February 1). 'Just micro-size me'--tiny diabetes device to the rescue? The Free Library. (2007). Retrieved April 08, 2012. Link available here.