No edit summary |
(→References: added links from biofuel page) Tag: n |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
==External links== | |||
* [http://www.woodgas.com/proximat.htm assessing differing feed stocks for woodgas systems] | |||
* [http://www.eng-tips.com/viewthread.cfm?qid=201009&page=2 Engine & fuel engineering - designing long-life engines for home biomass energy systems] | |||
* [http://www.vedbil.se/indexe.shtml Around Sweden with wood in the tank] | |||
* [http://www.gekgasifier.com/ Gasifier Experimenters Kit (GEK)] | |||
[[Category:Energy]] | [[Category:Energy]] | ||
[[Category:Biofuels]] | [[Category:Biofuels]] | ||
Revision as of 13:01, 19 July 2012
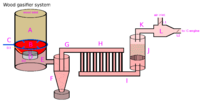
This article deals around the use of wood gas in internal combustion engines.
Overview
schematic of complete system (production unit, fuel generator + ICE-engine) see http://woodgas.nl/GB/project.html , http://www.whatiamupto.com/gasification/woodgastruck.html
Questions --> is a complete system more efficient than seperate units ? From the text at http://www.gekgasifier.com/forums/showthread.php?t=22, and given the fact that wood gas has a low energetic value on itself, it seems so, but why ?
- Possibly because thermal heat generated for fuel generator (=the gasifier) is reused in the IC-engine (heated gas expands more) ?
- and/or because the storage of the wood gas is either not possible or requires high pressure and/or heating or cooling
- in what way is wood gas different from smoke ?
Woodgas generator types
- The fixed bed gasifier; for small applications such as camp-site burners.
- The fluidized bed gasifier; for electricity power plants.
- The updraft and crossdraft gasifier; for central heating systems (used to gasify charcoal or coals)
- The downdraft gasifier; for IC engines (used to gasify wood). This type is the only type used with IC engines given that it produces little tar.[1][2]
Production
For schematics, see
- http://woodgas.nl/GB/woodgasification.html (Main Imbert dawndraft generator setup)
- http://www.allpowerlabs.org/gasification/resources/papers/Handbook.Reed.Das.pdf (Imbert gas generator schematic, page 93)
- http://wiki.gekgasifier.com/w/page/29160712/GEK-v4_0-CAD-drawings-for-all-sheet-metal-parts
- http://wiki.gekgasifier.com/w/page/6123754/How-to-Build-and-Run-the-GEK-Gasifier
- http://wiki.gekgasifier.com/w/page/6123797/Practical-Engineering
Storage
http://www.gekgasifier.com/forums/showthread.php?t=22
Use
Transport --> not suitable see Comparison of engines Home generation (combined heat and power) --> by means of a regular internal combustion (car) engine, or a lawnmower engine Note: could possibly be combined with a stirling engine, see Comparison_of_engines#The_appropriate_use_of_the_different_engines