Canadienito (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Canadienito (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 7: | ||
Essentially, a solar hot water system is made up of a [[solar thermal hot water collector]]’, a well-insulated storage container, and a system for transferring the heat from the collector to the container vis-à-vis a fluid medium, which in some circumstances is the water to be used itself. | Essentially, a solar hot water system is made up of a [[solar thermal hot water collector]]’, a well-insulated storage container, and a system for transferring the heat from the collector to the container vis-à-vis a fluid medium, which in some circumstances is the water to be used itself. | ||
==Background== | |||
Hot water is considered by some to have less application in the field of appropriate technology and to mostly be a luxury afforded the developed world. The authors suggest that what hot water is needed can be heated using a fuel simultaneously heating their home. Such dismissals are dangerous on two counts: | |||
*First, if appropriate technology is at all concerned with reducing waste and increasing efficiency of use of precious natural resources then there are many opportunities to do so using solar thermal energy and technologies in the context of sustainable development. | |||
*Second, and perhaps imperatively, the potential to displace the ecological and social externalities associated with [[conventional methods for heating water]] in the more affluent and developed regions on the planet where there is a path dependency to use hot water regularly and in abundance, even for such luxuries as long, hot showers, clothes washing and heated tubs and pools is extremely important for many SDHW applications are cost-effective and available and thus there could be a significant reduction in the size of a regions Ecological Footprint associated with conventional means of heating water (site Wiki for conventional hot water). | |||
| Line 28: | Line 35: | ||
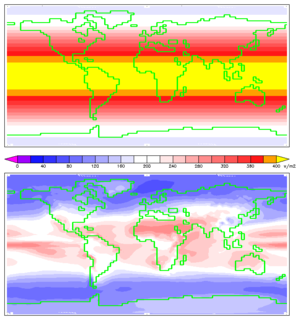
[[Image:Insolation.png|thumb|Theoretical annual mean insolation, at the top of Earth's atmosphere (top) and at the surface on a horizontal square meter.]] | [[Image:Insolation.png|thumb|Theoretical annual mean insolation, at the top of Earth's atmosphere (top) and at the surface on a horizontal square meter.]] | ||
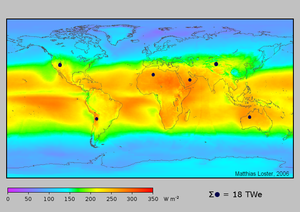
[[Image:Solar_land_area.png|thumb|Map of global solar energy resources. The colours show the average available solar energy on the surface (as measured from 1991 to 1993). For comparison, the dark disks represent the land area required to supply the total primary energy demand using PVs with a conversion efficiency of 8%.]] | [[Image:Solar_land_area.png|thumb|Map of global solar energy resources. The colours show the average available solar energy on the surface (as measured from 1991 to 1993). For comparison, the dark disks represent the land area required to supply the total primary energy demand using PVs with a conversion efficiency of 8%.]] | ||
[[Image:Solarboiler.jpg|thumb]] | |||
[[Image:Solar_heater.jpg|thumb]] | |||
Revision as of 21:01, 8 August 2007
Introduction
Solar Hot Water describes active and passive solar technologies that utilize the sun’s freely abundant solar thermal energy in order to heat water for a desired application.
If you have ever felt hot water trickle out of a garden hose that’s been sitting in the sun, you’ve experienced solar hot water in action.
Essentially, a solar hot water system is made up of a solar thermal hot water collector’, a well-insulated storage container, and a system for transferring the heat from the collector to the container vis-à-vis a fluid medium, which in some circumstances is the water to be used itself.
Background
Hot water is considered by some to have less application in the field of appropriate technology and to mostly be a luxury afforded the developed world. The authors suggest that what hot water is needed can be heated using a fuel simultaneously heating their home. Such dismissals are dangerous on two counts:
- First, if appropriate technology is at all concerned with reducing waste and increasing efficiency of use of precious natural resources then there are many opportunities to do so using solar thermal energy and technologies in the context of sustainable development.
- Second, and perhaps imperatively, the potential to displace the ecological and social externalities associated with conventional methods for heating water in the more affluent and developed regions on the planet where there is a path dependency to use hot water regularly and in abundance, even for such luxuries as long, hot showers, clothes washing and heated tubs and pools is extremely important for many SDHW applications are cost-effective and available and thus there could be a significant reduction in the size of a regions Ecological Footprint associated with conventional means of heating water (site Wiki for conventional hot water).
Appropriate Techology
Potential Applications
System Types
Availability of Solar Thermal Energy
Direct solar heat gain is one of the most efficient ways to heat water (in terms of energy/waste), as it requires no energy conversion, unlike electric-resistance heating or fuel burning. It is a simple transfer and concentration of heat energy from one place to another.
Hot water can be used for a number of applications, including sanitation (it's easier to wash a lot of things with hot water), and space heating.