Smart Shade Literature Review[edit | edit source]
Please refer smart shade literature Review.
Methods[edit | edit source]
Introduction about the Project[edit | edit source]
During night, when window shades are left open, a lot of heat from the inside is lost. This project aims to implement photovoltaic cells in the shades such that they cause the shades to open and generate electricity during the day, and automatically close the shades at night. The key feature is the dual implementation of PV cells as power sources and as light sensors. Due to this, the heat lost during the night through windows can be conserved, which in-turn reduces the heating energy costs for buildings and improves their energy efficiency.[1-2]
General review of method[edit | edit source]
The logic is to compare the desired temperature to room temperature and opens or closes the blinds based on temperature difference. Rather than sensing temperature, this could also be done in another way, by sensing the amount of voltage produced by the PV cell, thereby gauging the amount of ambient light and controlling the shades based on that.
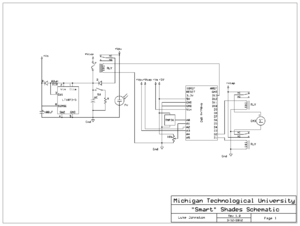
This schematic was developed using the components listed in the hardware list below. For this project, a battery will replace the ultracapacitor.
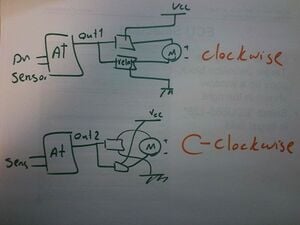
This is a basic diagram for dual direction motor control. The circuit schematics
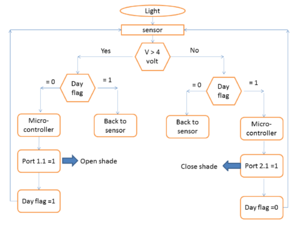
experimental analysis
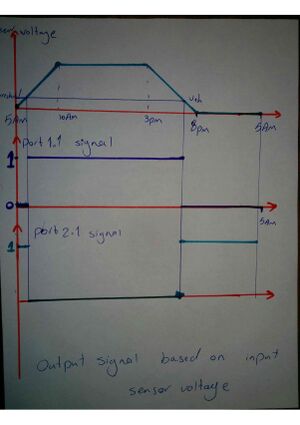
this figure is a result which we are looking for
Hardware Components[edit | edit source]
PV Panel[edit | edit source]
A small C-Si PV panel is used to act as a light-controlled switch for the window shade, and also charge the battery. It was tested under bright light conditions and found to generate a no-load voltage upto 6V DC.
DC-DC Converter[edit | edit source]
The Arduino Uno micro-controller requires 5V DC for power, so a DC-DC Boost converter is used to maintain a constant 5V voltage across the battery terminals. As the converter has to deal with low input voltages, The LT1073-5 was selected due to the few number of external components needed, as well as its low required input voltage (1V).
Electric Motor[edit | edit source]
Due to its cheap cost, a small geared hobby motor was selected, utilizing a potentiometer for position feedback. The GM3 geared hobby motor provides up to.34 Nm of torque at rated voltage.
Battery[edit | edit source]
For energy storage, a Li-ion battery will be used to provide 5V output to the micro-controller circuit and the motor. It's specifications are yet to be determined.
Hardware List[edit | edit source]
| Description | Function | Model/Part # | Supplier | Unit Price | Quantity | URL | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC Motor | Blind actuation | GM3 | Solarbotics.com | 5.75 | Blind_Number | http://www.solarbotics.com/products/gm3/ | In hand |
| SPDT Relay | Switching motor/cutting charging | V23105A5001A201 | Axicom | 1.55 | 2 | http://www.mouser.com/ProductDetail/TE-Connectivity-Axicom/V23105A5001A201/?qs=CizG3IxbuFMuVNcxrZR29g== | 2 Required |
| PV panel | Power source | 1 | In hand | ||||
| Battery | Power storage | P015-ND | Digikey | 3.43 | 1 | http://www.digikey.com/product-detail/en/HHR-150AAC8/P015-ND/271832 | 2 Required |
| Controller | Arduino Uno | Arduino | In hand | ||||
| Perf board | PCB | Final PCB to be designed | |||||
| Project Box | Enclosure for components | In hand | |||||
| Misc electronics | For DC-DC converter | In hand | |||||
| Power resistor | For discharging ultracapacitor | Digikey | In hand | ||||
| DC-DC Converter | Boost from UC to +5V | LT1073-5 | Digikey | 1 | http://search.digikey.com/us/en/products/LT1073CN8%23PBF/LT1073CN8%23PBF-ND/889104 | In hand | |
| Fuse holder | Holds fuse | Digikey | 1.21 | 1 | http://search.digikey.com/us/en/products/02540101Z/F1471-ND/553102 | In hand | |
| Fuse | To fuse power from battery | Digikey | 0.71 | 3 | http://search.digikey.com/us/en/products/0229003.HXP/F2470-ND/777186 | In hand | |
| Misc hardware | For mounting components in project box | ||||||
| Wire | For wiring components | In hand | |||||
| Diode | Circuit protection | 1N5817 | Digikey | 0.42 | 2 | http://search.digikey.com/us/en/products/1N5817-TP/1N5817-TPCT-ND/950586 | In hand |
Future Works[edit | edit source]
This project's design aims to be safer due to the lack of an ultra-capacitor, more compact and cheaper. If more time was available, it is possible to have developed future iterations of this project to extend its functionality beyond just window shade control, such as utilizing the window shade position to change the indoor electrical lighting intensity. More complex models may be used to operate the blinds at many different angles to allow varying amounts of sunlight depending on the time of the day, rather than just open/close positions. An additional PV cell could be placed indoors too, close to a light source, so that it can generate electricity to charge the battery using the indoor electrical lighting at night. Based on the data that is to be found on potential energy savings for a building outfitted with these smart shades, we can extrapolate that to find the savings for a small town or city block if all buildings utilize them.
References[edit | edit source]
- Tzempelikos, Athanassios; Andreas K. Athienitis (2007). "The impact of shading design and control on building cooling and lighting demand". Solar Energy 81 (3): 369 – 382. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2006.06.015. ISSN 0038-092X
- M., Zaheer-Uddin (1987). "The influence of automated window shutters on the design and performance of a passive solar house". Building and Environment 22 (1): 67-75. doi:10.1016/0360-1323(87)90043-6. ISSN 0360-1323