Source
- Aubrey L. Woern, Joseph R. McCaslin, Adam M. Pringle, and Joshua M. Pearce. RepRapable Recyclebot: Open Source 3-D Printable Extruder for Converting Plastic to 3-D Printing Filament. HardwareX 4C (2018) e00026 doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ohx.2018.e00026 open access
- Just the code: OSF
- FreeCAD users: On the OSF link above the entire assembly is available in the STP file. Open it in FreeCAD and pick what part you would like to modify, export it as .stp, and you will be left with just the part you need. Once you have that, you can save it as just about anything.
- Smaller FreeCAD 55 MB version - compliments of Marcin at Open Source Ecology - removed all the nuts and bolts and screws
- Please note that all the instructions are in the HardwareX article above
Updates and Improvements
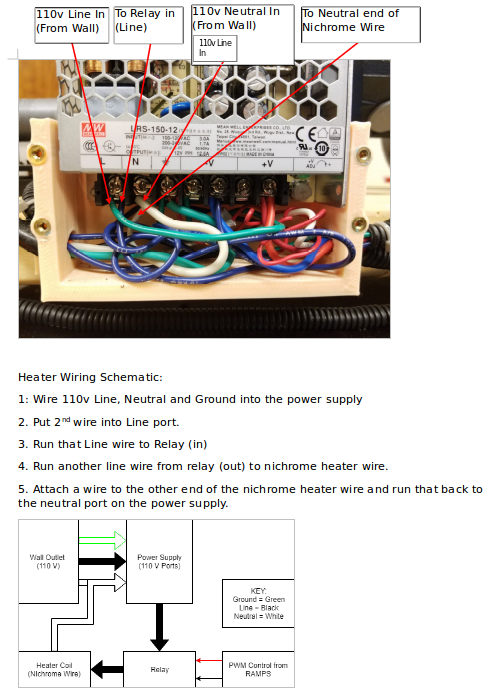
Open Source Ecology Improvements
- OSE 3D printable roller - https://osf.io/9hsmb/
Abstract

In order to assist researchers explore the full potential of distributed recycling of post-consumer polymer waste, this article describes a recyclebot, which is a waste plastic extruder capable of making commercial quality 3-D printing filament. The device design takes advantage of both the open source hardware methodology and the paradigm developed by the open source self-replicating rapid prototyper (RepRap) 3-D printer community. Specifically, this paper describes the design, fabrication and operation of a RepRapable Recyclebot, which refers to the Recyclebot’s ability to provide the filament needed to largely replicate the parts for the Recyclebot on any type of RepRap 3-D printer. The device costs less than $700 in mate rials and can be fabricated in about 24 h. Filament is produced at 0.4 kg/h using 0.24 kWh/kg with a diameter ±4.6%. Thus, filament can be manufactured from commercial pellets for <22% of commercial filament costs. In addition, it can fabricate recycled waste plastic into filament for 2.5 cents/kg, which is <1000X commercial filament costs. The system can fabricate filament from polymers with extrusion temperatures <250 °C and is thus capable of manufacturing custom filament over a wide range of thermopolymers and composites for material science studies of new materials and recyclability studies, as well as research on novel applications of fused filament based 3-D printing.
Keywords
Circular economy; Distributed recycling; Energy conservation; Polymer recycling; Sustainable development; distributed manufacturing; life cycle analysis; recycling; recyclebot; 3-D printing; polymer filament; Open source hardware; Open hardware; Fused filament fabrication; RepRap; Recycling; Polymers; Plastic; Recyclebot; Waste plastic; Composites; Polymer composites; Extruder; Upcycle; Materials science
See Also
| RepRapable Recyclebot |
|---|
Error in widget YouTube: Unable to load template 'wiki:YouTube' |
- Recyclebot
- Tightening the loop on the circular economy: Coupled distributed recycling and manufacturing with recyclebot and RepRap 3-D printing
- Energy Payback Time of a Solar Photovoltaic Powered Waste Plastic Recyclebot System
- Wood Furniture Waste-Based Recycled 3-D Printing Filament
- Life cycle analysis of distributed recycling of post-consumer high density polyethylene for 3-D printing filament
- Evaluation of Potential Fair Trade Standards for an Ethical 3-D Printing Filament
- Mechanical Properties of Components Fabricated with Open-Source 3-D Printers Under Realistic Environmental Conditions
- Mechanical testing of polymer components made with the RepRap 3-D printer
- Development and feasibility of applications for the RepRap 3-D printer
- Life cycle analysis of distributed polymer recycling
- Solar powered distributed customized manufacturing
- Distributed recycling of post-consumer plastic waste in rural areas
- Ethical Filament Foundation
- Economist article on U. of Washington's HDPE boat, Oprn3dp.me
- Fused Particle Fabrication 3-D Printing: Recycled Materials’ Optimization and Mechanical Properties
- 3-D Printable Polymer Pelletizer Chopper for Fused Granular Fabrication-Based Additive Manufacturing
- Cruz, F., Lanza, S., Boudaoud, H., Hoppe, S., & Camargo, M. Polymer Recycling and Additive Manufacturing in an Open Source context: Optimization of processes and methods. http://sffsymposium.engr.utexas.edu/sites/default/files/2015/2015-127-Cruz.pdf
- https://ultimaker.com/en/resources/52444-ocean-plastic-community-project
Literature Reviews
- Solar powered recyclebot literature review
- Waste plastic extruder: literature review
- Life cycle analysis of polymer recycling literature review
In the News
- Michigan Tech Researchers Publish Paper on New Recyclebot 3D Printer- 3D Print, Ichiban Electronics
- Recyclebot an Open-Source 3D Printable Extruder for Converting Plastic to 3D Printing Filament - Inside 3D Printing
- RepRapable Recyclebot: Open-Source-Extruder recycelt Filament - Make Germany (1521)
- LSWDD turns recyclable plastics into 3D printer filament - The Island's Weekly
- [https://3dprint.com/215471/michigan-tech-r
- Recycle at Home with 3D Printing - Machine Design
- Equipment spotlight: Boost for at-home filament extrusion - Plastics Recycling Update
- Plastic-eating robot turns waste into printer filament HardwareX 616
- 3D Printing is Turning the Economics of Scale on its Head Cape and Islands (listen)
- 3D printers inspire creativity and help those in need Newsday 11.7k





