Background
Team BGRZ is made up of four Humboldt State University students and alumni: Brianna Diaz, Gabriela Pecina Escobar, Robert Duncan and Zach Estela. Brianna is an Art Education/Spanish major. Gabriela is a Spanish Education major. Robert has graduated with a B.S. in NRPI(Natural Resources Planning Interpretation). Zach has graduated with a B.S. in *insert major here*.
Project Scope
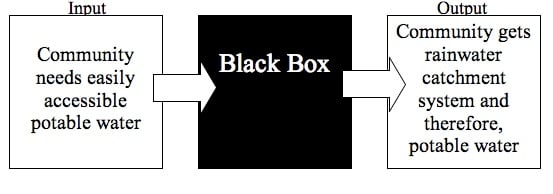
Directing and capturing rainwater is an ancient science that is still in practice today. In regions where water is scarce during a few or all seasons, maximizing the collection and storage of rainwater is vitally important. Rainwater catching systems can replace or supplement municipal water sources which can be expensive or undependable. Our group was contacted by |Otros Mundos, a local activist and human rights organization, to design and build three different water collection systems in Chiapas, Mexico. The first location is an appropriate tech demonstration house in San Cristobal de las Casas, the other two systems will be in an indigenous community. Another project that could happen if we have time left in the program will be a small installation for Rancho Esquipulas.
Here in the mountainous region of Chiapas, Mexico, the rainy season normally starts around May or early June and continues until late fall.This is opportune for our group as we will have many torrential downpours to test our systems. From late fall to late spring the municipal water is sporadic; for many locals that rely on city provided water, this can be a hard season. The indiginous community we are working with, water is obtained from a local stream. There are at least three months when water is scarce making it extremely difficult for them to obtain potable water.
Literature Review
A background on rainwater catchment
- Rainwater Harvesting|The Engineers Journal
- rainwater quality
- There are four main reasons for rainwater contamination:
- Polluted while passing through atmosphere
- filth collected during dry season
- Dirty roof, ie; animal or bird droppings
- pollution through collection unit
- tipping gutter and floating ball
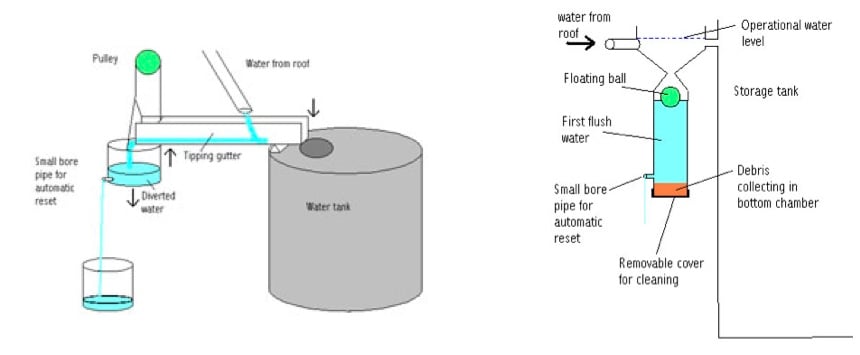
- The tipping gutter system works by filling up a bucket with dirty water, when bucket weighs enough it will change the direction of the gutter to fill up the storage tank.
- The floating ball technique functions by having the contaminated water fill up a pipe that has a ball in it. The ball floats to the top as the pipe is fill and eventually seals the pipe so the clean water is diverted to the water harvesting tank.
- | floating ball system demo
- Table of Precipitation gathered depending on roof size and annual precipitation (see table on right)
Source for Figure 1: http://www.austinenergy.com/energy%20efficiency/Programs/Green%20Building/Sourcebook/rainwaterHarvesting.htm 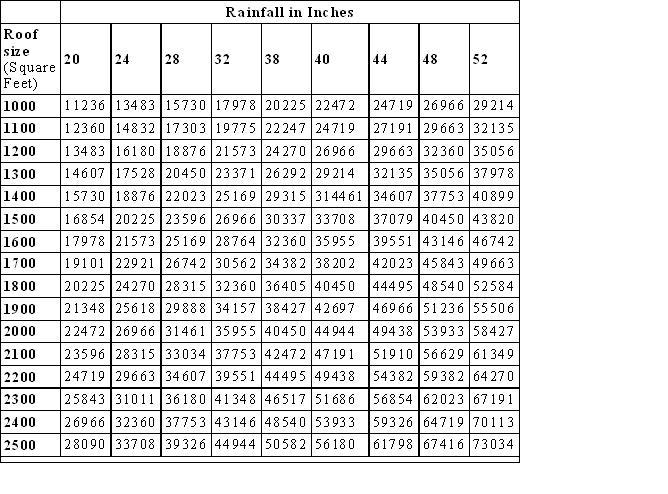
- According to Rainwater Harvesting Industries, one mm of rain roughly equates to on liter for every square meter of roof surface. http://www.rainharvesting.com.au/roof_surface_and_area.asp
- Very Concise E-Book called Design for Water : Rainwater Harvesting, Stormwater Catchment, and Alternate Water Reuse Written by: Kinkade-Levario, Heather Published by: New Society Publishers,Call number: Limited TD353 -- .K56 2007eb NOTE: must be logged in to HSU library to view this book. [Design For Water]
Materials
Toxicity
- http://www.ehow.com/facts_5685358_pvc-water-pipe-safety.html
- Pvc can be carcinogenic, Greenpeace Recommends Polyethylene (PE) or Polypropylene (PP) as a safer alternative.
- http://fscimage.fishersci.com/msds/25490.htm
- Zinc oxide, from corrosion of Galvanized corrugated roofing material has a reportedly low toxicity and is considered a 'nuisance particle, unless in vapor form.'
- Furthermore - If the roofs themselves are made of galvanized steel, a gutter made of the same materials is not a significant increase in surface area.
Tank types, filter materials, availability in SCDLC,
- Citation
- Content
System Design
Components needed, purpose (potable), overflow, filter, first flush
- http://www.scribd.com/doc/12748968/Rainwater-Harvesting-from-the-roof
- E book for general design of system and components. Includes sections on guttering, storage, costs, etc.
- Rainwater Catchment Systems Association
- Provides photos of various systems installed.
- http://www.eastfremantle.wa.gov.au/uploaded/pdf/rain.pdf
- Safety Protocols for rainwater catchment and storage
- Rainwater System Comeponents
- A solid overview of the various possible components of a RC system. Detailed quality images.
Making Rainwater Safe to Drink
A Community Guide to Environmental Health by Jeff Conant & Pam Fadem
Rainwater must be kept free of contamination to be safe to drink. To make sure the water you collect will be safe:
- Clean the tank, entrance pipe, and roof gutters before the rainy season.
- Allow the first rains of each year to run through the tank to clean it.
- Connect a water filter to the tank (slow sand filter is a simple way to do this).
Location
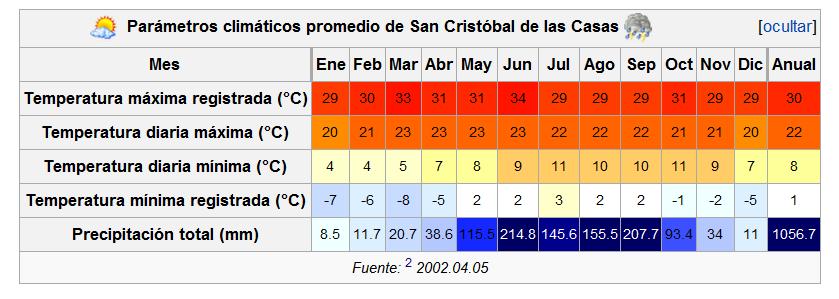
- Juan Marco's Demonstration House in San Cristóbal
- Rancho Esquipulas: an organic farm that provides vegetables for La Casa del Pan restaurant
- An indigenous Community
Data
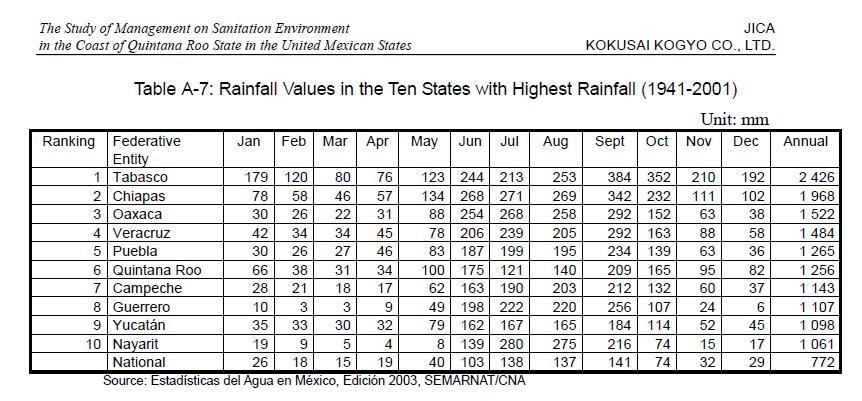
rainfall
Equations
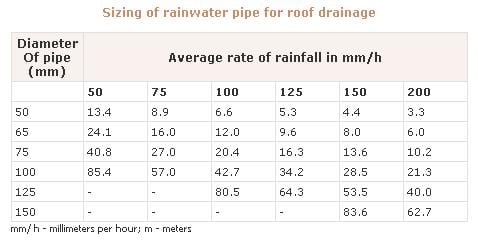
Roof size to pipe size Volume of tank size
- | Simple, low maintenance first flush system
- Equation to determine how much water should be diverted for the first flush:
meters squared (roof area) X pollution factor = liters to be diverted.
- "As a rule of thumb, the more water that is diverted the better the quality of water in the tank."
- Contamination Equation
- Equation based off of contamination on roads but correlates to roof contamination: "Y =ax−bx2 +c (3) Where
Y is the contaminant loading on a road at time x a, b and c are constants ax bx2 c represents the process of dirt accumulation represents the various processes of dirt removal (such as traffic and wind) represents some initial dirt loading"
Criteria
-Weighted Table-
- Criteria
- Constraint
- Cost
- Must be within budget
- What is budget? Depends on client and program
- Must be within budget
- Appropriateness
- Must fit appropriate technology ethos
- Must have local/reused materials when possible
- Client needs
- Construction time
- Must fit within 4 weeks
- Labor
- Modular Design
- Must incorporate modular design principles (weighed behind cost)
- Maintainence must be realistic
- Must be built to be replenishable by average rain in wet season
- Must be long lasting
- Must be easy to reproduce by other builders
Note- criteria varies for each of the 1-3 clients
| Criteria | Weight | Constraints |
| culturally Appropriate Design | 9 | accepted by community as indicated by communication |
| educational ability | 6 | an appropedia page where internet is available, also building together with clients and discussing maintenance needs |
| level of material locality | 6 | locals have access to these materials and where not available shipped from US |
| maintainability | 8 | excess plant matter may need to be removed and first flush system may need to be manual |
| size | 6 | varies greatly by location, tank must be out of the way |
| cost | 10 | affordable for the client |
| Durability of material | 7 | last several years with maintenance... |
| Life Use of rainwater catchment system | 6 | at least 30 years of use... |
| Reduces erosion | 5 | reduces erosion |
| Local labor and Local skills | 9 | must be easily repeatable with local skills and labor |
| Improves Health | 8 | improves water quality and therefore overall health |