J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{MOST}} {{Pearce-pubs}} right ==Source== * C. Zhang, D. O. Guney, J. M. Pearce. [http://dx.doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/3/10/105034 Plasmonic enhancement...") |
Sophivorus (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "| affiliations = " to "| organizations = ") |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Solar menu}} | |||
[[File:hexarray.png|thumb]] | |||
{{Source data | |||
| type = Paper | |||
| cite-as = C. Zhang, D. O. Guney, J. M. Pearce. [https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/3/10/105034 Plasmonic enhancement of amorphous silicon solar photovoltaic cells with hexagonal silver arrays made with nanosphere lithography]. ''Materials Research Express'' '''3'''(10) 105034 (2016). DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/3/10/105034 [https://www.academia.edu/29215685/Plasmonic_enhancement_of_amorphous_silicon_solar_photovoltaic_cells_with_hexagonal_silver_arrays_made_with_nanosphere_lithography open access] | |||
}} | |||
{{Project data | |||
| authors = C. Zhang, D. O. Guney, User:J.M.Pearce | |||
| status = Designed, Modelled | |||
| links = https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/2053-1591/3/10/105034|, https://www.academia.edu/29215685/Plasmonic_enhancement_of_amorphous_silicon_solar_photovoltaic_cells_with_hexagonal_silver_arrays_made_with_nanosphere_lithography| | |||
| location = Michigan, USA | |||
}} | |||
{{MOST}} | {{MOST}} | ||
Nanosphere lithography (NSL) provides an opportunity for a low-cost and scalable method to optically engineer solar photovoltaic (PV) cells. For PV applications, NSL is widely used in rear contact scenarios to excite surface plasmon polariton and/or high order diffractions, however, the top contact scenarios using NSL are rare. In this paper a systematic simulation study is conducted to determine the capability of achieving efficiency enhancement in hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) solar cells using NSL as a top contact plasmonic optical enhancer. The study focuses on triangular prism and sphere arrays as they are the most commonly and easily acquired through direct deposition or low-temperature annealing, respectively. For optical enhancement, a characteristic absorption profile is generated and analyzed to determine the effects of size, shape and spacing of plasmonic structures compared to an un-enhanced reference cell. The factors affecting NSL-enhanced PV performance include absorption, shielding effects, diffraction, and scattering. In the triangular prism array, parasitic absorption of the silver particles proves to be problematic, and although it can be alleviated by increasing the particle spacing, no useful enhancement was observed in the triangular prism arrays that were simulated. Sphere arrays, on the other hand, have broad scattering cross-sections that create useful scattering fields at several sizes and spacing intervals. For the simulated sphere arrays the highest enhancement found was 7.4%, which was fabricated with a 250 nm radius nanosphere and a 50 nm silver thickness, followed by annealing in inert gas. These results are promising and provide a path towards the commercialization of plasmonic a-Si:H solar cells using NSL fabrication techniques. | |||
{{Pearce publications notice}} | |||
== | == Method == | ||
* [[Perkin-Elmer RF Sputtering System-6 Inch protocol: MOST]] | * [[Perkin-Elmer RF Sputtering System-6 Inch protocol: MOST]] | ||
* | * [[Chenlong Nanobeads Project]] | ||
== See also == | |||
* [[Fabricating Ordered 2-D Nano-Structured Arrays Using Nanosphere Lithography]] | |||
*[[A new method of preparing highly conductive ultra-thin indium tin oxide for plasmonic-enhanced thin film solar photovoltaic devices]] | * [[A new method of preparing highly conductive ultra-thin indium tin oxide for plasmonic-enhanced thin film solar photovoltaic devices]] | ||
*[[Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | * [[Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | ||
*[[Influence of Oxygen Concentration on the Performance of Ultra-Thin RF Magnetron Sputter Deposited Indium Tin Oxide Films as a Top Electrode for Photovoltaic Devices]] | * [[Influence of Oxygen Concentration on the Performance of Ultra-Thin RF Magnetron Sputter Deposited Indium Tin Oxide Films as a Top Electrode for Photovoltaic Devices]] | ||
*[[Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | * [[Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices]] | ||
* [[Controlling optical absorption in metamaterial absorbers for plasmonic solar cells]] | * [[Controlling optical absorption in metamaterial absorbers for plasmonic solar cells]] | ||
*[[Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices]] | * [[Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices]] | ||
*[[Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review]] | * [[Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review]] | ||
*[[Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation]] | * [[Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation]] | ||
*[[Effect of ambient combinations of argon, oxygen, and hydrogen on the properties of DC magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide films]] | * [[Effect of ambient combinations of argon, oxygen, and hydrogen on the properties of DC magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide films]] | ||
*[[A novel synthesis of tin oxide thin films by the sol-gel process for optoelectronic applications]] | * [[A novel synthesis of tin oxide thin films by the sol-gel process for optoelectronic applications]] | ||
* [[Enhancement of hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells with front-surface hexagonal plasmonic arrays from nanoscale lithography]] | |||
* [[Ambiance-dependent Agglomeration and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Response of Self-assembled Silver Nano-particles for Plasmonic Photovoltaic Devices]] | |||
* [[Optimal Design of Thin-film Plasmonic Solar Cells using Differential Evolution Optimization Algorithms]] | |||
* [[Scalable honeycomb top contact to increase the light absorption and reduce the series resistance of thin film solar cells]] | |||
* [[Optoelectronic Properties: Carrier Transport, Recombination, and Stability]] | |||
{{Page data | |||
| title-tag = Plasmonic Enhancement of a-Si Solar Cells (Hexagonal) | |||
| keywords = Plasmonic enhancement, silicon solar photovoltaic cells, Photovoltaics, hexagonal silver arrays, nanosphere lithography, pv, Materials processing | |||
| sdg = SDG09 Industry innovation and infrastructure | |||
| organizations = MTU, MOST | |||
}} | |||
[[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | [[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:30, 28 February 2024
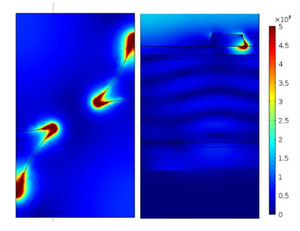
Nanosphere lithography (NSL) provides an opportunity for a low-cost and scalable method to optically engineer solar photovoltaic (PV) cells. For PV applications, NSL is widely used in rear contact scenarios to excite surface plasmon polariton and/or high order diffractions, however, the top contact scenarios using NSL are rare. In this paper a systematic simulation study is conducted to determine the capability of achieving efficiency enhancement in hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) solar cells using NSL as a top contact plasmonic optical enhancer. The study focuses on triangular prism and sphere arrays as they are the most commonly and easily acquired through direct deposition or low-temperature annealing, respectively. For optical enhancement, a characteristic absorption profile is generated and analyzed to determine the effects of size, shape and spacing of plasmonic structures compared to an un-enhanced reference cell. The factors affecting NSL-enhanced PV performance include absorption, shielding effects, diffraction, and scattering. In the triangular prism array, parasitic absorption of the silver particles proves to be problematic, and although it can be alleviated by increasing the particle spacing, no useful enhancement was observed in the triangular prism arrays that were simulated. Sphere arrays, on the other hand, have broad scattering cross-sections that create useful scattering fields at several sizes and spacing intervals. For the simulated sphere arrays the highest enhancement found was 7.4%, which was fabricated with a 250 nm radius nanosphere and a 50 nm silver thickness, followed by annealing in inert gas. These results are promising and provide a path towards the commercialization of plasmonic a-Si:H solar cells using NSL fabrication techniques.
Method[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
- Fabricating Ordered 2-D Nano-Structured Arrays Using Nanosphere Lithography
- A new method of preparing highly conductive ultra-thin indium tin oxide for plasmonic-enhanced thin film solar photovoltaic devices
- Limitations of ultra-thin transparent conducting oxides for integration into plasmonic-enhanced thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Influence of Oxygen Concentration on the Performance of Ultra-Thin RF Magnetron Sputter Deposited Indium Tin Oxide Films as a Top Electrode for Photovoltaic Devices
- Advances in plasmonic light trapping in thin-film solar photovoltaic devices
- Controlling optical absorption in metamaterial absorbers for plasmonic solar cells
- Plasmonic Perfect Meta-Absobers for a-Si PV Devices
- Optical modelling of thin film microstructures literature review
- Multi-resonant silver nano-disk patterned thin film hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells for Staebler-Wronski effect compensation
- Effect of ambient combinations of argon, oxygen, and hydrogen on the properties of DC magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide films
- A novel synthesis of tin oxide thin films by the sol-gel process for optoelectronic applications
- Enhancement of hydrogenated amorphous silicon solar cells with front-surface hexagonal plasmonic arrays from nanoscale lithography
- Ambiance-dependent Agglomeration and Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Response of Self-assembled Silver Nano-particles for Plasmonic Photovoltaic Devices
- Optimal Design of Thin-film Plasmonic Solar Cells using Differential Evolution Optimization Algorithms
- Scalable honeycomb top contact to increase the light absorption and reduce the series resistance of thin film solar cells
- Optoelectronic Properties: Carrier Transport, Recombination, and Stability





