J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) m (→Source) |
J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) m (→Use) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Source== | ==Source== | ||
[[image:RepRapsci.jpg|right|500px]] | [[image:RepRapsci.jpg|right|500px]] | ||
* Chenlong Zhang, Bas Wijnen, Joshua M. Pearce. Open-source 3-D Platform for Low-cost Scientific Instrument Ecosystem. Journal of Laboratory Automation ( | * Chenlong Zhang, Bas Wijnen, Joshua M. Pearce. Open-source 3-D Platform for Low-cost Scientific Instrument Ecosystem. ''Journal of Laboratory Automation'' 21(4) 517-525 (2016). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/2211068215624406 [https://www.academia.edu/27067106/Open-source_3-D_Platform_for_Low-cost_Scientific_Instrument_Ecosystem open access] | ||
* This project derived from: [[Delta Build Overview:MOST| MOST Delta RepRap]] and the [[Athena_Build_Overview| MOST Athena RepRap]] | |||
* This project derived from: [[]] | * Bill of materials https://osf.io/5kev4/ | ||
* | * OpenSCAD code: https://osf.io/v2pwa/ | ||
* OpenSCAD code: | * Open Source Software: [[Franklin]] | ||
* Open Source Software: | |||
==Abstract== | ==Abstract== | ||
| Line 22: | Line 21: | ||
The combination of open-source software and hardware provide technically feasible methods to create low-cost, highly-customized scientific research equipment. Open-source 3-D printers have proven useful for fabricating scientific tools. Here the capabilities of an open-source 3-D printer are expanded to become a highly-flexible scientific platform. An automated low-cost 3-D motion control platform is presented having the capacity to perform scientific applications including: i) 3-D printing of scientific hardware, ii) laboratory auto-stirring, measuring and probing, iii) automated fluid handling and iv) shaking and mixing. The open-source 3-D platform not only facilities routine research while radically reducing the cost, but it also inspires the creation of a diverse array of custom instruments that can be shared and replicated digitally throughout the world to drive down the cost of research and education further. | The combination of open-source software and hardware provide technically feasible methods to create low-cost, highly-customized scientific research equipment. Open-source 3-D printers have proven useful for fabricating scientific tools. Here the capabilities of an open-source 3-D printer are expanded to become a highly-flexible scientific platform. An automated low-cost 3-D motion control platform is presented having the capacity to perform scientific applications including: i) 3-D printing of scientific hardware, ii) laboratory auto-stirring, measuring and probing, iii) automated fluid handling and iv) shaking and mixing. The open-source 3-D platform not only facilities routine research while radically reducing the cost, but it also inspires the creation of a diverse array of custom instruments that can be shared and replicated digitally throughout the world to drive down the cost of research and education further. | ||
==Keywords | ==Keywords== | ||
[[3-D printing]], 3-D platform, [[fluid handling]], [[open source hardware]], [[laboratory equipment]] | [[3-D printing]], 3-D platform, [[fluid handling]], [[open source hardware]], [[laboratory equipment]] | ||
==BOM== | ==BOM== | ||
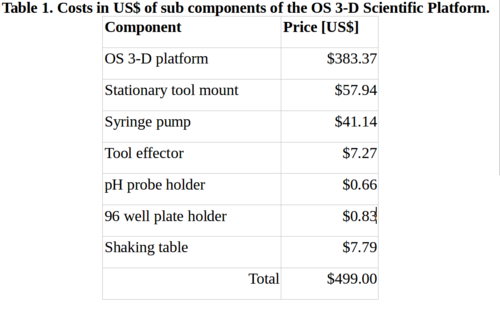
* Full Bill of Materials https://osf.io/5kev4/ | |||
[[image:cost3dplatform.png|500px]] | |||
==Assembly== | ==Assembly== | ||
* Follow basic build instructions for [[Delta Build Overview:MOST| MOST Delta RepRap]] and the [[Athena_Build_Overview| MOST Athena RepRap]] and then fashion the [[Athena Mobile Tool Effector]] and [[Athena Fixed Tool Mount]] | |||
==Use== | ==Use== | ||
* Use [[Franklin]] directly or through scripting to do whatever experiment you want. | |||
* Use as a [[free and open-source automated 3-D microscope]] | |||
[[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | [[Category:MOST completed projects and publications]] | ||
| Line 35: | Line 40: | ||
[[Category:Open source scientific hardware]] | [[Category:Open source scientific hardware]] | ||
[[category:3D printing]] | [[category:3D printing]] | ||
[[category:MOST methods]] | |||
Revision as of 00:22, 2 September 2016
Template:Statusboxtop Template:Status-design Template:Status-model Template:Status-prototype Template:Status-verified You can help Appropedia by contributing to the next step in this OSAT's status. Template:Boxbottom
Source
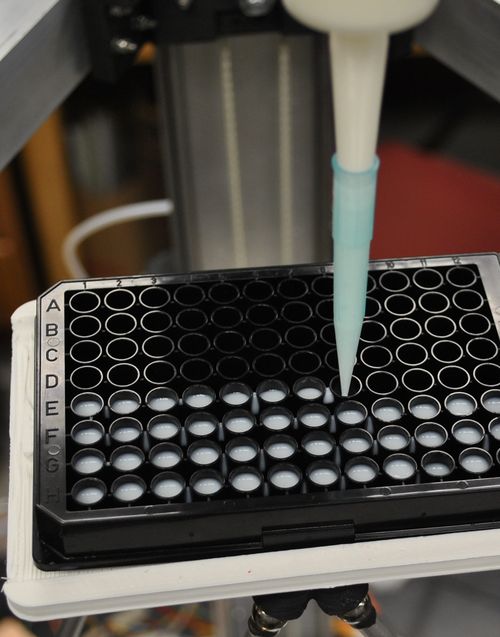
- Chenlong Zhang, Bas Wijnen, Joshua M. Pearce. Open-source 3-D Platform for Low-cost Scientific Instrument Ecosystem. Journal of Laboratory Automation 21(4) 517-525 (2016). DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/2211068215624406 open access
- This project derived from: MOST Delta RepRap and the MOST Athena RepRap
- Bill of materials https://osf.io/5kev4/
- OpenSCAD code: https://osf.io/v2pwa/
- Open Source Software: Franklin
Abstract
The combination of open-source software and hardware provide technically feasible methods to create low-cost, highly-customized scientific research equipment. Open-source 3-D printers have proven useful for fabricating scientific tools. Here the capabilities of an open-source 3-D printer are expanded to become a highly-flexible scientific platform. An automated low-cost 3-D motion control platform is presented having the capacity to perform scientific applications including: i) 3-D printing of scientific hardware, ii) laboratory auto-stirring, measuring and probing, iii) automated fluid handling and iv) shaking and mixing. The open-source 3-D platform not only facilities routine research while radically reducing the cost, but it also inspires the creation of a diverse array of custom instruments that can be shared and replicated digitally throughout the world to drive down the cost of research and education further.
Keywords
3-D printing, 3-D platform, fluid handling, open source hardware, laboratory equipment
BOM
- Full Bill of Materials https://osf.io/5kev4/
Assembly
- Follow basic build instructions for MOST Delta RepRap and the MOST Athena RepRap and then fashion the Athena Mobile Tool Effector and Athena Fixed Tool Mount
Use
- Use Franklin directly or through scripting to do whatever experiment you want.
- Use as a free and open-source automated 3-D microscope