| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
=Concerns= | =Concerns= | ||
* Moisture must be controlled to avoid mold growth. | |||
* Plants will attract insects. | |||
* Must be careful to choose plants that won't release excessive pollen. | |||
* Plants must be maintained. Including, trimming, watering, replanting, and washing. | |||
Revision as of 00:18, 14 November 2009
What are Living Walls?
- Living walls are vertically oriented gardens usually climbing a wall of a building or structure.
- Living walls are a relatively untapped art and architecture medium. Dynamic and evolving artwork that requires periodic upkeep.
- Living walls can be purely decorative, produce food or medicinal plants in small areas, provide energy savings through reduced heat absorption and even improve the quality of indoor air. The larger the living wall, the more benefit is derived in these sectors
Why build living walls?
Health benefits
Indoor air quality can sometimes be 4-5 times worse than outdoor air quality. This is often due to poor ventilation and offgassing of Volatile Organic Compounds from carpets, paints, upholstery, insulation,and countless other common products. Living walls can improve air quality through the photosynthesizing; absorbing CO2 and emitting oxygen.
Energy savings
Exterior walls Reduces heat island effect- The suns energy that used to reflect and radiate heat off of buildings is now absorbed by the growing plants. Reduces indoor cooling needs and costs- Shading from the plants on an exterior wall can decrease the temperature inside the building. Lower temperatures indoors reduce the need for air conditioning.
Application/Uses
How do living walls improve indoor air quality?
air can be forced past the plants and the soil medium containing microbes that actually removes VOC's, dust and dirt particles from the air. The air is then pumped through the traditional HVAC system and is redistributed in to the building.
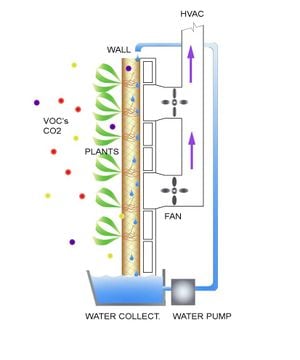
How do Living Walls reduces cooling costs?
shading from the plants on a sunlight wall reduces the amount of direct light hitting the structure. The energy absorbed by the plants is converted in to sugars through photosynthesis instead of reflecting and radiating most of the energy (heat) striking the wall.
indoor living walls can also reduce cooling/heating costs. Traditional HVAC systems must, by code, replace a certain amount of indoor air with fresh outdoor air. While this is being accomplished the outdoor air must be heated/cooled to the desired temperature. With an indoor living wall system the same air is used over and over again. The air is filtered by the living wall and maintains its temperature, eliminating the need to heating and/or cool outdoor air.
Design
How are Living walls made?
Any plant requires a type of growing medium. Some plants require a lot of medium in order to flourish, other plants need very little. The first element to building a living wall is the physical structure of the wall. Plants need water and moist soil, two things not commonly found anywhere near drywall. Some method of retaining the drip from plants and soil is a good first step.
- build the medium, a rectangle with little cubbies at slight upward angles.
- For a home:
- For a large scale HVAC inter-tied system:
What is the scale of a living wall? can I have one in my home or is it just for arboretums and large buildings?
- Living walls can be adapted to almost any size
- Examples of large scale
- Examples of small scale, household size
Concerns
- Moisture must be controlled to avoid mold growth.
- Plants will attract insects.
- Must be careful to choose plants that won't release excessive pollen.
- Plants must be maintained. Including, trimming, watering, replanting, and washing.