J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) m (→Source) |
J.M.Pearce (talk | contribs) m (→Source) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Source== | ==Source== | ||
* Dennis J. Byard, Aubrey L. Woern, Robert B. Oakley, Matthew J. Fiedler, Samantha L. Snabes, and Joshua M. Pearce. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221486041830695X Green Fab Lab Applications of Large-Area Waste Polymer-based Additive Manufacturing]. ''Additive Manufacturing'' (2019, | * Dennis J. Byard, Aubrey L. Woern, Robert B. Oakley, Matthew J. Fiedler, Samantha L. Snabes, and Joshua M. Pearce. [https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S221486041830695X Green Fab Lab Applications of Large-Area Waste Polymer-based Additive Manufacturing]. ''Additive Manufacturing'' 27, (2019), pp. 515-525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.03.006 [https://www.academia.edu/38728877/Fab_Lab_Applications_of_Large-Area_Waste_Polymer-based_Additive_Manufacturing open access] | ||
** https://re3d.org/ | ** https://re3d.org/ | ||
** [https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1TJ5fPkWCu9RxRyw7Sog3i4oeuqigKe0e All source files for Gigabot X] | ** [https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1TJ5fPkWCu9RxRyw7Sog3i4oeuqigKe0e All source files for Gigabot X] | ||
Revision as of 08:24, 10 April 2019
| Money and Tech Viability of Gigabot X for FabLabs and Small Biz |
|---|
Error in widget YouTube: Unable to load template 'wiki:YouTube' |
Source
- Dennis J. Byard, Aubrey L. Woern, Robert B. Oakley, Matthew J. Fiedler, Samantha L. Snabes, and Joshua M. Pearce. Green Fab Lab Applications of Large-Area Waste Polymer-based Additive Manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing 27, (2019), pp. 515-525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.03.006 open access
Abstract
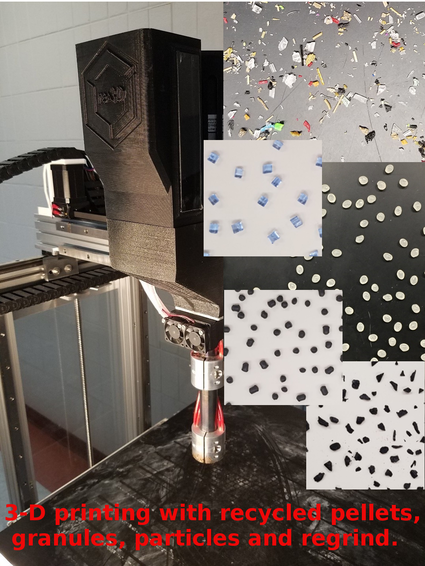
Fab labs, which offer small-scale distributed digital fabrication, are forming a Green Fab Lab Network, which embraces concepts of an open source symbiotic economy and circular economy patterns. With the use of industrial 3D printers capable of fused particle fabrication/ fused granular fabrication (FPF/FGF) printing directly from waste plastic streams, green fab labs could act as defacto recycling centers for converting waste plastics into valuable products for their communities. Clear financial drivers for this process have not been studied in the past. Thus, in this study the Gigabot X, an open source industrial 3D printer, which has been shown to be amenable to a wide array of recyclables for FPF/FGF 3D printing, is used to evaluate this economic potential. An economic life cycle analysis of the technology is completed comprised of three cases studies using FPF for large sporting equipment products. Sensitivities are run on the electricity costs for operation, materials costs from various feed stocks and the capacity factors of the 3D printers. The results showed that FPF/FGF 3D printing is capable of energy efficient production of a wide range of large high-value sporting goods products. In all cases, a substantial economic savings was observed when comparing the materials and energy related costs to commercial goods (even for customized goods). Using locally-sourced shredded plastic represented not only the best environmental option, but also the most economic. For the case study products analyzed even the lowest capacity factor (starting only one print per week) represented a profit when comparing to high-end value products. For some products the profit potential and return on investment was substantial (e.g. over 1000%) for high capacity use of a Gigabot X. The results clearly show that open source industrial FPF/FGF 3D printers have significant economic potential when used as a distributed recycling/manufacturing system using recyclable feed stocks in the green fab lab context.
Keywords
Circular economy; Distributed recycling; Energy conservation; Polymer recycling; Sustainable development; distributed manufacturing; life cycle analysis; recycling; recyclebot; 3-D printing; Open source hardware; Open hardware; RepRap; Recycling; Polymers; Plastic; Recyclebot; Waste plastic; Composites; Polymer composites; Extruder; Upcycle; Materials science;additive manufacturing; distributed manufacturing; open-source; waste plastic; extruder; upcycle
See Also



- Fused Particle Fabrication 3-D Printing: Recycled Materials’ Optimization and Mechanical Properties
- Recyclebot
- 3-D Printable Polymer Pelletizer Chopper for Fused Granular Fabrication-Based Additive Manufacturing
- Tightening the loop on the circular economy: Coupled distributed recycling and manufacturing with recyclebot and RepRap 3-D printing
- Energy Payback Time of a Solar Photovoltaic Powered Waste Plastic Recyclebot System
- Wood Furniture Waste-Based Recycled 3-D Printing Filament
- Life cycle analysis of distributed recycling of post-consumer high density polyethylene for 3-D printing filament
- Evaluation of Potential Fair Trade Standards for an Ethical 3-D Printing Filament
- Development and feasibility of applications for the RepRap 3-D printer
- Life cycle analysis of distributed polymer recycling
- Solar powered distributed customized manufacturing
- Distributed recycling of post-consumer plastic waste in rural areas
- Ethical Filament Foundation
- Economist article on U. of Washington's HDPE boat, Oprn3dp.me
- Cruz, F., Lanza, S., Boudaoud, H., Hoppe, S., & Camargo, M. Polymer Recycling and Additive Manufacturing in an Open Source context: Optimization of processes and methods. http://sffsymposium.engr.utexas.edu/sites/default/files/2015/2015-127-Cruz.pdf
- https://ultimaker.com/en/resources/52444-ocean-plastic-community-project





